Registration rights are contractual provisions that allow investors to demand a company to register their private shares with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), enabling public sale and enhanced liquidity. These rights protect your investment by ensuring access to public markets and the potential for higher returns when selling shares. Explore the rest of this article to understand the types and strategic importance of registration rights in your investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
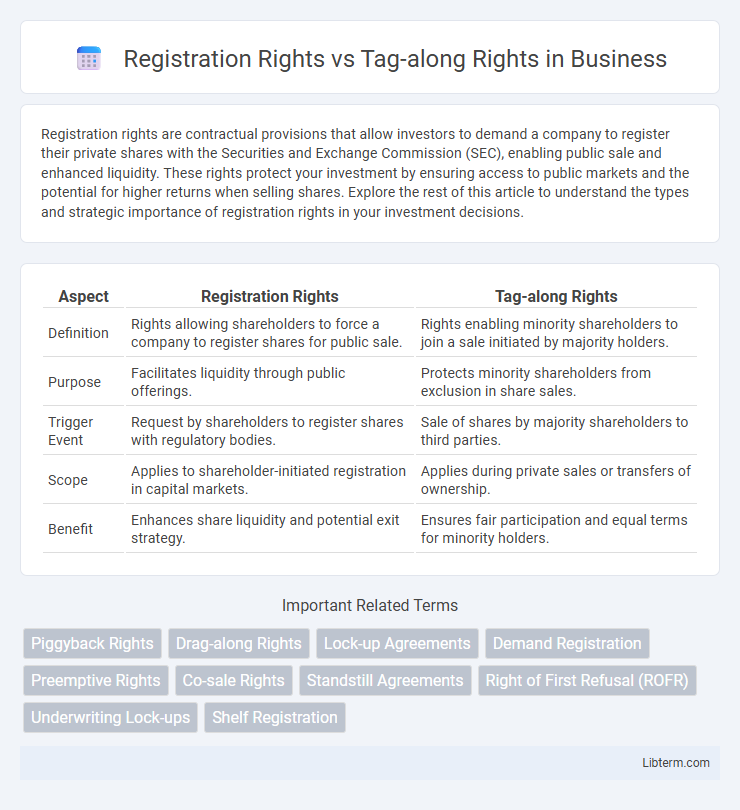
| Aspect | Registration Rights | Tag-along Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rights allowing shareholders to force a company to register shares for public sale. | Rights enabling minority shareholders to join a sale initiated by majority holders. |
| Purpose | Facilitates liquidity through public offerings. | Protects minority shareholders from exclusion in share sales. |
| Trigger Event | Request by shareholders to register shares with regulatory bodies. | Sale of shares by majority shareholders to third parties. |
| Scope | Applies to shareholder-initiated registration in capital markets. | Applies during private sales or transfers of ownership. |
| Benefit | Enhances share liquidity and potential exit strategy. | Ensures fair participation and equal terms for minority holders. |
Introduction to Registration Rights and Tag-along Rights
Registration rights grant investors the ability to demand or participate in the registration of securities with the SEC, facilitating liquidity through public offerings. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join a sale of shares initiated by majority stakeholders, ensuring equitable exit opportunities. Both rights are essential tools in venture capital agreements to balance control, liquidity, and investor protection.
Defining Registration Rights in Shareholder Agreements
Registration rights in shareholder agreements grant certain investors the ability to require a company to register their shares with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for public sale, ensuring liquidity and marketability. These rights are crucial for protecting investors' interests by facilitating public offerings, secondary sales, or other forms of public distribution of shares. Unlike tag-along rights, which provide minority shareholders the option to join in a sale by majority shareholders, registration rights specifically address the administrative process of making shares eligible for public trading.
Understanding Tag-along Rights: An Overview
Tag-along rights ensure minority shareholders can join a sale of shares by majority holders, protecting their interests in exit transactions. These rights allow minority investors to sell their shares on the same terms and conditions as majority shareholders, preventing them from being left behind in liquidity events. Understanding tag-along rights is crucial for safeguarding minority stakes during ownership transfers and maintaining equitable treatment in private equity deals.
Key Differences Between Registration and Tag-along Rights
Registration rights primarily grant investors the ability to force a company to register their shares for public sale, enhancing liquidity by facilitating access to public markets. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to sell their shares alongside majority shareholders during a sale, ensuring equal treatment in exit opportunities. The key difference lies in registration rights focusing on public offering processes, while tag-along rights emphasize participatory rights in private sales.
Legal Framework Governing Registration Rights
The legal framework governing registration rights is primarily rooted in the Securities Act of 1933, which mandates the registration of securities offerings to protect investors and ensure transparency in public markets. Registration rights agreements typically grant shareholders the ability to compel a company to register their shares for public sale, subject to specific regulatory requirements and exemptions under the SEC. In contrast, tag-along rights are governed by contractual agreements between shareholders and focus on protecting minority investors during a sale, rather than involving SEC registration procedures.
Benefits of Registration Rights for Investors
Registration rights empower investors by ensuring their securities can be publicly sold through a company's registration statement, enhancing liquidity and marketability. These rights provide investors with the ability to trigger or piggyback on a registration, facilitating timely exit strategies and maximizing return on investment. Registration rights also reduce the risk of holding unregistered shares, thereby increasing investor confidence and potential resale value.
Advantages and Purpose of Tag-along Rights
Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join a sale of shares initiated by majority shareholders, ensuring they receive the same price and terms. These rights prevent minority investors from being left behind during significant ownership changes, thereby preserving their investment value and exit opportunities. By aligning interests between major and minor stakeholders, tag-along rights foster fairness and liquidity in private company transactions.
Typical Scenarios Involving Registration and Tag-along Rights
Registration rights commonly arise during venture capital financing when investors seek the ability to sell their shares through a public offering, ensuring liquidity and exit opportunities. Tag-along rights typically emerge in minority shareholder situations, allowing these shareholders to join a sale initiated by majority holders and protect against being left behind. Both rights play crucial roles in maintaining investor protections during company transactions and liquidity events.
Negotiating Registration and Tag-along Rights in Deals
Negotiating registration rights involves ensuring investors can require a company to register their shares for public sale, enhancing liquidity and exit options during an IPO or secondary offering. Tag-along rights protect minority shareholders by allowing them to join a sale initiated by majority shareholders, ensuring they receive equitable treatment and fair value. Effective negotiation balances control over share sales with protection mechanisms to align interests and maximize investment returns.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Protective Rights in Investments
Selecting the appropriate protective rights depends on an investor's priority between liquidity and exit flexibility; registration rights enable shareholders to demand a company to register shares for public sale, ensuring smoother access to public markets. Tag-along rights provide minority investors protection by allowing them to sell their shares alongside majority stakeholders during a private sale, preserving their exit opportunities. Balancing these rights can optimize investment security and maximize potential returns in varying market scenarios.
Registration Rights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com