Low-leverage strategies minimize risk by limiting the amount of borrowed capital used in investments, helping investors maintain more control over their portfolios. These approaches prioritize steady, sustainable growth over high-risk, high-reward opportunities, making them ideal for conservative investors or those new to the market. Explore the rest of the article to understand how low-leverage techniques can protect and enhance your financial future.
Table of Comparison
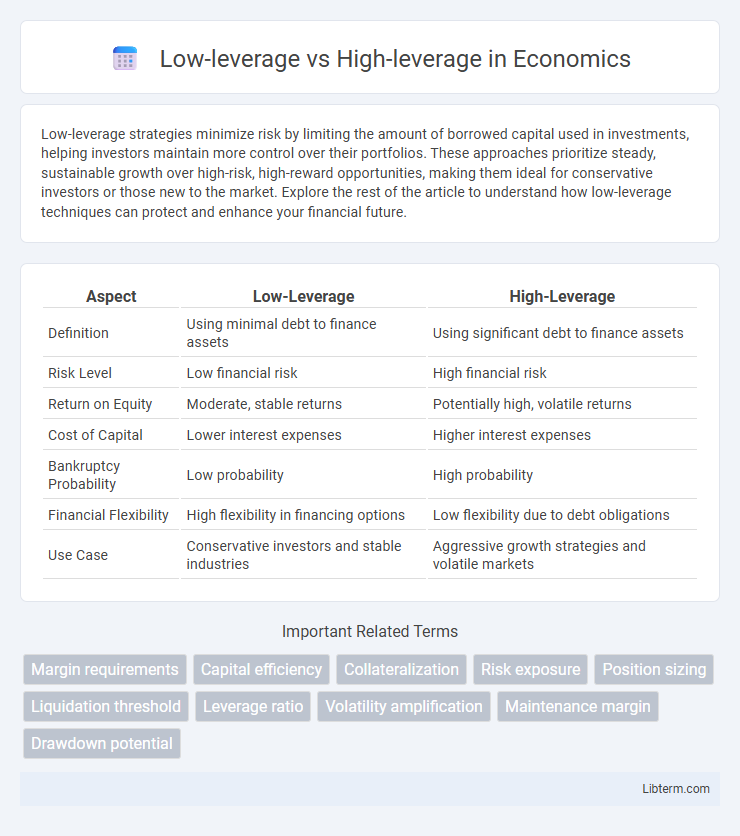
| Aspect | Low-Leverage | High-Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using minimal debt to finance assets | Using significant debt to finance assets |
| Risk Level | Low financial risk | High financial risk |
| Return on Equity | Moderate, stable returns | Potentially high, volatile returns |
| Cost of Capital | Lower interest expenses | Higher interest expenses |
| Bankruptcy Probability | Low probability | High probability |
| Financial Flexibility | High flexibility in financing options | Low flexibility due to debt obligations |
| Use Case | Conservative investors and stable industries | Aggressive growth strategies and volatile markets |
Understanding Leverage: Definition and Importance
Leverage refers to the use of borrowed capital to increase the potential return on investment, with low-leverage involving minimal debt and high-leverage relying heavily on borrowed funds. Understanding leverage is crucial for financial management as it directly impacts risk exposure, profitability, and the ability to scale operations. Properly balancing leverage enhances capital efficiency and helps in optimizing returns while mitigating financial distress risks.
Key Differences Between Low-Leverage and High-Leverage
Low-leverage investments involve using minimal borrowed funds, reducing risk and limiting potential losses, while high-leverage investments amplify both gains and risks by utilizing significant debt. Key differences include risk exposure, with low-leverage promoting financial stability and high-leverage offering higher profit potential but increased volatility. Investors must balance the trade-off between risk tolerance and return expectations when choosing between low and high leverage strategies.
Advantages of Low-Leverage Strategies
Low-leverage strategies minimize financial risk by limiting debt exposure, improving a company's stability during economic downturns. They enhance operational flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to market changes without the strain of high interest obligations. This conservative approach often results in stronger credit ratings and increased investor confidence, promoting long-term sustainability.
Risks and Rewards of High-Leverage Approaches
High-leverage approaches involve using borrowed capital or financial instruments to amplify potential returns, significantly increasing the possible reward but also escalating the risk of substantial losses. These strategies can lead to amplified profits during favorable market conditions but expose investors to heightened risks of margin calls, liquidity crises, and insolvency in adverse scenarios. Effective risk management and strict leverage limits are essential to mitigate the dangers associated with high-leverage financial positions.
Impact of Leverage on Investment Performance
Low-leverage investments limit risk exposure, resulting in more stable but often lower returns, while high-leverage strategies amplify both potential gains and losses, increasing overall investment volatility. The impact of leverage on investment performance depends significantly on market conditions, with high-leverage positions benefiting in bullish trends but suffering substantial drawdowns in downturns. Effective leverage management is crucial for optimizing risk-adjusted returns and preserving capital during market fluctuations.
Leverage in Different Financial Markets
Leverage in financial markets varies significantly between low-leverage and high-leverage strategies, influencing risk and potential returns. Low-leverage investments, common in equity markets, typically involve borrowing small amounts relative to capital, reducing risk exposure but limiting profit potential. High-leverage approaches, often used in forex and derivatives markets, involve significant borrowing, magnifying both gains and losses, and require careful risk management due to increased volatility and margin calls.
Managing Risk With Leverage Selection
Managing risk with leverage selection involves balancing exposure to potential gains and losses; low-leverage positions reduce the risk of significant drawdowns, making them suitable for conservative traders prioritizing capital preservation. High-leverage trading amplifies both profits and losses, requiring stringent risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and margin monitoring to prevent catastrophic losses. Optimal leverage selection depends on individual risk tolerance, market volatility, and trading strategy, with disciplined position sizing essential to maintaining sustainable trading performance.
Real-World Examples: Low vs High-Leverage Outcomes
Low-leverage decisions, such as subtasks in project management, tend to produce incremental improvements with minimal risk, exemplified by routine administrative changes that enhance efficiency without significant impact on overall success. High-leverage decisions, like strategic pivots or major investments in emerging technologies, can dramatically alter outcomes, demonstrated by companies such as Tesla shifting to electric vehicles and dominating the market. Understanding the difference allows organizations to allocate resources effectively, balancing minor optimizations against transformative growth opportunities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Leverage
Factors to consider when choosing leverage include the risk tolerance of the investor, as high-leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses, increasing financial exposure. Market volatility and the specific asset's liquidity play crucial roles in determining appropriate leverage, with low-leverage preferred in unstable markets to prevent margin calls. Additionally, regulatory constraints and the cost of borrowing impact leverage decisions, influencing overall investment strategy and risk management.
Best Practices for Leveraged Investment Success
Best practices for leveraged investment success emphasize thorough risk assessment and disciplined capital allocation to balance potential returns with the increased exposure of high-leverage positions. Low-leverage strategies typically prioritize preservation of capital and steady growth, making them suitable for risk-averse investors, while high-leverage approaches require stringent stop-loss mechanisms and constant market analysis to mitigate significant losses. Leveraged investment success depends on consistent monitoring of market trends, employing diversification, and leveraging analytics tools to optimize entry and exit points.
Low-leverage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com