Perspective projection simulates how objects appear smaller as they get further from the viewer, creating a realistic depth effect on a flat surface. This technique is essential in fields like computer graphics, photography, and art to represent three-dimensional scenes accurately. Explore the rest of the article to understand how perspective projection transforms your visual experiences.
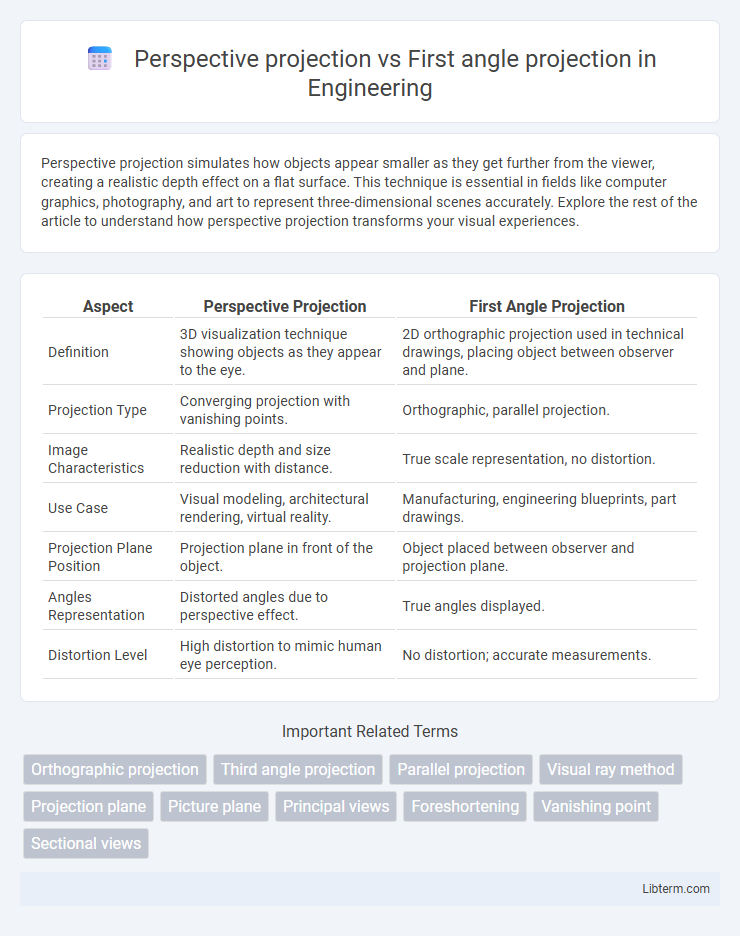
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Perspective Projection | First Angle Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 3D visualization technique showing objects as they appear to the eye. | 2D orthographic projection used in technical drawings, placing object between observer and plane. |
| Projection Type | Converging projection with vanishing points. | Orthographic, parallel projection. |
| Image Characteristics | Realistic depth and size reduction with distance. | True scale representation, no distortion. |
| Use Case | Visual modeling, architectural rendering, virtual reality. | Manufacturing, engineering blueprints, part drawings. |
| Projection Plane Position | Projection plane in front of the object. | Object placed between observer and projection plane. |
| Angles Representation | Distorted angles due to perspective effect. | True angles displayed. |
| Distortion Level | High distortion to mimic human eye perception. | No distortion; accurate measurements. |
Introduction to Projection Methods
Perspective projection creates a realistic representation by converging parallel lines at a vanishing point, simulating human eye perception in 3D visualization. First angle projection, a standardized orthographic method used mainly in Europe and Asia, displays object views by projecting features onto planes placed between the observer and the object. These projection methods serve as fundamental techniques in technical drawing and computer graphics, each optimizing visualization for different design and engineering applications.
What is Perspective Projection?
Perspective projection is a drawing technique that represents three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane, where objects appear smaller as they get further from the viewer, mimicking human vision. It uses a single viewpoint to create depth and spatial relationships, providing a realistic depiction of size and distance. This method contrasts with first angle projection, which is an orthographic technique that lacks depth perception and displays multiple views without perspective distortion.
What is First Angle Projection?
First angle projection is a method of orthographic projection used primarily in Europe and Asia where the object is placed between the observer and the projection plane, creating views that are arranged opposite to those in third angle projection. This technique represents the front view, top view, and side views on specific quadrants: the top view is placed below the front view, and the right side view is placed on the left side of the front view. First angle projection is standardized under ISO conventions, making it essential for interpreting technical drawings in mechanical engineering and manufacturing industries.
Key Differences Between Perspective and First Angle Projection
Perspective projection creates a realistic 3D image where objects appear smaller as they recede into the distance, mimicking human eye perception, while first angle projection is a standardized 2D technical drawing method used primarily in Europe, presenting orthographic views in a specific arrangement. In perspective projection, the projection rays converge on a single point, offering depth and spatial understanding, whereas first angle projection uses parallel projection rays, producing scale-accurate but non-perspective views. The key difference lies in perspective projection's emphasis on visual realism versus first angle projection's focus on precise, measurable engineering communication.
Applications of Perspective Projection
Perspective projection is widely used in architectural visualization and computer graphics to create realistic, three-dimensional representations of objects and environments. It accurately simulates human eye perception by depicting depth and spatial relationships, essential for virtual reality, video games, and design simulations. Unlike first angle projection, which is primarily used in technical drawings and engineering for precise measurements, perspective projection enhances visual realism and intuitive spatial understanding.
Applications of First Angle Projection
First Angle Projection is predominantly utilized in Europe and Asia for technical drawings and engineering design documentation. This projection method effectively represents three-dimensional objects on two-dimensional planes, aiding manufacturing processes and mechanical design communication. Its application is critical in industries requiring standardized, clear visualization of components, such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery engineering.
Advantages of Perspective Projection
Perspective projection offers realistic depth perception by simulating how the human eye views objects, making it ideal for visualizations and presentations where spatial relationships are important. It accurately represents size and distance variations, which enhances comprehension in architectural designs, virtual reality, and gaming applications. This projection method facilitates intuitive interpretation of complex 3D structures, improving communication between designers and clients.
Advantages of First Angle Projection
First Angle Projection offers a clear and standardized method widely used in Europe and Asia, facilitating straightforward interpretation of technical drawings by placing the object between the observer and the plane of projection. This technique allows for easier visualization of the true size and shape of object features, improving accuracy in dimensioning and reducing errors in manufacturing. Its advantages in communication among engineers and manufacturers result in enhanced collaboration and consistency within global engineering projects.
Limitations of Each Projection Technique
Perspective projection often suffers from distortion as objects farther from the viewer appear smaller, making it unsuitable for precise technical drawings. First angle projection can cause confusion due to its flipped view orientation, leading to misinterpretation in complex assemblies or engineering blueprints. Both techniques face limitations in accurately conveying spatial relationships, where perspective excels in realism but lacks measurement accuracy, while first angle projection ensures dimensional consistency but sacrifices intuitive visualization.
Choosing the Right Projection Method for Your Needs
First angle projection places the object between the viewer and the projection plane, widely used in European engineering drawings for its intuitive layout. Perspective projection mimics human eye perception by converging parallel lines, ideal for realistic visualizations and architectural renderings. Selecting the right projection depends on the project's requirements: use first angle projection for standardized technical documentation and perspective projection for presentations requiring depth and spatial accuracy.
Perspective projection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com