BRICS economies, including Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, showcase rapid growth driven by natural resources, manufacturing, and expanding consumer markets. EU economies, on the other hand, emphasize advanced technology, services, and regulatory frameworks promoting stability and innovation across member states. Explore this article to understand how these economic blocs influence global trade and investment trends impacting your financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
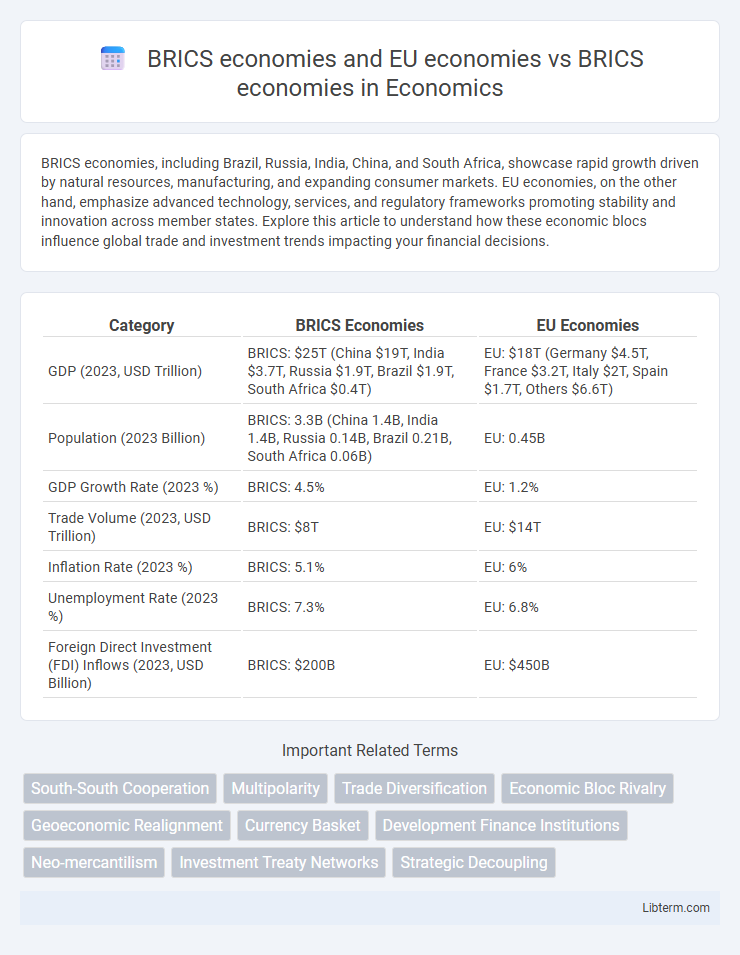
| Category | BRICS Economies | EU Economies |
|---|---|---|
| GDP (2023, USD Trillion) | BRICS: $25T (China $19T, India $3.7T, Russia $1.9T, Brazil $1.9T, South Africa $0.4T) | EU: $18T (Germany $4.5T, France $3.2T, Italy $2T, Spain $1.7T, Others $6.6T) |
| Population (2023 Billion) | BRICS: 3.3B (China 1.4B, India 1.4B, Russia 0.14B, Brazil 0.21B, South Africa 0.06B) | EU: 0.45B |
| GDP Growth Rate (2023 %) | BRICS: 4.5% | EU: 1.2% |
| Trade Volume (2023, USD Trillion) | BRICS: $8T | EU: $14T |
| Inflation Rate (2023 %) | BRICS: 5.1% | EU: 6% |
| Unemployment Rate (2023 %) | BRICS: 7.3% | EU: 6.8% |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Inflows (2023, USD Billion) | BRICS: $200B | EU: $450B |
Overview of BRICS and EU Economies
BRICS economies--comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa--collectively represent over 40% of the world's population and contribute approximately 25% of global GDP, driven by rapid industrialization and expanding consumer markets. The European Union, with 27 member states, boasts a highly integrated economic bloc characterized by a combined GDP surpassing $15 trillion and advanced infrastructure supporting trade, innovation, and financial services. While BRICS economies emphasize emerging market growth and resource exports, EU economies excel in technological advancement, regulatory frameworks, and high-value manufacturing, creating contrasting but complementary global economic roles.
Economic Growth: BRICS vs EU
BRICS economies, including Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, have demonstrated higher average GDP growth rates compared to the EU, driven by rapid industrialization, expanding consumer markets, and significant infrastructure investments. The EU economies, characterized by mature markets and higher GDP per capita, generally show slower GDP growth rates but benefit from advanced technology, stable institutions, and diversified economic structures. Despite volatility in some BRICS regions, their combined economic growth contributes significantly to global GDP expansion, contrasting with the EU's more steady, but moderate, economic growth profile.
Trade Relations and Global Influence
BRICS economies, comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, have significantly expanded their trade relations through diversified partnerships and growing intra-BRICS commerce, positioning themselves as key players in global supply chains. The European Union maintains a dominant role in global trade with advanced technological exports and extensive trade agreements, yet faces competition from BRICS nations' rapidly increasing economic influence and resource-driven markets. While the EU leverages regulatory frameworks and innovation leadership to sustain global influence, BRICS countries capitalize on demographic advantages and natural resources to reshape global economic governance and trade balance.
Industrial Development and Innovation
BRICS economies demonstrate rapid industrial development driven by large-scale manufacturing and infrastructure investments, with China leading advancements in technology and innovation ecosystems. The EU economies exhibit mature industrial sectors characterized by high-value manufacturing, strong emphasis on research and development (R&D), and integration of digital technologies to enhance productivity. Comparing both, BRICS focus on expanding industrial capacity and technology adoption, while the EU prioritizes innovation quality, sustainability, and advanced industrial automation.
Currency Power and Monetary Policies
BRICS economies exhibit diverse currency power, with the Chinese yuan gaining international prominence through strategic monetary policies and increasing global trade influence, while currencies like the Brazilian real and South African rand face volatility due to economic and political challenges. In contrast, EU economies benefit from the euro's status as a major global reserve currency, supported by the European Central Bank's coordinated monetary policy aimed at stability and inflation control across member states. The euro area's unified monetary approach contrasts with the fragmented and often inflation-targeted policies within BRICS, impacting currency stability and international investment attractiveness.
Investment Trends: BRICS and EU Comparison
BRICS economies show robust inward foreign direct investment growth, driven by expanding consumer markets and infrastructure development, contrasting with the EU's more mature markets which attract steady but slower FDI inflows primarily in high-tech and service sectors. While EU economies benefit from established regulatory frameworks and integration fostering cross-border investments, BRICS countries leverage cost advantages and resource availability to draw manufacturing and energy sector investments. The divergence in investment trends highlights the EU's focus on innovation and sustainability, whereas BRICS emphasize rapid industrialization and urbanization as key drivers for economic expansion.
Socioeconomic Challenges and Opportunities
BRICS economies face significant socioeconomic challenges including income inequality, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, and educational disparities, whereas EU economies leverage advanced social welfare systems and higher living standards to mitigate such issues. Despite slower GDP growth rates, EU economies benefit from more stable political institutions and robust regulatory frameworks, enhancing social cohesion and economic resilience. BRICS countries present opportunities in rapid urbanization, expanding middle classes, and demographic dividends that can drive innovation and market expansion if socioeconomic inequalities and infrastructure deficits are addressed effectively.
Geopolitical Roles and Global Strategy
BRICS economies--comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa--play a pivotal geopolitical role by leveraging their vast natural resources, large populations, and growing industrial capacities to challenge Western dominance in global governance. The European Union, as an integrated economic and political bloc, maintains a strategic approach centered on regulatory influence, technological innovation, and multilateral diplomacy to safeguard its economic interests and promote global stability. In the evolving global strategy landscape, BRICS focuses on fostering alternative financial systems and South-South cooperation, while the EU emphasizes rule-based international order and transatlantic alliances.
Sustainability and Green Economy Initiatives
BRICS economies are increasingly investing in renewable energy projects and sustainable infrastructure to reduce carbon emissions and support green growth, with countries like China leading in solar and wind capacity expansion. EU economies maintain advanced environmental policies, such as the European Green Deal, promoting circular economy principles, carbon neutrality by 2050, and significant funding for innovation in green technologies. Comparing both, EU economies demonstrate more comprehensive sustainability frameworks and regulatory enforcement, while BRICS nations emphasize scaling up green investments to balance industrial growth with environmental protection.
Future Outlook: Collaboration or Competition
BRICS economies, comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, project robust growth fueled by demographic advantages, resource wealth, and technological advancements, positioning them as key drivers of global economic transformation. The European Union economies, with advanced infrastructure, strong regulatory frameworks, and high innovation capacity, continue to emphasize sustainable growth and digital transition, maintaining significant influence in international markets. Future outlook suggests a nuanced blend of collaboration and competition, where strategic partnerships in technology, trade, and climate initiatives coexist with rivalry in market share and geopolitical influence.
BRICS economies and EU economies Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com