Phosphating is a critical metal surface treatment process that enhances corrosion resistance and improves paint adhesion by applying a chemical phosphate coating. This coating creates a durable, protective layer that extends the lifespan of metals used in automotive, industrial, and construction applications. Discover how phosphating can optimize your metal finishing processes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
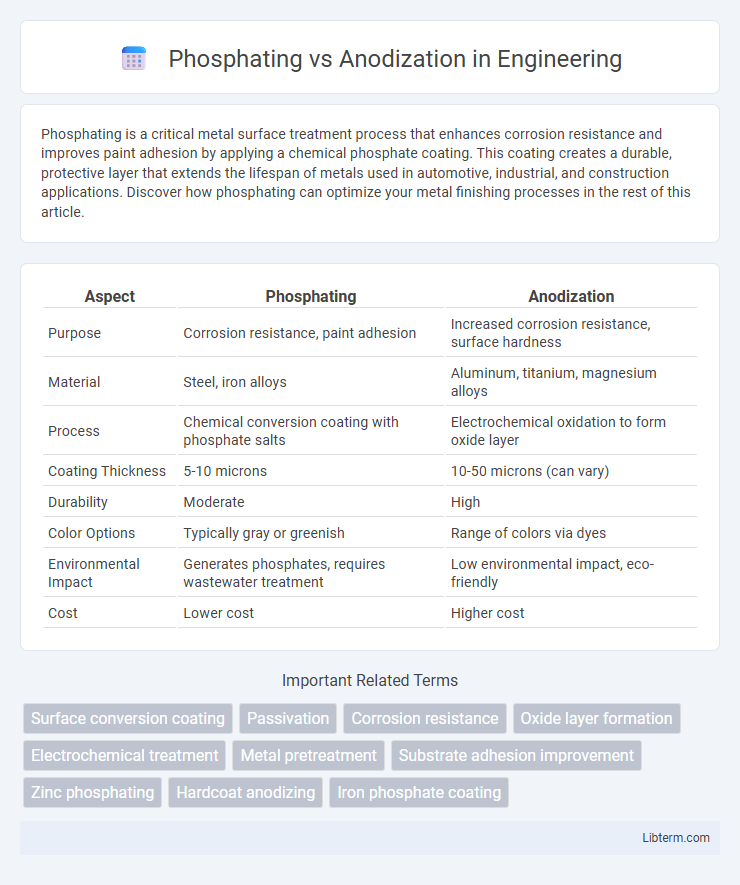
| Aspect | Phosphating | Anodization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Corrosion resistance, paint adhesion | Increased corrosion resistance, surface hardness |
| Material | Steel, iron alloys | Aluminum, titanium, magnesium alloys |
| Process | Chemical conversion coating with phosphate salts | Electrochemical oxidation to form oxide layer |
| Coating Thickness | 5-10 microns | 10-50 microns (can vary) |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Color Options | Typically gray or greenish | Range of colors via dyes |
| Environmental Impact | Generates phosphates, requires wastewater treatment | Low environmental impact, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Surface Treatment Methods
Phosphating and anodization are essential surface treatment methods used to enhance metal durability and corrosion resistance. Phosphating involves creating a crystalline phosphate coating on steel surfaces, improving paint adhesion and reducing wear. Anodization primarily applies to aluminum, forming a thick oxide layer that increases hardness and provides excellent corrosion and abrasion protection.
What is Phosphating?
Phosphating is a chemical conversion coating process used primarily on steel surfaces to improve corrosion resistance and enhance paint adhesion by creating a layer of insoluble phosphate crystals. This treatment involves immersing the metal in an acidic phosphate solution, which reacts with the surface to form a durable, crystalline phosphate coating. Phosphating is commonly applied in automotive, industrial, and appliance manufacturing to prepare metal parts for subsequent coating or painting processes.
What is Anodization?
Anodization is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant, and aesthetically appealing oxide layer, primarily used on aluminum. This oxide layer enhances surface hardness, wear resistance, and provides better adhesion for paint or adhesives. Unlike phosphating, which deposits a thin phosphate coating, anodization creates an integral oxide film that is harder and more resistant to environmental degradation.
Key Differences Between Phosphating and Anodization
Phosphating creates a crystalline phosphate layer on metal surfaces, primarily for corrosion resistance and paint adhesion, while anodization produces a thick oxide layer increasing surface hardness and wear resistance, mainly on aluminum. Phosphating is a chemical conversion process used on steel and iron, whereas anodization is an electrolytic process specific to aluminum and titanium. The phosphate coating is porous and can be painted or sealed, whereas anodized surfaces are denser, non-porous, and integral to the metal substrate.
Applications of Phosphating
Phosphating is widely used in automotive applications for corrosion resistance and as a base layer for paint adhesion on steel parts. This chemical conversion coating enhances durability and wear resistance in machinery components, such as gears and fasteners. Its metal surface preparation benefits industries like aerospace and manufacturing by improving coating performance and extending part lifespan.
Applications of Anodization
Anodization is widely applied in aerospace, automotive, and architectural industries for enhancing corrosion resistance and surface durability of aluminum components. It creates a protective oxide layer that improves wear resistance and provides a base for further coating or painting. Common applications include aircraft parts, automotive trim, electronic device casings, and decorative architectural panels.
Advantages of Phosphating
Phosphating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent paint adhesion, making it ideal for metal surface preparation before painting or coating processes. It provides a cost-effective and environmentally friendly treatment, suitable for large-scale industrial applications with consistent layer formation. The phosphate coating's crystalline structure enhances wear resistance and reduces friction, extending the service life of metal components.
Advantages of Anodization
Anodization offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced surface hardness compared to phosphating, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications requiring long-lasting durability. The process produces a uniform, non-toxic oxide layer that improves adhesion for paints and adhesives without compromising the metal's structural integrity. Anodized finishes also provide excellent aesthetic options and better wear resistance, contributing to reduced maintenance costs and improved product lifespan.
Choosing the Right Process: Phosphating vs Anodization
Phosphating provides a cost-effective corrosion-resistant coating ideal for steel parts requiring paint adhesion, while anodization enhances aluminum surfaces with durable oxide layers that improve wear resistance and visual appeal. Selecting between phosphating and anodization depends on the base metal, desired protective qualities, and environmental conditions, with anodization preferred for light metals and phosphating suitable for ferrous materials. Consider factors like corrosion resistance, surface finish, and subsequent coating compatibility to determine the optimal surface treatment process.
Conclusion: Which Surface Treatment is Best?
Phosphating provides excellent corrosion resistance and paint adhesion, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring durable coatings. Anodization enhances surface hardness and wear resistance, along with superior aesthetic qualities, primarily benefiting aluminum components in aerospace and decorative industries. The best surface treatment depends on specific requirements: phosphating suits heavy-duty protection with paint compatibility, while anodization excels in improving aluminum's durability and appearance.
Phosphating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com