Strategic alliances enable businesses to combine resources, expertise, and market access, creating competitive advantages that might be difficult to achieve independently. These partnerships often lead to enhanced innovation, shared risks, and expanded customer bases, driving growth and value creation. Discover how forming a strategic alliance can transform Your business by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
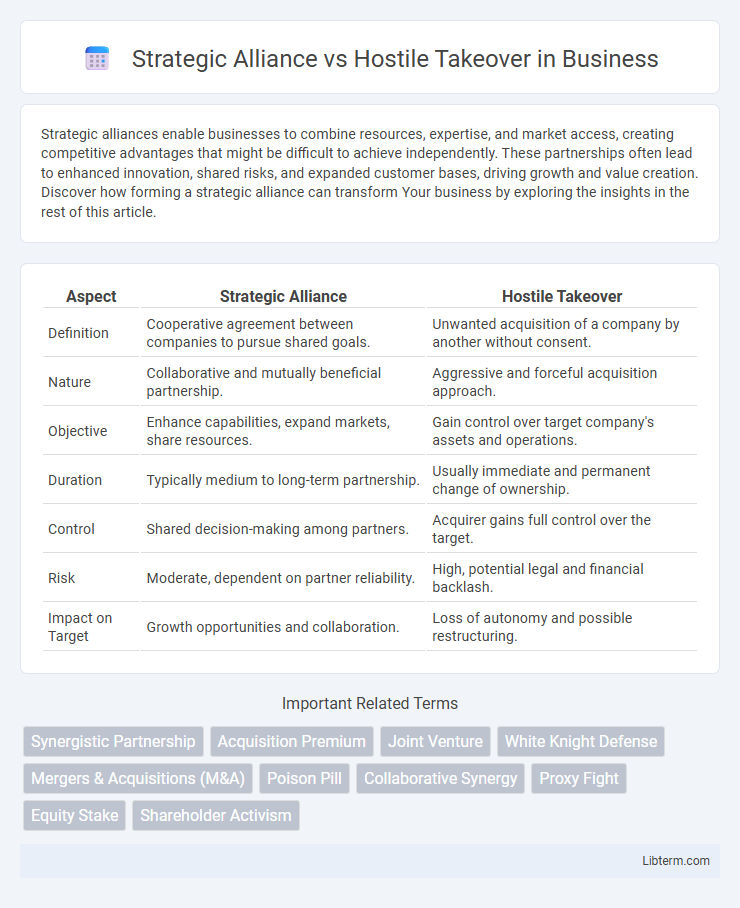
| Aspect | Strategic Alliance | Hostile Takeover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooperative agreement between companies to pursue shared goals. | Unwanted acquisition of a company by another without consent. |
| Nature | Collaborative and mutually beneficial partnership. | Aggressive and forceful acquisition approach. |
| Objective | Enhance capabilities, expand markets, share resources. | Gain control over target company's assets and operations. |
| Duration | Typically medium to long-term partnership. | Usually immediate and permanent change of ownership. |
| Control | Shared decision-making among partners. | Acquirer gains full control over the target. |
| Risk | Moderate, dependent on partner reliability. | High, potential legal and financial backlash. |
| Impact on Target | Growth opportunities and collaboration. | Loss of autonomy and possible restructuring. |
Introduction to Strategic Alliances and Hostile Takeovers
Strategic alliances involve collaborative agreements between companies to leverage shared resources, enhance market reach, and drive innovation without full ownership changes. Hostile takeovers occur when one company attempts to acquire another against the wishes of the target company's management, typically through direct purchase of shares. These contrasting approaches highlight cooperation versus control in corporate growth strategies.
Defining Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances are collaborative agreements between two or more companies aimed at achieving mutual business objectives while retaining their independence. Unlike hostile takeovers, which involve one company aggressively acquiring control of another without consent, strategic alliances focus on cooperation, resource sharing, and joint ventures to enhance competitive advantage. Key examples include partnerships in technology development, marketing collaborations, and supply chain integration.
Understanding Hostile Takeovers
Hostile takeovers occur when one company attempts to acquire another without the consent of its management, often by directly appealing to shareholders or using aggressive tactics such as tender offers and proxy battles. Understanding hostile takeovers requires analyzing factors like target company vulnerabilities, defense mechanisms including poison pills and white knight strategies, and the impact on shareholder value and corporate governance. These takeovers contrast sharply with strategic alliances, where collaboration and mutual agreement drive shared business objectives.
Key Differences Between Strategic Alliances and Hostile Takeovers
Strategic alliances involve voluntary partnerships where companies collaborate to achieve mutual goals, sharing resources and expertise without exchanging ownership. Hostile takeovers occur when one company acquires another against its consent, often through aggressive stock purchases or proxy battles, leading to a change in control. The fundamental difference lies in cooperation versus coercion, with strategic alliances fostering joint growth and hostile takeovers enforcing ownership changes regardless of the target's wishes.
Benefits of Forming Strategic Alliances
Forming strategic alliances enables companies to share resources, reduce risks, and access new markets more effectively than hostile takeovers, which often involve significant financial and operational disruption. Collaborative partnerships enhance innovation through combined expertise and foster long-term growth without antagonizing existing management or stakeholders. Strategic alliances also improve competitive advantage by leveraging complementary strengths and aligning goals for mutual benefit.
Risks and Challenges in Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances face risks such as cultural clashes, misaligned objectives, and potential loss of proprietary information, which can undermine collaboration effectiveness. Challenges include managing trust, coordinating operations across different organizational structures, and ensuring equitable value sharing between partners. Failure to address these issues may lead to conflicts, decreased innovation, and weakened competitive advantage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hostile Takeovers
Hostile takeovers allow acquiring companies to bypass management resistance and gain control quickly, often leading to increased market share and operational efficiencies. However, they can result in significant disruption, high costs from legal battles and buyout premiums, and damage to employee morale and corporate culture. The aggressive nature of hostile takeovers may also lead to long-term integration challenges and potential loss of key talent.
Real-World Examples: Strategic Alliance vs Hostile Takeover
Strategic alliances, such as the collaboration between Starbucks and PepsiCo to market ready-to-drink coffee beverages, exemplify mutually beneficial partnerships that leverage complementary strengths without ownership changes. In contrast, hostile takeovers like Vodafone's acquisition of Mannesmann in 2000 demonstrate aggressive attempts to gain control against the target company's resistance, often leading to major corporate restructuring. These real-world examples highlight the distinct dynamics where strategic alliances foster cooperation for shared growth, whereas hostile takeovers prioritize control and consolidation through adversarial means.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between Alliance and Takeover
Factors influencing the choice between a strategic alliance and a hostile takeover include company culture compatibility, financial resources, and market positioning. Strategic alliances are preferred when collaboration offers mutual benefits without the high costs and risks associated with acquisitions, especially in industries requiring innovation and shared expertise. Hostile takeovers are typically pursued when rapid control over a competitor is crucial, often driven by undervalued target companies and aggressive growth strategies.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Growth Strategy
Choosing between a strategic alliance and a hostile takeover depends on a company's long-term objectives, risk tolerance, and resource availability. Strategic alliances foster collaborative growth and innovation with shared risks, while hostile takeovers offer rapid market entry but involve higher financial and reputational risks. Evaluating industry dynamics, corporate culture compatibility, and regulatory environment is crucial for selecting the most effective growth strategy.
Strategic Alliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com