Business intelligence (BI) transforms raw data into actionable insights, enabling companies to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency. By leveraging advanced analytics, visualization tools, and data integration, organizations can identify trends, optimize operations, and improve customer experiences. Explore the rest of this article to discover how BI can unlock your business's full potential.
Table of Comparison
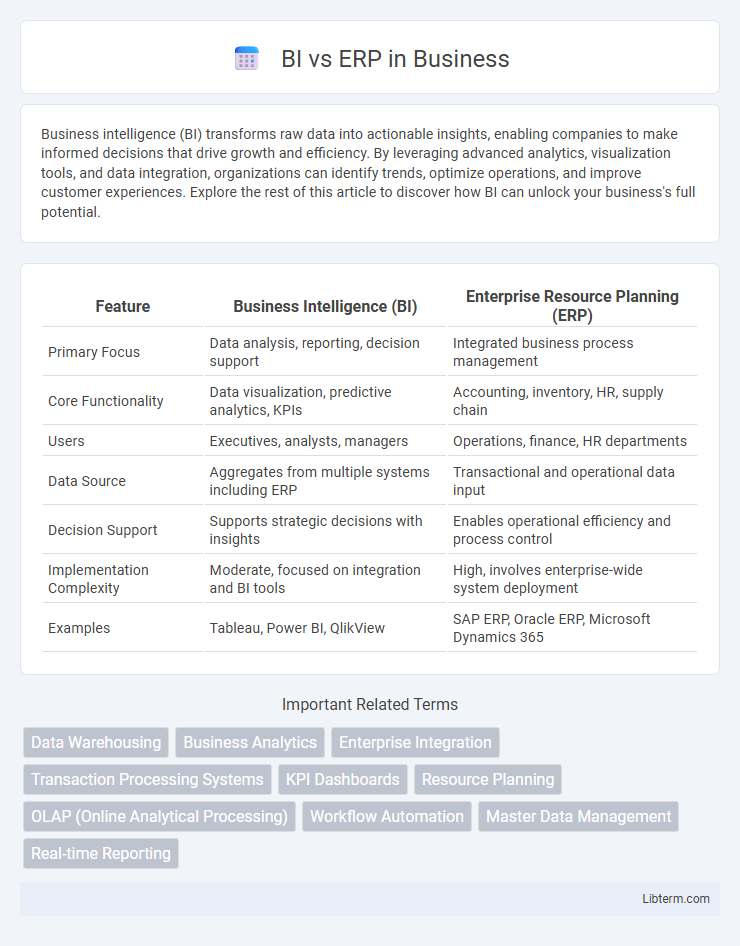
| Feature | Business Intelligence (BI) | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Data analysis, reporting, decision support | Integrated business process management |
| Core Functionality | Data visualization, predictive analytics, KPIs | Accounting, inventory, HR, supply chain |
| Users | Executives, analysts, managers | Operations, finance, HR departments |
| Data Source | Aggregates from multiple systems including ERP | Transactional and operational data input |
| Decision Support | Supports strategic decisions with insights | Enables operational efficiency and process control |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate, focused on integration and BI tools | High, involves enterprise-wide system deployment |
| Examples | Tableau, Power BI, QlikView | SAP ERP, Oracle ERP, Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
Introduction to BI and ERP
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses technologies and strategies used to analyze data and provide actionable insights for decision-making. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business processes such as finance, supply chain, and human resources into a unified platform for operational efficiency. While BI focuses on data analysis and reporting, ERP emphasizes process automation and resource management across an organization.
Core Functions of BI
Business Intelligence (BI) focuses on data analysis, reporting, and visualization to support data-driven decision-making, enabling companies to uncover insights from historical and real-time data. Core functions of BI include data mining, dashboards, performance metrics, and predictive analytics that help identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for optimization. Unlike ERP systems that manage operational processes like inventory, finance, and human resources, BI systems enhance strategic planning and business performance monitoring through advanced data integration and analysis tools.
Core Functions of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate core business functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and manufacturing into a unified platform, streamlining operations and improving data accuracy. ERP centralizes transactional data and automates routine processes, enabling real-time visibility and operational efficiency across departments. This foundational capability distinguishes ERP from Business Intelligence (BI), which primarily focuses on analyzing and interpreting data for strategic decision-making rather than managing daily business activities.
Key Differences Between BI and ERP
Business Intelligence (BI) primarily focuses on analyzing data to provide actionable insights and improve decision-making through reporting, dashboards, and data visualization. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates core business processes like finance, supply chain, and human resources into a unified system that manages daily operations. BI enhances strategic planning and performance measurement, while ERP streamlines operational workflows and resource management.
Integration of BI and ERP Systems
Integration of BI and ERP systems enhances organizational decision-making by combining real-time operational data from ERP with advanced analytics capabilities of BI tools. This synergy enables seamless data flow, ensuring accurate reporting, improved forecasting, and strategic insights across departments. Efficient integration reduces data silos, accelerates performance analysis, and supports proactive business management.
Benefits of Using BI
Business Intelligence (BI) enhances decision-making by providing real-time data analytics, trend identification, and predictive insights that ERP systems alone may not offer. BI tools enable companies to optimize operations, improve financial performance, and gain competitive advantage through customizable dashboards and advanced reporting. Integrating BI with ERP systems unlocks deeper data visibility, driving strategic planning and faster response to market changes.
Benefits of Using ERP
ERP systems streamline business processes by integrating core functions like finance, supply chain, and human resources into a single platform, enhancing operational efficiency. They provide real-time data visibility, enabling better decision-making and resource management across departments. Implementing ERP reduces manual errors and improves compliance through standardized workflows and automated reporting.
Use Cases: BI vs ERP in Real Businesses
Business Intelligence (BI) drives data-driven decision-making by analyzing historical and real-time data, enabling companies to identify sales trends, customer preferences, and operational inefficiencies. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems streamline core business processes such as inventory management, finance, and supply chain operations by integrating various departments into a unified platform. In real businesses, BI tools uncover actionable insights for strategic planning and market analysis, while ERP solutions enhance day-to-day operational efficiency and resource allocation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing BI or ERP
Choosing between Business Intelligence (BI) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems depends on organizational needs such as data analysis capabilities versus integrated process management. Consider factors like real-time data access, scalability, customization options, and the specific business functions each system supports. Evaluating cost, user interface, and compatibility with existing software infrastructure is crucial for maximizing return on investment and operational efficiency.
Future Trends in BI and ERP
Future trends in Business Intelligence (BI) emphasize advanced AI-driven analytics, increased integration with machine learning models, and real-time data processing to enhance decision-making accuracy and speed. ERP systems are evolving with cloud-native architectures, automation via robotic process automation (RPA), and deeper cognitive capabilities for predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization. The convergence of BI and ERP will drive smarter enterprise ecosystems, leveraging massive data sets for proactive insights and operational efficiency across industries.
BI Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com