Accurate forecasting plays a crucial role in business success by predicting future trends, customer behaviors, and market demands. Utilizing advanced data analysis and machine learning techniques enhances the precision of forecasts, enabling better strategic planning and resource allocation. Discover how improving your forecasting methods can unlock new opportunities and drive growth in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
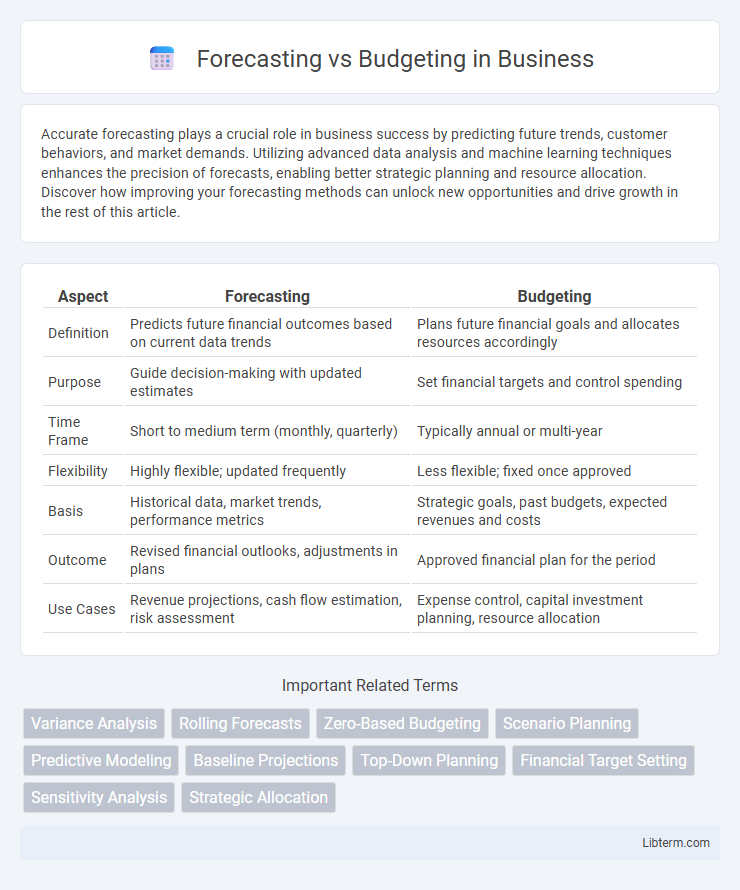
| Aspect | Forecasting | Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predicts future financial outcomes based on current data trends | Plans future financial goals and allocates resources accordingly |
| Purpose | Guide decision-making with updated estimates | Set financial targets and control spending |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term (monthly, quarterly) | Typically annual or multi-year |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; updated frequently | Less flexible; fixed once approved |
| Basis | Historical data, market trends, performance metrics | Strategic goals, past budgets, expected revenues and costs |
| Outcome | Revised financial outlooks, adjustments in plans | Approved financial plan for the period |
| Use Cases | Revenue projections, cash flow estimation, risk assessment | Expense control, capital investment planning, resource allocation |
Introduction to Forecasting and Budgeting
Forecasting involves predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data, trends, and market analysis, enabling organizations to anticipate revenue, expenses, and cash flow. Budgeting, in contrast, is the process of creating a detailed financial plan that allocates resources and sets spending limits aligned with strategic goals. Both forecasting and budgeting are essential financial management tools that guide decision-making and ensure organizational stability.
Defining Forecasting: Purpose and Process
Forecasting involves predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data, trends, and market analysis to support strategic decision-making. The process typically includes data collection, statistical modeling, and continuous refinement to improve accuracy over time. Forecasting aims to provide dynamic and forward-looking insights that help organizations anticipate changes and allocate resources efficiently.
Understanding Budgeting: Role and Method
Budgeting plays a crucial role in financial management by setting a detailed plan for allocating resources over a specific period, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. It involves identifying expected revenues, estimating expenses, and establishing spending limits to control costs effectively. The budgeting process uses historical data and strategic priorities to guide resource distribution and monitor financial performance.
Key Differences Between Forecasting and Budgeting
Forecasting estimates future financial outcomes based on historical data and current trends, providing a dynamic view of possible scenarios. Budgeting sets fixed financial goals and allocations for a specific period, acting as a financial plan and control mechanism. Forecasting is flexible and updated regularly, while budgeting is typically static and approved before the period begins.
The Importance of Forecasting in Financial Planning
Forecasting plays a critical role in financial planning by providing data-driven predictions that enable businesses to anticipate future revenues, expenses, and cash flows with greater accuracy than static budgets. Unlike budgeting, which sets fixed financial targets based on historical data, forecasting offers dynamic adjustments reflecting real-time market trends and operational changes, enhancing decision-making and resource allocation. Accurate financial forecasting minimizes risks, improves strategic planning, and supports sustainable growth by enabling organizations to respond proactively to economic fluctuations.
The Role of Budgeting in Organizational Strategy
Budgeting plays a crucial role in organizational strategy by allocating financial resources to align with strategic goals, ensuring operational efficiency and financial discipline. It provides a structured framework for setting performance targets, monitoring progress, and facilitating decision-making across departments. By establishing clear spending limits and priorities, budgeting supports long-term growth and risk management within companies.
When to Use Forecasting vs. Budgeting
Budgeting is essential for setting financial goals and allocating resources at the start of a fiscal period, providing a fixed plan based on historical data and expected expenses. Forecasting is best used throughout the year to adjust projections and respond to real-time business changes, using updated information for more accurate future financial insights. Organizations should rely on budgeting for annual planning and forecasting for dynamic decision-making and performance evaluation.
Benefits and Limitations of Forecasting
Forecasting provides dynamic insights by analyzing historical data and market trends to predict future financial performance, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changes and make informed decisions. Its benefits include improved accuracy in sales projections and resource allocation, but limitations stem from uncertainties in external factors and potential model overreliance, which can lead to inaccurate outcomes. Unlike budgeting, which sets fixed financial targets, forecasting offers flexibility but requires continuous updates to remain relevant amid evolving economic conditions.
Advantages and Challenges of Budgeting
Budgeting provides a structured financial plan that helps organizations allocate resources, control expenses, and set clear financial goals, enhancing accountability and operational efficiency. It enables monitoring of actual performance against planned targets, facilitating timely corrective actions and risk management. However, budgeting can be time-consuming and rigid, often limiting flexibility in responding to unexpected market changes or opportunities.
Integrating Forecasting and Budgeting for Effective Decision-Making
Integrating forecasting and budgeting enhances decision-making by aligning real-time data projections with financial plans, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to market changes. Forecasting provides dynamic insights into future performance, while budgeting establishes structured financial goals, together creating a flexible yet disciplined management approach. Utilizing software tools that combine predictive analytics with budget tracking improves accuracy and supports strategic resource allocation.
Forecasting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com