Concrete liners provide a durable and protective layer inside structures such as tanks, pipes, and channels to prevent wear, corrosion, and leakage. These liners enhance the longevity and structural integrity of concrete installations by creating a robust barrier against chemical, physical, and environmental damage. Discover how choosing the right concrete liner can safeguard your investment by exploring the detailed benefits and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
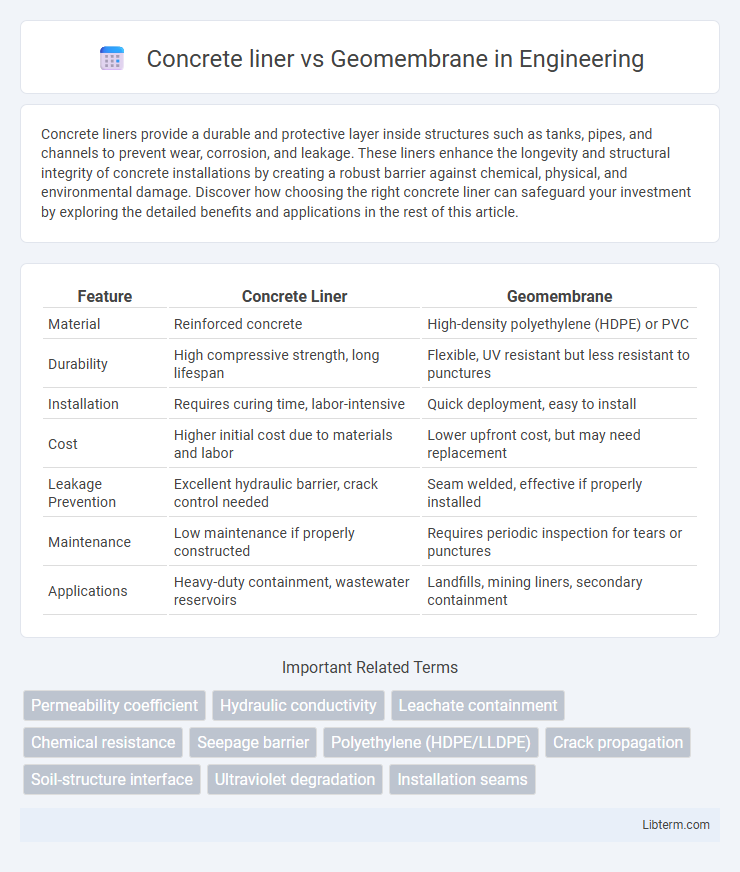
| Feature | Concrete Liner | Geomembrane |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Reinforced concrete | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or PVC |
| Durability | High compressive strength, long lifespan | Flexible, UV resistant but less resistant to punctures |
| Installation | Requires curing time, labor-intensive | Quick deployment, easy to install |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to materials and labor | Lower upfront cost, but may need replacement |
| Leakage Prevention | Excellent hydraulic barrier, crack control needed | Seam welded, effective if properly installed |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance if properly constructed | Requires periodic inspection for tears or punctures |
| Applications | Heavy-duty containment, wastewater reservoirs | Landfills, mining liners, secondary containment |
Introduction to Concrete Liners and Geomembranes
Concrete liners provide a durable, rigid barrier primarily used in water retention and containment systems due to their high compressive strength and resistance to environmental factors. Geomembranes are flexible, synthetic liners made from materials like HDPE or PVC, offering superior impermeability and chemical resistance for applications such as landfill liners and hazardous waste containment. Both solutions are essential in civil and environmental engineering, with concrete liners favored for structural stability and geomembranes chosen for flexibility and ease of installation.
Material Composition and Properties
Concrete liners consist primarily of cement, sand, and aggregates, forming a rigid and durable barrier with high compressive strength and resistance to mechanical damage. Geomembranes are synthetic membranes made from polymer materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering flexibility, chemical resistance, and impermeability to liquids and gases. The rigid nature of concrete liners provides structural support, while geomembranes deliver superior adaptability for sealing applications in diverse environmental conditions.
Installation Processes and Requirements
Concrete liners require skilled labor for mixing, pouring, and curing, demanding precise site preparation to ensure proper slope and reinforcement placement. Geomembranes utilize prefabricated sheets that are unrolled and welded on-site, requiring specialized heat-welding equipment and clean, smooth subgrades to prevent punctures. Both materials mandate quality control inspections, but geomembrane installation typically offers faster deployment with less curing time compared to the weeks-long concrete curing process.
Cost Comparison: Concrete Liner vs Geomembrane
Concrete liners typically involve higher initial installation costs due to material and labor expenses, but they offer long-term durability and low maintenance requirements. Geomembranes generally have lower upfront costs and faster installation times, making them more cost-effective for short-term applications or projects with budget constraints. Over the lifespan, concrete liners may prove more economical for large-scale, permanent containment, while geomembranes suit flexible, cost-sensitive solutions.
Durability and Service Life
Concrete liners offer exceptional durability due to their high resistance to abrasion, chemical attack, and temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for long-term applications in harsh environments. Geomembranes provide flexibility and chemical resistance but may be prone to punctures, UV degradation, and mechanical damage, which can reduce their overall service life compared to concrete. The service life of concrete liners often exceeds 50 years under proper maintenance, whereas geomembranes typically last 20 to 30 years before requiring replacement or repair.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Concrete liners provide long-term durability and structural stability but have a higher carbon footprint due to cement production's CO2 emissions and resource-intensive manufacturing. Geomembranes offer flexibility and lower initial environmental impact with minimal resource extraction, though their synthetic materials pose challenges in biodegradability and potential microplastic pollution. Sustainable landfill design increasingly favors geomembranes combined with natural liners to balance containment efficiency and reduced environmental degradation.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Concrete liners exhibit high durability with minimal maintenance requirements, though repairs can be labor-intensive and costly due to the need for specialized equipment and curing time. Geomembranes allow easier and quicker repairs; punctures or tears can be patched with compatible materials, reducing downtime significantly. Regular inspections are crucial for both, but geomembranes demand more frequent checks to detect and address damage promptly, ensuring long-term integrity.
Performance in Various Applications
Concrete liners provide robust structural integrity and exceptional abrasion resistance, making them ideal for applications involving heavy mechanical loads and high thermal variation. Geomembranes offer superior chemical resistance and impermeability, excelling in containment systems such as landfills, water reservoirs, and environmental protection barriers. The choice between concrete liners and geomembranes depends on specific performance requirements, including durability, flexibility, and exposure to corrosive substances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Lining System
Concrete liners offer high durability, excellent resistance to physical damage, and strong structural support, making them ideal for applications requiring permanent, load-bearing containment; however, they are prone to cracking, can be costly to install, and require skilled labor for proper curing and finishing. Geomembranes provide superior chemical resistance, are flexible for uneven surfaces, and allow faster, more cost-effective installation, but they are susceptible to punctures, have lower tensile strength compared to concrete, and may require frequent inspections and repairs to maintain integrity. Selecting between concrete liners and geomembranes depends on factors such as environmental conditions, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance capabilities.
Selecting the Right Liner for Your Project
Selecting the right liner for your project depends on factors including chemical resistance, durability, and installation requirements. Concrete liners offer structural strength and withstand heavy loads, making them ideal for industrial containment and wastewater treatment applications. Geomembranes provide superior flexibility, waterproofing, and ease of installation, which suit environmental protection projects and temporary containment needs.
Concrete liner Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com