Dividend investing focuses on acquiring stocks that regularly distribute profits to shareholders, providing a steady income stream and potential for capital appreciation. This strategy suits investors seeking reliable cash flow and long-term wealth growth through reinvested dividends. Explore the rest of the article to learn how dividend investing can enhance your portfolio and build financial security.
Table of Comparison
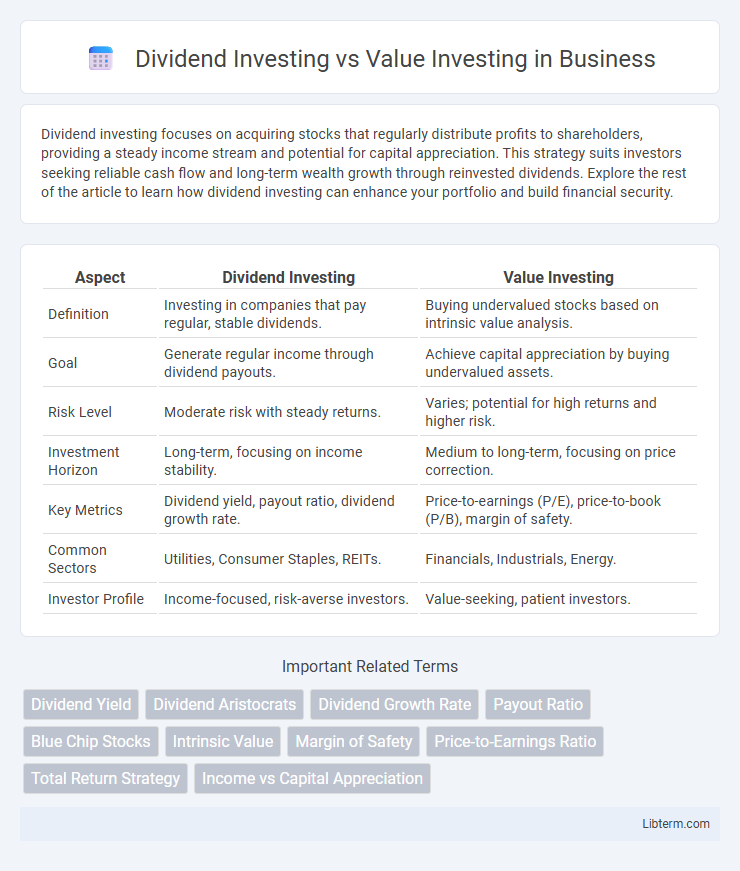
| Aspect | Dividend Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in companies that pay regular, stable dividends. | Buying undervalued stocks based on intrinsic value analysis. |
| Goal | Generate regular income through dividend payouts. | Achieve capital appreciation by buying undervalued assets. |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk with steady returns. | Varies; potential for high returns and higher risk. |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term, focusing on income stability. | Medium to long-term, focusing on price correction. |
| Key Metrics | Dividend yield, payout ratio, dividend growth rate. | Price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book (P/B), margin of safety. |
| Common Sectors | Utilities, Consumer Staples, REITs. | Financials, Industrials, Energy. |
| Investor Profile | Income-focused, risk-averse investors. | Value-seeking, patient investors. |
Introduction to Dividend Investing vs Value Investing
Dividend investing focuses on generating steady income through regular dividend payouts from established companies with consistent profit histories. Value investing targets undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value, aiming for capital appreciation as the market corrects the price disparity. Both strategies require thorough financial analysis but prioritize different investment goals and risk tolerances.
Core Principles of Dividend Investing
Dividend investing centers on generating consistent income through regular cash payments from companies with strong earnings and stable payout ratios. It prioritizes selecting stocks with a history of reliable dividend growth and solid balance sheets to ensure sustainability and minimize risk. Core principles include evaluating dividend yield, payout ratio, and dividend growth rate to balance income generation with long-term capital appreciation.
Core Principles of Value Investing
Value investing centers on identifying undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value by analyzing financial statements, cash flow, and earnings stability to ensure long-term growth potential. Dividend investing focuses on companies with consistent and growing dividend payouts, providing income streams alongside capital appreciation. Core principles of value investing include a margin of safety, patient capital deployment, and emphasis on fundamental analysis to uncover market inefficiencies.
Key Differences Between Dividend and Value Investing
Dividend investing focuses on generating regular income through stocks that pay consistent dividends, emphasizing cash flow and yield. Value investing targets undervalued companies based on fundamental analysis, aiming for capital appreciation by purchasing stocks priced below their intrinsic value. Key differences include dividend investing prioritizing income stability, while value investing centers on growth potential and market mispricing opportunities.
Potential Returns: Yield vs Capital Appreciation
Dividend investing focuses on generating steady income through regular dividend payments, providing a reliable yield that can supplement cash flow or be reinvested for compounding growth. Value investing emphasizes capital appreciation by identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, aiming for price gains as the market corrects mispricing. Investors seeking consistent income typically prefer dividend stocks, while those targeting long-term wealth accumulation lean towards value stocks for potential higher returns through price appreciation.
Risk Factors in Dividend and Value Strategies
Dividend investing carries risks such as dividend cuts during economic downturns, which can reduce expected income and signal financial distress in the underlying company. Value investing faces risks related to value traps, where stocks appear undervalued based on metrics like low price-to-earnings ratios but continue to decline due to deteriorating fundamentals. Both strategies require careful analysis of company financial health, market conditions, and sector-specific risks to mitigate potential losses.
Dividend Growth Stocks vs Undervalued Stocks
Dividend growth stocks provide consistent income with the potential for increasing payouts, appealing to investors seeking steady cash flow and long-term wealth accumulation. Undervalued stocks are identified by metrics such as low price-to-earnings ratios or discounted book values, presenting opportunities to buy shares below intrinsic value for capital appreciation. Balancing dividend growth with undervalued opportunities can optimize portfolio returns by combining income generation and value appreciation.
Portfolio Diversification in Each Strategy
Dividend investing emphasizes steady income through stocks of companies with consistent dividend payouts, enhancing portfolio diversification by balancing growth with reliable cash flow. Value investing targets undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, diversifying portfolios by capturing potential capital appreciation from market inefficiencies. Combining both approaches can achieve a well-rounded diversification strategy, blending income stability with growth opportunities.
Suitability for Different Investor Profiles
Dividend investing suits conservative investors seeking steady income and lower volatility, relying on companies with consistent dividend payouts. Value investing appeals to those with a higher risk tolerance aiming for capital appreciation by identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. Investors prioritizing cash flow should consider dividend strategies, while those willing to endure market swings might prefer value investing for growth potential.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Dividend investing suits investors seeking steady income and long-term financial stability through companies with consistent dividend payouts. Value investing appeals to those aiming for capital appreciation by identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and growth potential. Selecting the right approach depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon to align with desired outcomes.
Dividend Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com