Chain drives efficiently transfer mechanical power between rotating shafts using interconnected links or rollers that engage with sprockets. Highly durable and capable of handling high loads, they are commonly found in bicycles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a chain drive can enhance your equipment's performance and maintenance needs.
Table of Comparison
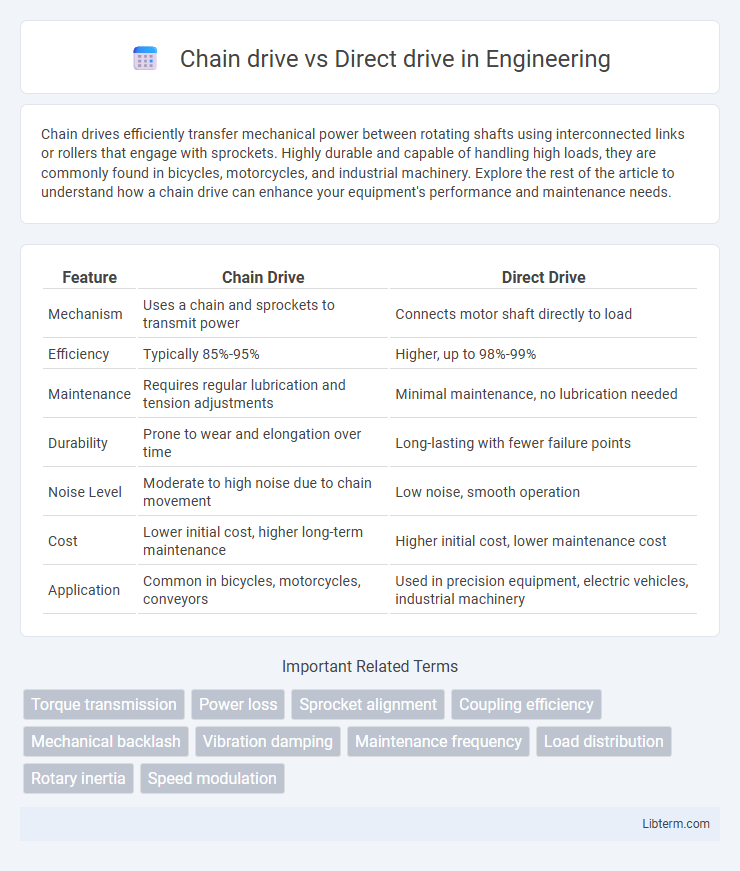
| Feature | Chain Drive | Direct Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses a chain and sprockets to transmit power | Connects motor shaft directly to load |
| Efficiency | Typically 85%-95% | Higher, up to 98%-99% |
| Maintenance | Requires regular lubrication and tension adjustments | Minimal maintenance, no lubrication needed |
| Durability | Prone to wear and elongation over time | Long-lasting with fewer failure points |
| Noise Level | Moderate to high noise due to chain movement | Low noise, smooth operation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher long-term maintenance | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance cost |
| Application | Common in bicycles, motorcycles, conveyors | Used in precision equipment, electric vehicles, industrial machinery |
Introduction to Chain Drive and Direct Drive
Chain drive systems transmit power through a roller chain linking sprockets, offering high torque transfer and durability in industrial machinery and bicycles. Direct drive eliminates intermediate components by connecting the motor shaft directly to the driven load, enhancing efficiency and reducing mechanical losses in applications like electric vehicles and turntables. Both mechanisms play critical roles in optimizing performance based on torque requirements, maintenance needs, and operational environments.
How Chain Drive Works
Chain drives operate by transferring mechanical power through a roller chain that meshes with sprockets, converting rotary motion from the drive shaft to the driven shaft. The chain engages teeth on the sprockets, ensuring synchronized movement and efficient torque transmission, commonly used in bicycles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery. Proper tension and lubrication are essential for minimizing wear and maximizing performance in chain drive systems.
How Direct Drive Works
Direct drive systems transmit torque directly from the motor to the load without intermediate components like chains or belts, utilizing powerful, high-torque electric motors. This design minimizes mechanical losses and reduces maintenance by eliminating wear-prone parts such as chains, sprockets, and tensioners. The efficiency of direct drive is evident in applications like electric bicycles and turntables, where smooth, precise, and quiet operation is essential.
Performance Comparison: Chain vs Direct Drive
Chain drive systems offer superior torque transmission and responsiveness, making them ideal for high-performance applications with rapid acceleration needs. Direct drive systems excel in efficiency and low maintenance by eliminating chain slack and mechanical losses, resulting in smoother power delivery and quieter operation. For maximum performance, chain drives provide better power transfer under heavy loads, while direct drives deliver consistent efficiency with minimal wear over time.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Chain drive systems typically offer high power transmission efficiency, often around 95-98%, due to their mechanical advantage and minimal slippage, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable torque transfer. Direct drive, by eliminating intermediaries like chains or belts, provides superior energy efficiency with virtually no power loss, enhancing performance in precision machinery and electric motors. While chain drives can face efficiency reduction from wear and maintenance issues, direct drives maintain consistent power transmission efficiency with lower maintenance demands.
Maintenance Requirements
Chain drive systems require regular lubrication, tension adjustments, and cleaning to prevent wear and ensure optimal performance, making their maintenance more frequent and labor-intensive. Direct drive systems eliminate the need for chain or belt maintenance, offering lower upkeep due to fewer moving parts and reduced mechanical wear. Maintenance requirements for direct drive are primarily limited to periodic inspection and minimal servicing of the motor and bearings.
Durability and Longevity
Chain drive systems typically offer high durability due to their robust metal construction and ability to withstand heavy loads and harsh environments. Direct drive mechanisms, with fewer moving parts, often provide greater longevity by reducing wear and maintenance requirements over time. Choosing between the two depends on application needs, but chain drives excel in durability while direct drives favor extended lifespan with consistent performance.
Noise and Vibration Analysis
Chain drive systems typically generate higher noise and vibration levels due to metal-on-metal contact and chain tension variations, which can lead to resonance and mechanical fatigue. Direct drive systems offer significantly reduced noise and vibration because they eliminate intermediate components, providing smoother power transmission with fewer moving parts. This results in lower maintenance requirements and enhanced operational stability, making direct drive preferable for noise-sensitive applications.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Chain drive systems generally offer lower upfront costs compared to direct drive options due to simpler components and widely available parts. Installation of chain drives can be more time-consuming and require periodic tension adjustments and lubrication, increasing maintenance efforts. Direct drives, while more expensive initially, feature simpler installation processes and reduced maintenance needs, resulting in lower long-term operational costs.
Best Applications for Each Drive Type
Chain drives excel in applications requiring efficient power transmission over long distances, such as bicycles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery, due to their durability and ability to handle high torque. Direct drives are best suited for precision equipment like electric motors, turntables, and hard drives, where minimal maintenance, high efficiency, and quiet operation are critical. Choosing between chain drive and direct drive depends on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and required maintenance levels.
Chain drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com