Asset liquidation involves converting company or personal assets into cash, often to pay off debts or streamline operations. Understanding the most effective methods can maximize returns and minimize losses during this process. Explore the article to learn how your assets can be efficiently liquidated for optimal financial outcomes.
Table of Comparison
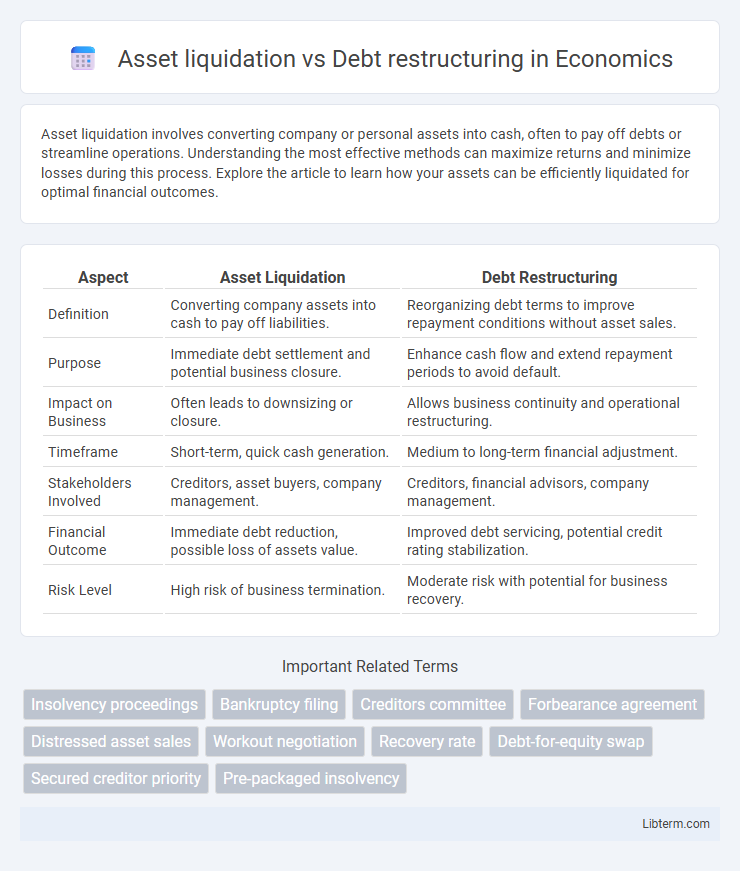
| Aspect | Asset Liquidation | Debt Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting company assets into cash to pay off liabilities. | Reorganizing debt terms to improve repayment conditions without asset sales. |
| Purpose | Immediate debt settlement and potential business closure. | Enhance cash flow and extend repayment periods to avoid default. |
| Impact on Business | Often leads to downsizing or closure. | Allows business continuity and operational restructuring. |
| Timeframe | Short-term, quick cash generation. | Medium to long-term financial adjustment. |
| Stakeholders Involved | Creditors, asset buyers, company management. | Creditors, financial advisors, company management. |
| Financial Outcome | Immediate debt reduction, possible loss of assets value. | Improved debt servicing, potential credit rating stabilization. |
| Risk Level | High risk of business termination. | Moderate risk with potential for business recovery. |
Introduction to Asset Liquidation and Debt Restructuring
Asset liquidation involves converting a company's assets into cash to pay off creditors, often used during bankruptcy or financial distress. Debt restructuring modifies the terms of existing debt agreements to improve liquidity and avoid default, allowing companies to negotiate reduced interest rates, extended payment periods, or debt forgiveness. Both strategies aim to alleviate financial burdens but differ in approach: liquidation focuses on asset conversion, while restructuring emphasizes renegotiation of debt obligations.
Key Differences Between Asset Liquidation and Debt Restructuring
Asset liquidation involves selling company assets to generate cash for settling debts, often signaling business closure or downsizing, while debt restructuring renegotiates existing obligations to improve repayment terms without asset disposal. Key differences include the impact on business continuity, as liquidation typically ends operations whereas restructuring aims to preserve the company. Asset liquidation directly converts tangible and intangible assets into funds, whereas debt restructuring modifies payment schedules, interest rates, or principal amounts to enhance financial stability.
Situations Favoring Asset Liquidation
Situations favoring asset liquidation typically arise when a company faces severe cash flow shortages, and immediate conversion of physical or financial assets into cash is essential to satisfy creditor demands or operational expenses. Asset liquidation is preferred when market conditions allow for favorable asset valuations, minimizing losses compared to prolonged debt restructuring negotiations. This approach is often chosen in cases where restructuring options are limited due to creditor resistance or when the business model is no longer viable, making continued operations unsustainable.
When to Consider Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring should be considered when a company faces temporary cash flow issues but anticipates future profitability, allowing it to avoid asset liquidation and preserve operational continuity. This approach helps optimize debt terms, such as interest rates and payment schedules, reducing financial strain without sacrificing core assets. It is particularly effective when market conditions are expected to improve, enabling the business to regain stability and maintain long-term value.
Advantages of Asset Liquidation
Asset liquidation offers immediate cash flow by converting non-performing or underutilized assets into liquid funds, enabling companies to meet urgent financial obligations without incurring additional debt. This strategy reduces ongoing maintenance costs and eliminates the financial burden associated with holding depreciating assets. Furthermore, liquidating assets provides a straightforward, transparent process that can improve balance sheet health and restore creditor confidence.
Pros and Cons of Debt Restructuring
Debt restructuring offers the advantage of preserving company operations and maintaining stakeholder relationships by renegotiating payment terms and reducing financial distress. It can improve cash flow management and avoid the negative impact on credit ratings often associated with asset liquidation. However, debt restructuring may lead to prolonged financial uncertainty, potential loss of creditor trust, and may not fully resolve underlying business issues if operational inefficiencies persist.
Impact on Creditors and Stakeholders
Asset liquidation typically results in creditors receiving payment based on the sale of a company's tangible and intangible assets, often at a reduced rate due to distressed sale conditions, which can lead to significant financial losses for stakeholders. In contrast, debt restructuring aims to renegotiate terms with creditors, such as extending payment periods, reducing interest rates, or converting debt to equity, potentially preserving more value for both creditors and stakeholders by maintaining business operations. The choice between liquidation and restructuring critically influences creditor recovery rates and stakeholder equity retention, with restructuring generally offering a more favorable outcome for all parties involved.
Effects on Business Continuity and Operations
Asset liquidation often disrupts business continuity by reducing operational capacity and limiting available resources, potentially leading to downsizing or closure. Debt restructuring aims to improve cash flow management and preserve operational integrity, allowing the business to continue functioning while addressing financial obligations. The choice between these strategies significantly impacts long-term viability, with debt restructuring generally supporting sustained operations better than asset liquidation.
Legal and Financial Implications
Asset liquidation involves selling company assets to repay creditors, often resulting in the dissolution of the business and potential tax consequences such as capital gains or losses. Debt restructuring legally renegotiates loan terms to improve cash flow and avoid bankruptcy, impacting credit ratings and requiring compliance with contractual obligations and bankruptcy laws. Financially, liquidation provides immediate funds but may yield lower value for assets, whereas restructuring aims to preserve business operations and long-term viability but involves complex legal documentation and potential lender consents.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Asset Liquidation vs Debt Restructuring
Choosing between asset liquidation and debt restructuring hinges on a company's financial health and long-term goals. Asset liquidation involves selling physical or financial assets to quickly generate cash, often suitable for companies facing insolvency or severe liquidity crises. Debt restructuring restructures existing obligations to improve repayment terms, ideal for businesses aiming to maintain operations while managing debt sustainably.
Asset liquidation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com