Overhead cranes are essential equipment used in manufacturing and construction for lifting and moving heavy loads efficiently across a workspace. These cranes maximize productivity by enabling precise load placement and enhancing workplace safety. Discover how overhead cranes can transform your operations by exploring the key types, applications, and maintenance tips detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
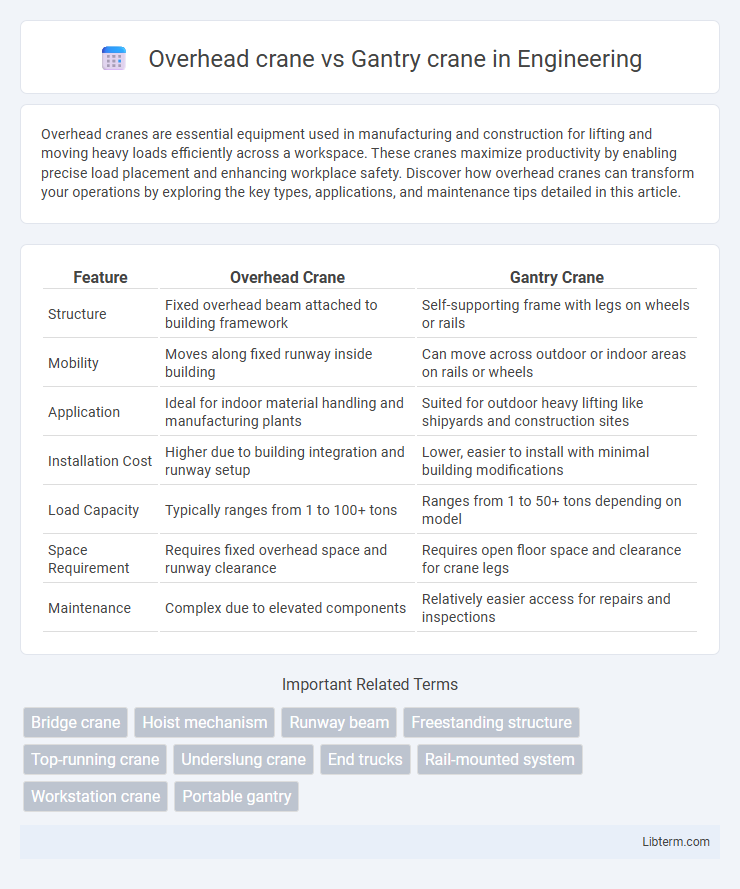
| Feature | Overhead Crane | Gantry Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed overhead beam attached to building framework | Self-supporting frame with legs on wheels or rails |
| Mobility | Moves along fixed runway inside building | Can move across outdoor or indoor areas on rails or wheels |
| Application | Ideal for indoor material handling and manufacturing plants | Suited for outdoor heavy lifting like shipyards and construction sites |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to building integration and runway setup | Lower, easier to install with minimal building modifications |
| Load Capacity | Typically ranges from 1 to 100+ tons | Ranges from 1 to 50+ tons depending on model |
| Space Requirement | Requires fixed overhead space and runway clearance | Requires open floor space and clearance for crane legs |
| Maintenance | Complex due to elevated components | Relatively easier access for repairs and inspections |
Introduction to Overhead Cranes and Gantry Cranes
Overhead cranes operate on elevated rails fixed to the building structure, enabling heavy lifting and precise horizontal movement primarily within factories or warehouses. Gantry cranes feature a bridge supported by freestanding legs that move on ground rails, allowing flexible outdoor or indoor heavy load handling where overhead structures are absent. Both crane types optimize material handling efficiency but differ in structural requirements and application environments.
Key Differences Between Overhead and Gantry Cranes
Overhead cranes operate on elevated runways fixed within buildings, allowing smooth lifting and horizontal movement of heavy loads across a defined indoor workspace, while gantry cranes feature a mobile framework with legs supporting a bridge, enabling mobility across outdoor or varied terrain without fixed runways. Overhead cranes are ideal for repetitive, heavy-duty industrial applications with limited space, whereas gantry cranes provide versatility for construction sites, shipyards, and large outdoor projects. Key differences include their structural design, mobility options, and application environments, which influence load capacity, installation cost, and operational flexibility.
Structural Design Comparison
Overhead cranes feature a fixed bridge supported by end trucks that run on elevated runway beams, enabling efficient lifting within industrial buildings, while gantry cranes utilize a freestanding structure with legs that move on ground rails, offering greater mobility and flexibility for outdoor or large-area operations. The structural design of overhead cranes emphasizes load distribution through rigid runway systems, ensuring stability and precision in heavy lifting tasks, whereas gantry cranes rely on a robust welded frame with adjustable spans to accommodate varying load sizes and workspace configurations. Material selection, such as high-strength steel for beams and girders, is crucial in both designs to withstand dynamic loads and ensure safety under repetitive operational stresses.
Installation Requirements and Mobility
Overhead cranes require a robust building structure with substantial support beams for installation, limiting their mobility to fixed locations inside factories or warehouses. Gantry cranes feature a freestanding frame with wheels that allow them to move along rails or flat surfaces, providing greater flexibility in outdoor or temporary job sites. The installation of gantry cranes demands minimal structural support, making them easier to set up and relocate compared to overhead cranes.
Load Capacity and Application Suitability
Overhead cranes typically offer higher load capacities ranging from several tons up to 500 tons, making them ideal for heavy industrial applications like steel mills and shipyards. Gantry cranes provide versatile load capacity options, generally from 1 ton to 100 tons, and are favored in outdoor or temporary setups such as construction sites and container yards. The selection between overhead and gantry cranes depends on specific operational needs, with overhead cranes excelling in fixed, high-load environments and gantry cranes suited for flexible, medium-load tasks.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Overhead cranes generally incur higher installation costs due to their fixed structural requirements and integration into existing building frameworks, whereas gantry cranes offer more cost-effective flexibility with portable or semi-portable designs and minimal structural modifications. Maintenance expenses for overhead cranes can be elevated because of their complex electrical systems and elevated access needs, while gantry cranes benefit from easier ground-level maintenance and simpler mechanical components, reducing long-term upkeep costs. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment against ongoing maintenance budgets and operational demands within specific industrial environments.
Advantages of Overhead Cranes
Overhead cranes offer superior space efficiency by operating on fixed runways along building ceilings, maximizing floor area usage while providing precise load handling capabilities. Their enhanced lifting capacity and ability to cover long distances within industrial facilities make them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring consistent, repetitive movement. Maintenance is often simplified due to the fixed installation, resulting in increased operational uptime compared to mobile gantry cranes.
Benefits of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes offer greater versatility by operating both indoors and outdoors without the need for permanent overhead support structures, making them ideal for diverse industrial environments. Their mobility enables efficient transportation of heavy loads across large workspaces, enhancing workflow flexibility and reducing operational downtime. The lower installation and maintenance costs compared to overhead cranes increase cost-effectiveness, especially in applications involving frequent repositioning or varying load handling locations.
Choosing the Right Crane for Your Facility
Selecting the right crane for your facility depends on factors such as workspace layout, load capacity, and mobility requirements. Overhead cranes are ideal for facilities with permanent structures and needing high lifting capacities in fixed paths, offering efficient vertical and horizontal movement along elevated runways. Gantry cranes provide flexible operation without the need for overhead supports, making them suitable for outdoor or temporary setups where portability and adaptability are critical.
Conclusion: Overhead Crane vs Gantry Crane
Overhead cranes offer superior indoor space efficiency and are ideal for heavy lifting in manufacturing or warehouse environments. Gantry cranes provide versatility and portability, enabling outdoor use and handling large loads without permanent structural support. Choosing between overhead and gantry cranes depends on site-specific requirements, load capacity, and operational flexibility.
Overhead crane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com