Safety stock acts as a buffer inventory to protect your supply chain from uncertainties in demand and lead time fluctuations. Maintaining optimal safety stock levels reduces the risk of stockouts and ensures consistent product availability. Discover how to calculate and manage safety stock effectively in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
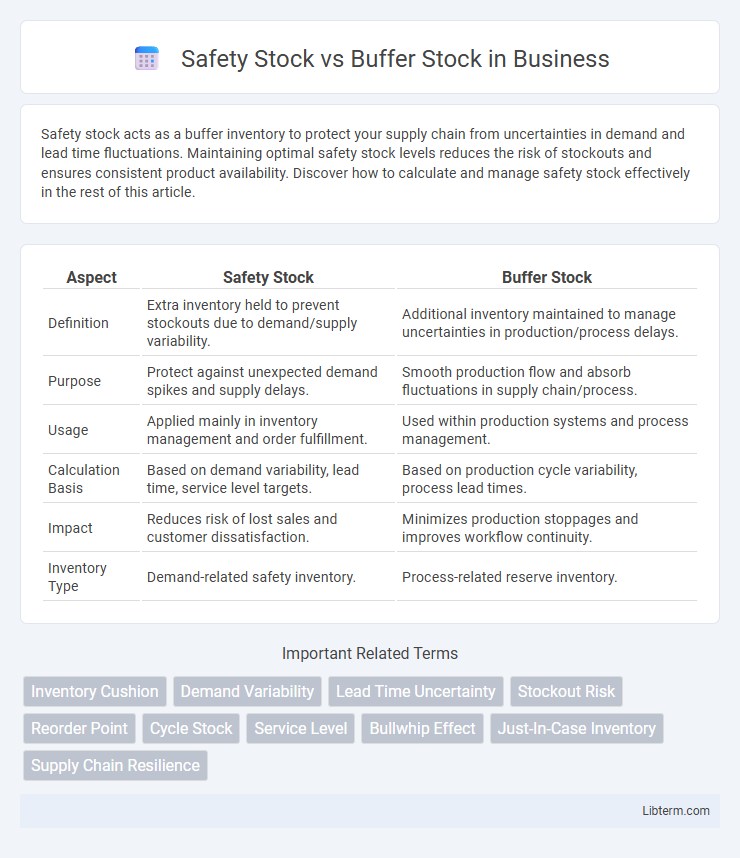
| Aspect | Safety Stock | Buffer Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extra inventory held to prevent stockouts due to demand/supply variability. | Additional inventory maintained to manage uncertainties in production/process delays. |
| Purpose | Protect against unexpected demand spikes and supply delays. | Smooth production flow and absorb fluctuations in supply chain/process. |
| Usage | Applied mainly in inventory management and order fulfillment. | Used within production systems and process management. |
| Calculation Basis | Based on demand variability, lead time, service level targets. | Based on production cycle variability, process lead times. |
| Impact | Reduces risk of lost sales and customer dissatisfaction. | Minimizes production stoppages and improves workflow continuity. |
| Inventory Type | Demand-related safety inventory. | Process-related reserve inventory. |
Introduction to Safety Stock and Buffer Stock
Safety stock refers to the extra inventory held to protect against uncertainty in demand or supply, ensuring service levels remain stable during fluctuations. Buffer stock, on the other hand, acts as a reserve to absorb disruptions in production or supply chain delays. Both concepts are essential for minimizing stockouts but differ in their specific applications and strategic focus within inventory management.
Defining Safety Stock
Safety stock refers to the extra inventory held to prevent stockouts caused by demand variability or supply delays, ensuring continuous production and customer satisfaction. It is calculated based on lead time, demand variability, and desired service level, acting as a critical risk management tool in inventory control. Unlike buffer stock, which mainly absorbs supply chain fluctuations, safety stock specifically targets uncertainties in demand and supply variations.
Understanding Buffer Stock
Buffer stock refers to the inventory held to absorb fluctuations in demand or supply, ensuring smooth production and order fulfillment during uncertainties. Unlike safety stock, which is specifically calculated to protect against variability in demand and lead times, buffer stock covers broader operational risks such as supplier delays and market disruptions. Effective management of buffer stock minimizes stockouts and prevents costly production halts, improving overall supply chain resilience.
Key Differences Between Safety Stock and Buffer Stock
Safety stock refers to the extra inventory held to protect against demand variability and supply chain uncertainties, ensuring service levels during unexpected spikes in demand or delays. Buffer stock, on the other hand, is specifically maintained to mitigate risks related to production disruptions, supplier delays, or logistical interruptions in the supply chain. The key difference lies in safety stock addressing demand fluctuations while buffer stock targets supply-side risks to maintain smooth operations.
Importance of Safety Stock in Inventory Management
Safety stock plays a critical role in inventory management by providing a cushion against demand variability and supply chain disruptions, ensuring product availability and preventing stockouts. Unlike buffer stock, which addresses planned fluctuations or anticipated delays, safety stock specifically guards against unforeseen uncertainties in lead times and demand forecasts. Maintaining an optimal level of safety stock enhances customer satisfaction and minimizes the risk of lost sales while balancing holding costs.
The Role of Buffer Stock in Supply Chain Stability
Buffer stock plays a crucial role in maintaining supply chain stability by absorbing fluctuations in demand and supply, preventing production interruptions and stockouts. Unlike safety stock, which is primarily calculated based on statistical demand variability, buffer stock accounts for broader uncertainties such as supplier delays and market disruptions. Efficient management of buffer stock ensures smoother operations and enhances resilience against unexpected supply chain shocks.
Methods for Calculating Safety Stock
Safety stock is typically calculated using statistical methods that consider demand variability and lead time uncertainty, such as the standard deviation of demand during lead time multiplied by a service level factor (z-score). Common formulas include the basic safety stock formula: Safety Stock = z * sLT, where sLT represents the standard deviation of demand during lead time. Buffer stock is often calculated more heuristically, based on fixed quantities or historical experience, rather than strict statistical models.
Strategies for Managing Buffer Stock
Strategies for managing buffer stock involve maintaining optimal inventory levels to prevent stockouts while minimizing holding costs. Utilizing demand forecasting techniques and real-time inventory monitoring helps adjust buffer stock dynamically according to market fluctuations and lead time variability. Implementing safety protocols, such as defining reorder points and safety thresholds, ensures consistent availability during supply chain disruptions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Approach
Safety stock ensures inventory availability by accounting for demand variability and supply delays, reducing stockouts but increasing holding costs and potential obsolescence. Buffer stock acts as a physical reserve to absorb supply chain disruptions, enhancing service levels yet potentially leading to excess inventory and higher storage expenses. Both strategies improve supply reliability, but safety stock offers a more data-driven approach, while buffer stock provides a tangible inventory cushion.
Choosing the Right Stock Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right stock strategy involves understanding the key differences between safety stock and buffer stock, where safety stock acts as a calculated extra inventory to protect against demand variability, while buffer stock accounts for uncertainties in supply chain disruptions. Evaluating factors such as lead time, demand volatility, and supplier reliability helps businesses determine the optimal stock level that minimizes stockouts and holding costs. Implementing data-driven inventory models enhances decision-making, ensuring the chosen stock strategy aligns with operational goals and customer service requirements.
Safety Stock Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com