Memorization techniques enhance your ability to retain and recall information efficiently by using methods like spaced repetition, visualization, and association. Applying these strategies improves learning outcomes and makes studying more effective and engaging. Explore the rest of this article to discover powerful memorization tips tailored to boost your memory skills.
Table of Comparison
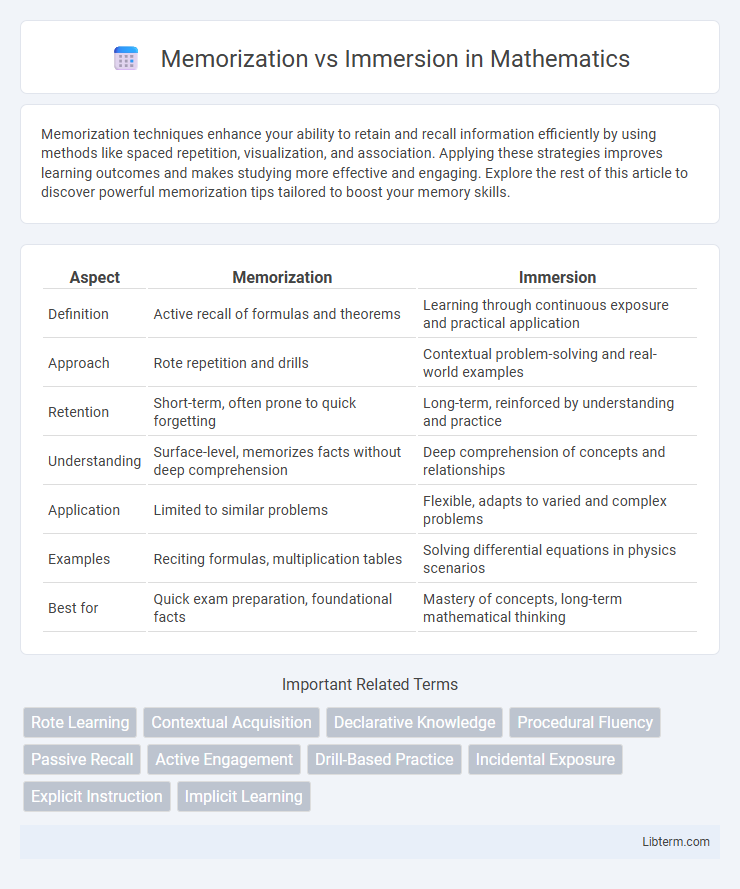
| Aspect | Memorization | Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active recall of formulas and theorems | Learning through continuous exposure and practical application |
| Approach | Rote repetition and drills | Contextual problem-solving and real-world examples |
| Retention | Short-term, often prone to quick forgetting | Long-term, reinforced by understanding and practice |
| Understanding | Surface-level, memorizes facts without deep comprehension | Deep comprehension of concepts and relationships |
| Application | Limited to similar problems | Flexible, adapts to varied and complex problems |
| Examples | Reciting formulas, multiplication tables | Solving differential equations in physics scenarios |
| Best for | Quick exam preparation, foundational facts | Mastery of concepts, long-term mathematical thinking |
Understanding Memorization: Definition and Key Features
Memorization involves the intentional encoding and retention of information through repetition and practice, allowing for quick recall without necessarily understanding context or meaning. Key features include rote learning, frequent review sessions, and the ability to reproduce facts or sequences accurately. This method is commonly used in language learning and academic studies to establish foundational knowledge before deeper comprehension is developed.
The Immersion Approach: What Does It Entail?
The immersion approach involves surrounding learners with the target language through consistent exposure in natural contexts, promoting intuitive understanding and practical usage without relying on rote memorization. This method emphasizes active communication, cultural engagement, and contextual learning to develop fluency and comprehension simultaneously. Immersion fosters deeper cognitive connections by integrating language with real-life experiences, enhancing retention and application.
Cognitive Processes Behind Memorization vs Immersion
Memorization relies on rote learning and repetition, engaging the brain's hippocampus to store and retrieve specific information quickly. Immersion activates multiple cognitive processes, including contextual learning and pattern recognition in the prefrontal cortex, enhancing deeper understanding and long-term retention. Neural networks formed during immersion promote stronger synaptic connections compared to the surface-level encoding typical of memorization.
Short-Term Gains: Strengths of Memorization
Memorization offers rapid acquisition of vocabulary and grammar rules, enabling learners to quickly recall essential language components for immediate use. This method efficiently boosts short-term test performance and conversational readiness by reinforcing specific phrases and structures. Targeted repetition in memorization strengthens neural pathways, facilitating swift retrieval during early language learning stages.
Long-Term Retention: The Power of Immersion
Immersion significantly enhances long-term retention by engaging multiple sensory pathways and contextual learning, which reinforces memory consolidation more effectively than rote memorization. Studies show learners immersed in a language environment retain vocabulary and grammar rules for extended periods, as active usage and contextual clues create stronger neural connections. Immersion's dynamic and repetitive exposure promotes durable memory traces, making it the superior method for sustained knowledge retention.
Practical Applications: When to Use Memorization
Memorization is essential for quickly recalling foundational knowledge such as vocabulary, formulas, and historical dates, which supports efficient problem-solving and communication in real-time scenarios. It proves particularly useful in standardized testing, language acquisition at beginner levels, and professions requiring rapid fact retrieval like medicine or law. Employing memorization strategically enhances learning efficiency when immediate recall of specific information is critical for performance.
Practical Applications: When to Embrace Immersion
Immersion is particularly effective for language learners aiming to develop natural fluency and real-world conversational skills rapidly. Practical applications include studying abroad, engaging in full-language environments, or using immersive technology like VR to simulate real-life situations. Embracing immersion enhances contextual understanding, cultural nuances, and accelerates retention beyond rote memorization methods.
Common Challenges and Pitfalls of Each Method
Memorization often leads to temporary retention and struggles with practical language application due to lack of contextual understanding, while immersion can overwhelm beginners with rapid input and insufficient structured learning. Common pitfalls of memorization include rote learning without grasping grammar or conversational flow, resulting in fragmented language skills. Immersion challenges include cognitive overload and frustration when learners lack foundational vocabulary, hindering progress and motivation.
Combining Memorization and Immersion for Optimal Learning
Combining memorization and immersion maximizes language acquisition by reinforcing vocabulary and grammar through active context use. Memorization provides a strong foundation of essential words and rules, while immersion fosters natural language processing and fluency by exposing learners to real-life communication. This integrated approach accelerates retention and enhances practical application, leading to more effective and lasting language skills.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Learning Goals
Memorization accelerates vocabulary retention and grammar rules, making it ideal for exam preparation or short-term language objectives. Immersion fosters natural language acquisition through contextual experiences, enhancing fluency and cultural understanding, which suits long-term conversational goals. Selecting the right approach depends on whether rapid recall or holistic comprehension aligns best with your personal learning targets.
Memorization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com