Authorized admission ensures that only individuals with proper permission can access restricted areas, enhancing security and compliance. Proper verification methods are essential to prevent unauthorized entry and protect sensitive environments. Discover how authorized admission systems can safeguard your premises by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
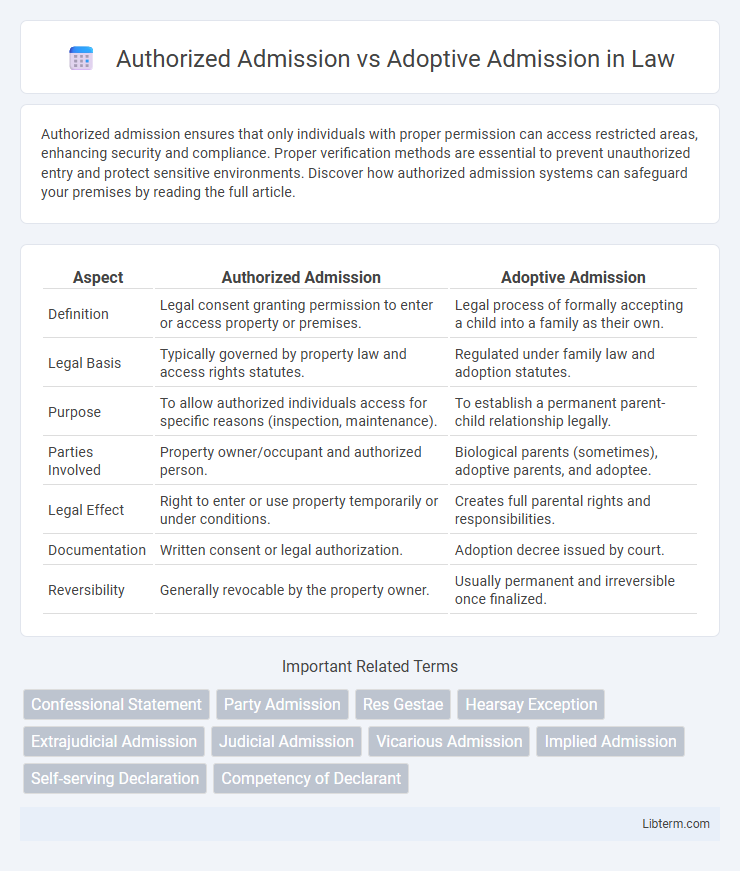
| Aspect | Authorized Admission | Adoptive Admission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal consent granting permission to enter or access property or premises. | Legal process of formally accepting a child into a family as their own. |
| Legal Basis | Typically governed by property law and access rights statutes. | Regulated under family law and adoption statutes. |
| Purpose | To allow authorized individuals access for specific reasons (inspection, maintenance). | To establish a permanent parent-child relationship legally. |
| Parties Involved | Property owner/occupant and authorized person. | Biological parents (sometimes), adoptive parents, and adoptee. |
| Legal Effect | Right to enter or use property temporarily or under conditions. | Creates full parental rights and responsibilities. |
| Documentation | Written consent or legal authorization. | Adoption decree issued by court. |
| Reversibility | Generally revocable by the property owner. | Usually permanent and irreversible once finalized. |
Introduction to Hospital Admissions
Authorized admission refers to the official approval granted by hospital administration or medical staff for a patient's entry into the hospital for treatment or observation. Adoptive admission involves admitting a patient under the care or guidance of another party, such as a legal guardian or family member, who takes responsibility during the hospital stay. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for hospital admissions protocols to ensure proper authorization and patient management.
Defining Authorized Admission
Authorized Admission refers to the formal consent granted by a governing body or institution allowing a patient to be admitted to a healthcare facility for treatment or observation. This process ensures compliance with legal and organizational protocols, differentiating it from Adoptive Admission, which involves admitting a patient based on decisions made by adoptive guardians or caregivers. Authorized Admission typically requires documentation such as a physician's order or administrative approval, emphasizing its official and regulated nature.
Understanding Adoptive Admission
Adoptive admission occurs when an individual is legally accepted as a member of a group or institution through a formal adoption process, granting them rights and responsibilities equivalent to those of original members. It involves a legal or institutional endorsement that validates the individual's status, often used in educational or organizational settings to integrate members who were not originally part of the entity. Understanding adoptive admission is crucial for recognizing the legitimacy and full inclusion of adoptive members, distinguishing it from authorized admission, which typically refers to permission granted without the full legal or formal adoption process.
Key Differences Between Authorized and Adoptive Admission
Authorized admission involves a legal or official permission granted by a governing body or institution allowing entry or participation, often requiring formal documentation or compliance with set standards. Adoptive admission refers to the acceptance or integration of an entity, such as a child or policy, into an existing system or family, emphasizing the process of inclusion and adaptation. The key differences lie in authorized admission's reliance on formal approval and regulatory criteria, whereas adoptive admission centers on acceptance and incorporation without mandatory regulatory oversight.
Legal Framework Governing Each Admission Type
Authorized Admission under immigration law is governed by statutory regulations that outline specific eligibility criteria, procedural requirements, and enforcement mechanisms established by national immigration acts such as the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) in the United States. Adoptive Admission operates within a distinct legal framework focusing on family law and international adoption treaties like the Hague Adoption Convention, ensuring the adoption process meets jurisdictional standards and the best interests of the child. Both admission types require compliance with separate regulatory bodies--immigration authorities for Authorized Admission and child welfare agencies or courts for Adoptive Admission--highlighting the specialized governance structures enforcing their respective legal protocols.
Patient Rights in Authorized vs Adoptive Admission
Authorized Admission ensures that patients or their legal representatives provide explicit consent before hospitalization, emphasizing respect for patient autonomy and informed decision-making. Adoptive Admission often involves decisions made by healthcare providers or institutions under emergency or incapacitation circumstances, which can limit immediate patient rights but prioritize urgent care needs. Protecting patient rights in both contexts requires clear communication, legal safeguards, and regular review of admission criteria to uphold dignity and legal compliance.
Roles of Family and Legal Representatives
Authorized admission grants family members or legal representatives the formal right to consent to medical treatment or facility entry for an incapacitated individual, ensuring decisions align with the patient's best interests. In adoptive admission, the adoptive family assumes full legal responsibility, including admission rights, with recognition of parental authority equivalent to biological relatives. Both roles involve safeguarding the individual's welfare, but adoptive admission confers permanent legal status, while authorized admission is often conditional or temporary.
Implications for Healthcare Providers
Authorized Admission allows healthcare providers to admit patients based on explicit legal consent, ensuring clear liability protections and streamlined care coordination. Adoptive Admission involves admitting patients without direct consent, often under emergency or protective statutes, which may increase provider responsibilities for documenting justification and adhering to stricter regulatory compliance. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for healthcare providers to manage risk, uphold patient rights, and optimize treatment outcomes within legal frameworks.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Authorized admission involves formal consent and strict adherence to legal protocols, ensuring patient rights and institutional accountability, yet challenges arise in maintaining transparency and avoiding coercion. Adoptive admission, often used in emergencies, may struggle with ethical concerns regarding informed consent, patient autonomy, and potential abuse of discretionary power. Balancing these admissions requires careful ethical scrutiny to protect vulnerable individuals while providing timely care.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Admission Process
Authorized admission involves formal approval by a governing body or institution, ensuring compliance with specific regulations and criteria. Adoptive admission emphasizes acceptance based on integration or alignment with existing frameworks, often allowing flexibility and inclusivity. Selecting the appropriate admission process depends on the organizational goals, legal requirements, and the desired balance between control and adaptability.
Authorized Admission Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com