Placebo and nocebo effects demonstrate the powerful influence of expectations on your health outcomes, where placebo induces positive effects from harmless treatments and nocebo triggers negative symptoms from inert substances or procedures. Understanding the psychological and neurological mechanisms behind these phenomena can enhance clinical practices and patient care. Explore the article to learn how these effects shape medical research and therapeutic strategies.
Table of Comparison
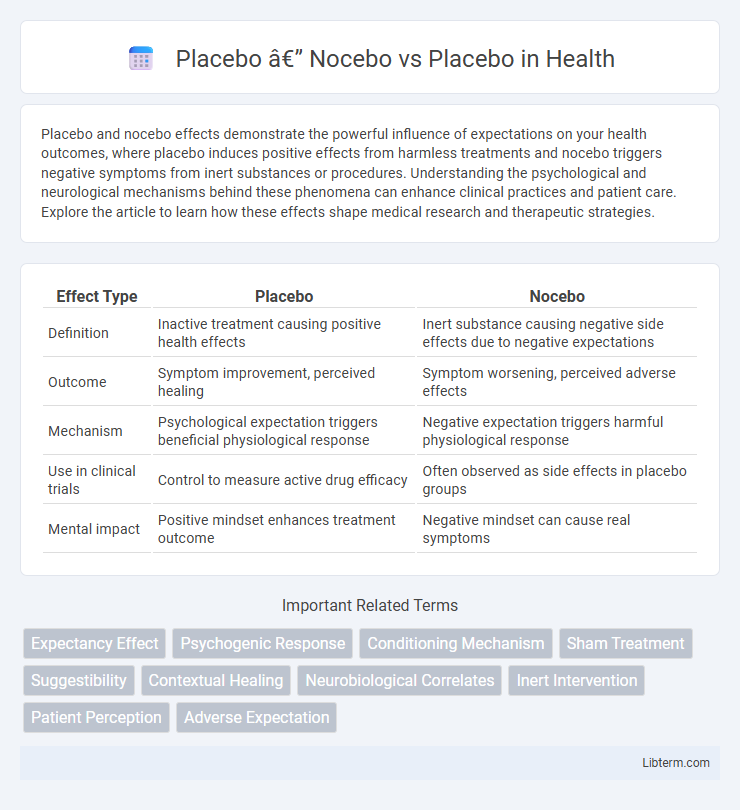
| Effect Type | Placebo | Nocebo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inactive treatment causing positive health effects | Inert substance causing negative side effects due to negative expectations |
| Outcome | Symptom improvement, perceived healing | Symptom worsening, perceived adverse effects |
| Mechanism | Psychological expectation triggers beneficial physiological response | Negative expectation triggers harmful physiological response |
| Use in clinical trials | Control to measure active drug efficacy | Often observed as side effects in placebo groups |
| Mental impact | Positive mindset enhances treatment outcome | Negative mindset can cause real symptoms |
Understanding the Placebo Effect
The placebo effect demonstrates how patients experience real physiological or psychological improvements after receiving a treatment with no therapeutic value, driven by their expectations and beliefs. Understanding the distinction between placebo and nocebo effects is crucial, as the nocebo effect causes negative outcomes due to negative expectations. Research highlights the importance of patient mindset and context in modulating treatment efficacy through complex neurobiological mechanisms involving brain regions like the prefrontal cortex and neurotransmitters such as endorphins and dopamine.
What Is the Nocebo Effect?
The nocebo effect occurs when negative expectations about a treatment cause harmful side effects or worsening symptoms, even though the treatment itself is inert. Unlike the placebo effect, where positive expectations improve outcomes, the nocebo effect demonstrates the powerful influence of the mind on physical health. Understanding the nocebo effect is crucial for clinicians to minimize patient anxiety and optimize therapeutic results by managing expectations carefully.
Placebo vs Nocebo: Key Differences
Placebo and nocebo represent opposite psychological responses to inert substances, where placebo elicits positive effects and nocebo triggers negative outcomes. Placebo effects enhance health by activating brain regions associated with reward and pain relief, while nocebo effects increase anxiety and pain perception through heightened activity in areas like the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Understanding these key differences informs clinical practices by optimizing therapeutic benefits and minimizing adverse reactions driven by patient expectations.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Placebo
The psychological mechanisms behind the placebo effect involve complex cognitive processes such as expectation, conditioning, and the brain's response to perceived treatment. Neurobiological factors include the release of endorphins and activation of brain regions like the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex, which modulate pain and emotional responses. In contrast, the nocebo effect triggers negative outcomes through anxiety and negative expectations, highlighting the powerful influence of the mind on physiological health.
How Nocebo Responses Develop
Nocebo responses develop through negative expectations and prior adverse experiences, triggering anxiety and activating brain regions such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Conditioning plays a significant role, where repeated exposure to negative cues leads to anticipatory symptoms without an actual harmful stimulus. Neurochemical changes, including increased cholecystokinin and decreased endorphins, contribute to the manifestation of nocebo effects, differentiating them from placebo responses driven by positive expectations and reward pathways.
Factors Influencing Placebo and Nocebo Outcomes
Placebo and nocebo effects are significantly influenced by factors such as patient expectations, conditioning, and the therapeutic environment. Neurobiological mechanisms involving neurotransmitters like dopamine and endorphins modulate the intensity of these responses. Psychological aspects, including anxiety and prior treatment experiences, also play crucial roles in determining placebo and nocebo outcomes.
Clinical Implications of Placebo and Nocebo
The clinical implications of placebo and nocebo effects are critical in patient care, as placebo responses can enhance treatment outcomes through positive expectations, while nocebo effects may cause adverse symptoms driven by negative expectations. Understanding neurobiological mechanisms underlying these effects helps clinicians optimize therapeutic strategies by harnessing placebo benefits and minimizing nocebo risks. Effective communication and patient-clinician interactions play a pivotal role in modulating placebo and nocebo responses, ultimately influencing medication adherence and treatment efficacy.
Ethical Considerations in Placebo and Nocebo Research
Ethical considerations in placebo and nocebo research center on informed consent and the potential harm to participants due to deception or negative expectations. Researchers must carefully balance the scientific value of placebo-controlled trials with respect for patient autonomy and minimizing psychological or physical risks. Transparency, risk assessment, and ethical review board approval are critical to ensuring that placebo and nocebo studies uphold ethical standards in clinical research.
Real-World Examples: Placebo and Nocebo in Medicine
Placebo and nocebo effects significantly influence patient outcomes in clinical settings, with placebo responses demonstrated in pain management and depression treatments, where inert substances can trigger real symptom relief. Nocebo effects manifest when negative expectations cause adverse side effects, evident in statin therapy where patients report muscle pain despite inactive treatments. Understanding these phenomena helps optimize therapeutic strategies by integrating patient perceptions to enhance efficacy and minimize harm in real-world medicine.
Enhancing Patient Care by Managing Placebo-Nocebo Effects
Managing placebo and nocebo effects is crucial for enhancing patient care by optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse reactions. Understanding patient expectations and leveraging positive communication can amplify placebo responses, while carefully addressing negative anticipations helps reduce nocebo-induced symptoms. Integrating these strategies into clinical practice improves overall therapeutic efficacy and patient satisfaction.
Placebo — Nocebo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com