Ratio control maintains a precise proportional relationship between two process variables, ensuring consistent product quality and process efficiency. By adjusting the output based on the ratio of input measurements, it stabilizes operations even when feed conditions fluctuate. Discover how implementing effective ratio control can optimize Your industrial processes in the following article.
Table of Comparison
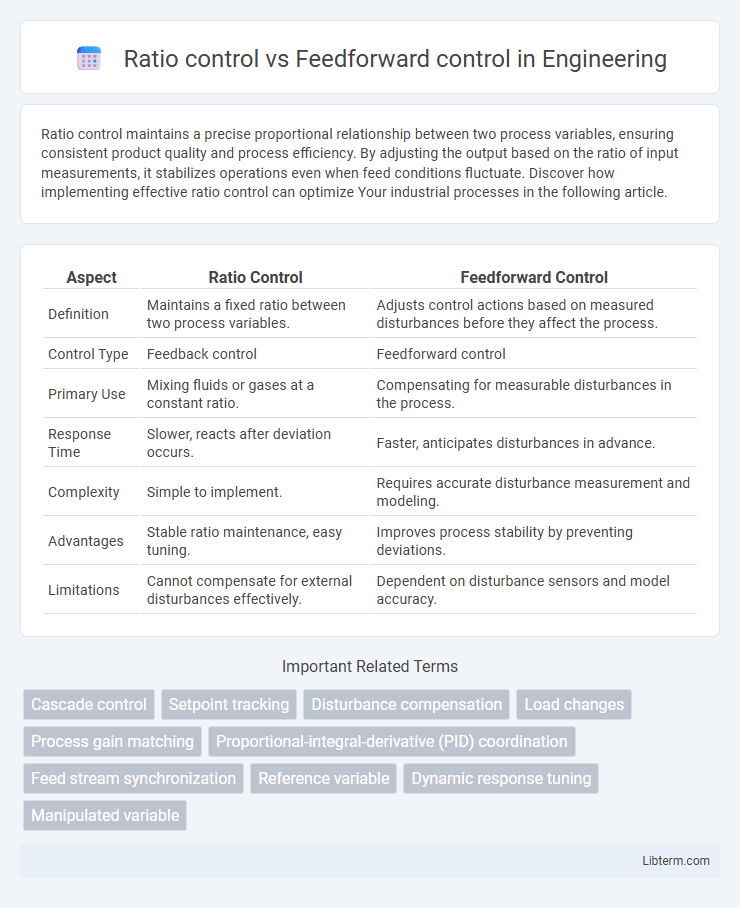
| Aspect | Ratio Control | Feedforward Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintains a fixed ratio between two process variables. | Adjusts control actions based on measured disturbances before they affect the process. |
| Control Type | Feedback control | Feedforward control |
| Primary Use | Mixing fluids or gases at a constant ratio. | Compensating for measurable disturbances in the process. |
| Response Time | Slower, reacts after deviation occurs. | Faster, anticipates disturbances in advance. |
| Complexity | Simple to implement. | Requires accurate disturbance measurement and modeling. |
| Advantages | Stable ratio maintenance, easy tuning. | Improves process stability by preventing deviations. |
| Limitations | Cannot compensate for external disturbances effectively. | Dependent on disturbance sensors and model accuracy. |
Introduction to Ratio Control and Feedforward Control
Ratio control maintains a constant proportion between two process variables, ensuring product consistency by adjusting one variable based on changes in another, commonly used in chemical and blending industries. Feedforward control anticipates disturbances by measuring input variables and adjusting the process proactively to maintain desired output, improving system stability and response time. Both control strategies enhance process efficiency, with ratio control focusing on proportional accuracy and feedforward control emphasizing disturbance rejection.
Definition and Core Principles of Ratio Control
Ratio control maintains a fixed proportion between two process variables by adjusting the manipulated variable based on the measured value of a reference variable, ensuring consistent product quality and process stability. It operates on the principle of direct proportionality, where the controlled variable is regulated as a multiple or fraction of the measured variable, often applied in blending or mixing operations. Feedforward control predicts disturbances by measuring them before they affect the process, unlike ratio control, which relies on real-time feedback of the reference variable.
Definition and Core Principles of Feedforward Control
Ratio control maintains a fixed proportion between two process variables to ensure consistent product quality, commonly used in blending and chemical reactions. Feedforward control anticipates disturbances by measuring them directly and adjusting the process input before the output is affected, enhancing system stability and response time. Core principles of feedforward control include accurate disturbance measurement, an effective process model to predict output changes, and timely corrective actions to minimize deviation from desired setpoints.
Key Differences Between Ratio Control and Feedforward Control
Ratio control maintains a consistent proportion between two process variables, ensuring stable product quality by adjusting one variable relative to another, typically in mixing or blending applications. Feedforward control anticipates disturbances by measuring them directly and proactively adjusts the process input to prevent output deviation, enhancing responsiveness and reducing lag. Key differences include ratio control's reliance on maintaining fixed relationships versus feedforward control's predictive adjustments based on disturbance measurement.
Applications and Use Cases of Ratio Control
Ratio control is extensively applied in chemical processing industries to maintain precise proportions between reactants, ensuring consistent product quality and reaction stability. It is crucial in blending operations, fuel-air mixing in combustion systems, and maintaining solvent-to-solute ratios in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Feedforward control is often combined with ratio control to anticipate disturbances, but ratio control's primary use lies in systems where maintaining fixed proportional relationships between multiple variables is essential.
Applications and Use Cases of Feedforward Control
Feedforward control is widely applied in chemical processing industries where precise adjustment of input variables, such as flow rates or temperatures, ensures consistent product quality despite disturbances. It is also crucial in HVAC systems to preemptively adjust air handling units based on external weather changes, improving energy efficiency and maintaining comfort levels. Unlike ratio control, feedforward control effectively handles measurable disturbances before they impact the system, making it ideal for processes requiring proactive correction and minimal lag.
Advantages and Limitations of Ratio Control
Ratio control offers precise management of process variables by maintaining a constant proportion between two streams, enhancing product quality and minimizing resource waste. It is particularly effective when the relationship between inputs is stable, but its performance deteriorates in the presence of significant disturbances or model inaccuracies. Limitations include difficulty handling nonlinear processes and the need for accurate measurement of input flows to ensure reliable control.
Advantages and Limitations of Feedforward Control
Feedforward control offers the advantage of anticipating disturbances by measuring them directly and adjusting the process proactively, leading to improved stability and reduced response time compared to ratio control. It enables precise handling of multivariable systems where input changes significantly impact output, providing better overall system performance. However, feedforward control requires an accurate process model and reliable disturbance measurement, making it less effective when these conditions are not met, and it cannot correct unmeasured disturbances or model inaccuracies without feedback mechanisms.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Ratio Control vs Feedforward Control
Ratio control is ideal when maintaining a fixed proportional relationship between two process variables, such as mixing chemicals or fuel-to-air ratios in combustion, ensuring consistent product quality despite flow variations. Feedforward control is preferred in processes where measurable disturbances can be anticipated and compensated before affecting the output, such as adjusting heating input based on incoming material temperature changes. Selection criteria depend on process dynamics, availability of disturbance measurements, and the need for proactive adjustments versus maintaining fixed ratios.
Future Trends in Industrial Control Strategies
Future trends in industrial control strategies emphasize integrating ratio control with advanced feedforward control to enhance process stability and responsiveness. The adoption of AI-driven predictive algorithms enables real-time adjustments by combining ratio control's set proportional outputs with feedforward control's anticipatory corrections. Emerging technologies like IIoT sensors and digital twins facilitate more accurate feedforward models, reducing lag and improving efficiency in complex industrial processes.
Ratio control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com