Water jet peening uses high-pressure water streams to improve metal surface strength by inducing compressive stress and reducing fatigue cracks. This environmentally friendly process enhances the durability and lifespan of components without altering their dimensions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how water jet peening can optimize your metal treatment solutions.
Table of Comparison
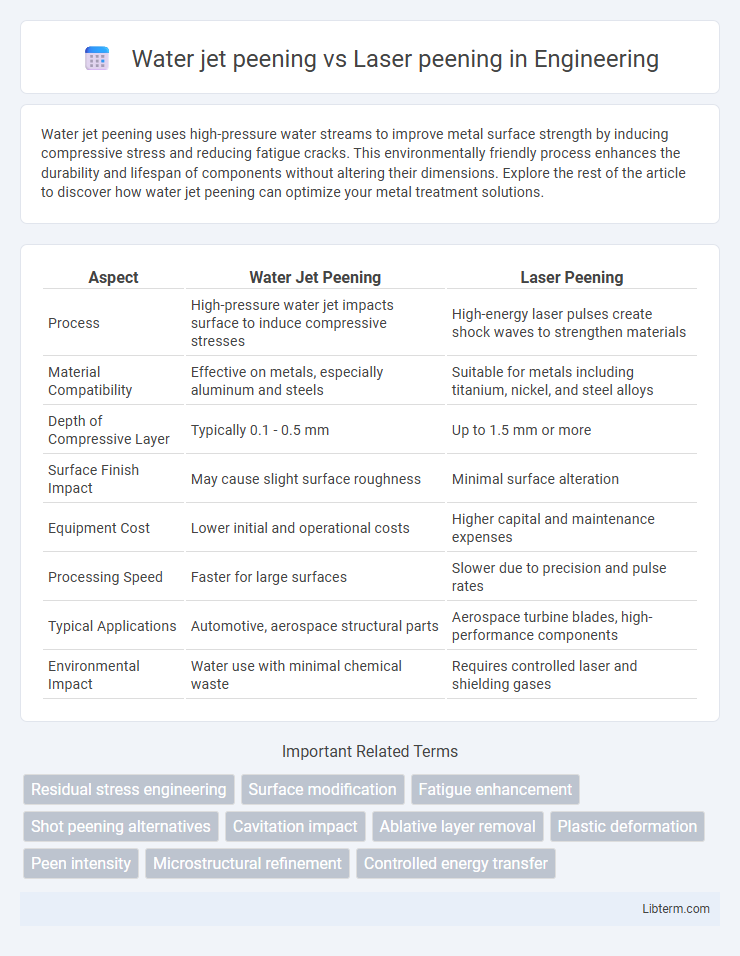
| Aspect | Water Jet Peening | Laser Peening |
|---|---|---|
| Process | High-pressure water jet impacts surface to induce compressive stresses | High-energy laser pulses create shock waves to strengthen materials |
| Material Compatibility | Effective on metals, especially aluminum and steels | Suitable for metals including titanium, nickel, and steel alloys |
| Depth of Compressive Layer | Typically 0.1 - 0.5 mm | Up to 1.5 mm or more |
| Surface Finish Impact | May cause slight surface roughness | Minimal surface alteration |
| Equipment Cost | Lower initial and operational costs | Higher capital and maintenance expenses |
| Processing Speed | Faster for large surfaces | Slower due to precision and pulse rates |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, aerospace structural parts | Aerospace turbine blades, high-performance components |
| Environmental Impact | Water use with minimal chemical waste | Requires controlled laser and shielding gases |
Introduction to Surface Enhancement Technologies
Water jet peening and laser peening are advanced surface enhancement technologies used to improve the fatigue life and stress corrosion resistance of metals. Water jet peening employs high-pressure water jets to induce compressive residual stresses on the material surface, while laser peening uses high-energy laser pulses to generate shock waves that create deeper and more uniform compressive stresses. Both methods enhance mechanical properties by modifying surface microstructure, but laser peening typically achieves greater depth and precision, making it suitable for critical aerospace and automotive components.
Overview of Water Jet Peening
Water jet peening employs high-pressure water streams to induce compressive residual stresses on metal surfaces, enhancing fatigue resistance and reducing stress corrosion cracking. This environmentally friendly method avoids thermal effects and surface melting, making it suitable for temperature-sensitive materials. Water jet peening offers cost-effective and flexible treatment for complex geometries compared to laser peening, which uses pulsed lasers for deeper stress penetration but involves higher operational costs.
Overview of Laser Peening
Laser peening uses high-energy laser pulses to generate shock waves that strengthen metal surfaces by inducing deep compressive residual stresses, enhancing fatigue resistance and corrosion performance. This process offers precise control over stress depth and distribution, making it ideal for critical aerospace and automotive components. Compared to water jet peening, laser peening achieves deeper stress penetration and superior surface hardness without causing surface contamination.
Mechanisms of Action: Water Jet vs Laser
Water jet peening utilizes high-velocity water jets to induce compressive residual stresses on metal surfaces through mechanical impact, enhancing fatigue resistance by plastic deformation at the microstructural level. Laser peening employs high-energy laser pulses to generate plasma and shock waves, creating deeper and more controlled compressive stresses that improve material strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. The distinct mechanisms--hydrodynamic shock from water jets versus photomechanical shock from laser pulses--result in varying depths and intensities of surface modification, influencing performance in demanding industrial applications.
Comparative Benefits and Drawbacks
Water jet peening offers superior surface coverage and is effective for treating complex geometries, with lower equipment costs and reduced thermal impact compared to laser peening. Laser peening provides deeper compressive residual stresses and enhanced fatigue resistance due to its precise, high-energy laser pulses but involves higher operational expenses and requires stringent safety measures. Both techniques improve material strength and fatigue life, yet selection depends on the specific application requirements, budget constraints, and desired depth of surface treatment.
Material Compatibility and Applications
Water jet peening is highly compatible with ductile materials such as aluminum alloys, titanium, and stainless steel, often used in aerospace and automotive industries to enhance fatigue resistance. Laser peening suits a broader range of materials, including hard-to-treat superalloys and composites, enabling deep compressive stress layers ideal for turbine blades and power generation components. Applications of water jet peening typically target surface treatments requiring minimal thermal impact, while laser peening excels in high-precision scenarios demanding deep residual stress profiles and improved wear resistance.
Process Efficiency and Operational Costs
Water jet peening utilizes high-pressure water streams to induce compressive residual stresses, offering faster processing speeds and lower operational costs due to reduced equipment complexity compared to laser peening. Laser peening delivers deeper and more precise stress profiles but requires higher capital investment, expensive maintenance, and longer cycle times related to laser calibration and operation. Choosing between the two depends on balancing efficiency demands with budget constraints, where water jet peening excels in cost-effectiveness and laser peening in performance precision.
Surface Quality and Residual Stress Profiles
Water jet peening produces a uniform compressive residual stress profile with moderate surface roughness, beneficial for fatigue resistance but sometimes limited in depth compared to laser peening. Laser peening generates deeper and higher magnitude compressive residual stresses with minimal surface damage, enhancing crack growth resistance and surface integrity significantly. Surface quality in laser peening remains superior due to lower surface roughness and reduced microstructural alterations compared to water jet peening.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Water jet peening utilizes high-pressure water streams, posing minimal environmental hazards and generating no harmful emissions, making it a safer option for operators due to its non-thermal process. Laser peening involves high-energy laser pulses that require strict safety measures to protect against eye and skin injury, and it produces minimal waste but demands controlled environments to manage potential laser hazards. Both techniques reduce residual stresses effectively, yet water jet peening offers a more environmentally friendly and operator-safe alternative compared to laser peening.
Future Trends in Peening Technologies
Water jet peening and laser peening are evolving with advances in precision and efficiency, driving innovations in surface treatment for aerospace and automotive industries. Future trends emphasize integration of AI-driven process control systems to optimize peening parameters, enhancing fatigue life and corrosion resistance. The development of hybrid peening technologies combining water jet and laser methods aims to achieve superior material properties while reducing environmental impact.
Water jet peening Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com