Rotameters and orifice plates are essential flow measurement devices used in various industrial applications to monitor fluid flow rates accurately. While rotameters offer a simple, visual flow indication with minimal pressure drop, orifice plates provide precise flow measurement by creating a differential pressure across a constriction. Discover how these devices work and when to choose each by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
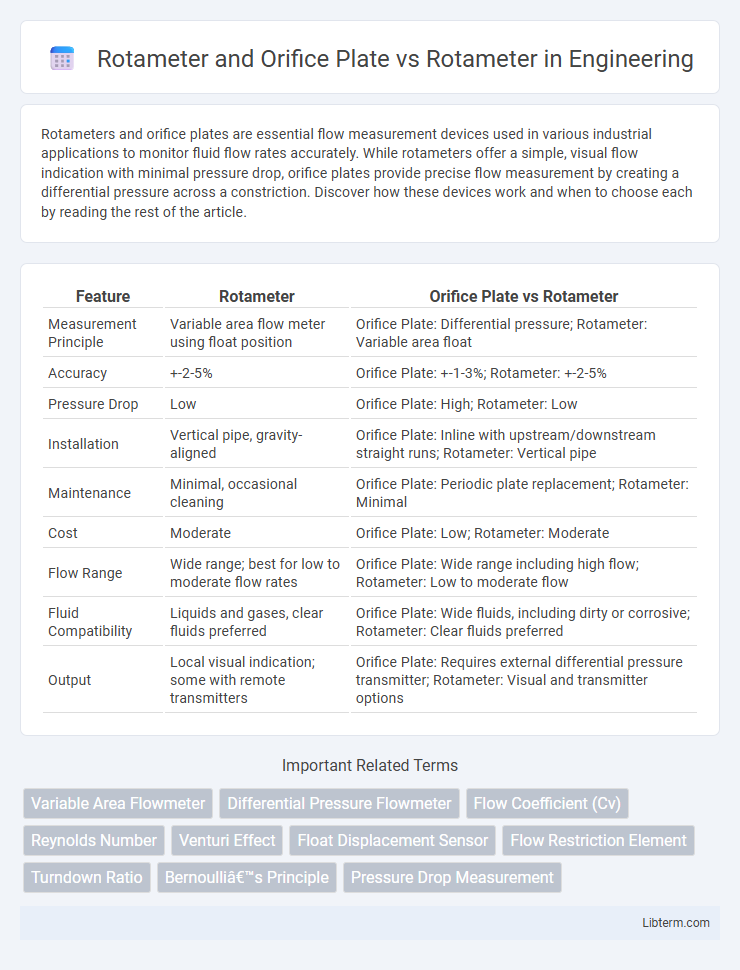
| Feature | Rotameter | Orifice Plate vs Rotameter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Variable area flow meter using float position | Orifice Plate: Differential pressure; Rotameter: Variable area float |
| Accuracy | +-2-5% | Orifice Plate: +-1-3%; Rotameter: +-2-5% |
| Pressure Drop | Low | Orifice Plate: High; Rotameter: Low |
| Installation | Vertical pipe, gravity-aligned | Orifice Plate: Inline with upstream/downstream straight runs; Rotameter: Vertical pipe |
| Maintenance | Minimal, occasional cleaning | Orifice Plate: Periodic plate replacement; Rotameter: Minimal |
| Cost | Moderate | Orifice Plate: Low; Rotameter: Moderate |
| Flow Range | Wide range; best for low to moderate flow rates | Orifice Plate: Wide range including high flow; Rotameter: Low to moderate flow |
| Fluid Compatibility | Liquids and gases, clear fluids preferred | Orifice Plate: Wide fluids, including dirty or corrosive; Rotameter: Clear fluids preferred |
| Output | Local visual indication; some with remote transmitters | Orifice Plate: Requires external differential pressure transmitter; Rotameter: Visual and transmitter options |
Introduction to Flow Measurement Devices
Rotameters are variable area flow meters that measure flow rate by observing the position of a float inside a tapered tube, providing direct visual indication without requiring external power. Orifice plates function as differential pressure devices by creating a pressure drop across a constricted aperture, which is then correlated to flow rate using Bernoulli's principle, often requiring additional instrumentation for measurement. The choice between Rotameter and Orifice Plate depends on factors such as pressure drop tolerance, accuracy requirements, installation complexity, and maintenance needs in various fluid flow measurement applications.
What is a Rotameter?
A Rotameter is a type of flow meter that measures the flow rate of liquids and gases using a float inside a tapered tube, where the float's position indicates the flow rate. Compared to an orifice plate, which measures flow by creating a pressure drop across a restriction, a Rotameter provides direct visual readings without requiring pressure sensors or complex calculations. Its simple design, reliability, and ease of installation make it suitable for various industrial applications requiring real-time flow monitoring.
Principle of Operation: Rotameter
Rotameters operate on the principle of variable area flow measurement, where a float rises and falls within a tapered tube based on the flow rate, balancing gravitational and drag forces. The float position corresponds to a precise flow rate indicated on the calibrated scale. Unlike orifice plates, which rely on differential pressure measurement and require additional equipment, rotameters provide direct visual readouts without pressure loss.
Overview of Orifice Plate Flow Meter
The Orifice Plate Flow Meter utilizes a flat plate with a central hole to create a pressure drop, enabling flow rate measurement based on differential pressure. This method offers high accuracy for measuring fluid flow in pipes, especially in applications with steady, incompressible fluids. Compared to Rotameters, Orifice Plates are better suited for high-pressure and high-temperature environments but require more maintenance due to potential wear and pressure loss.
How Orifice Plate Flow Meters Work
Orifice plate flow meters measure fluid flow by detecting the pressure drop across a precisely engineered plate with a central hole, causing a change in fluid velocity and pressure that correlates to flow rate. The flow causes a differential pressure between the upstream and downstream sides of the orifice plate, which is measured and converted into flow rate using Bernoulli's equation and calibration data. Unlike rotameters that provide a visual indication using a float in a tapered tube, orifice plates are widely used in industrial applications for their accuracy and ability to handle high-pressure, high-temperature fluids.
Rotameter vs Orifice Plate: Key Differences
Rotameters and orifice plates both measure fluid flow but operate on distinct principles; rotameters use a float rising in a tapered tube to indicate flow rate, while orifice plates create a pressure drop across an obstruction to calculate flow. Rotameters offer direct visual readings and are ideal for low to moderate flow rates with minimal pressure loss, whereas orifice plates handle high flow rates and high-pressure applications but require differential pressure measurement instruments. Accuracy of rotameters depends on fluid properties and orientation, while orifice plates provide high accuracy across various fluids but involve more complex installation and maintenance.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Rotameters provide moderate accuracy with typical measurement errors around +-1-5%, while orifice plates offer higher accuracy levels often better than +-1% when properly calibrated and installed. Reliability of rotameters is favored in low-pressure, low-turbulence applications due to their simple mechanical design and minimal maintenance requirements. Orifice plates, although more precise, are susceptible to wear and pressure drops, which can affect long-term reliability and demand periodic inspection.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Rotameters offer straightforward installation with vertical orientation requirements and minimal maintenance due to their simple mechanical design. Orifice plates demand precise pipe modifications and pressure taps for installation, increasing complexity and requiring regular inspection to prevent wear and buildup affecting accuracy. Maintenance for orifice plates involves frequent calibration and cleaning, while rotameters generally need less frequent attention, making them more suitable for low-maintenance environments.
Pros and Cons: Rotameter vs Orifice Plate
Rotameters provide direct, visual flow measurement with low pressure drop and simple installation, making them ideal for low to medium flow rates. Orifice plates offer high accuracy and durability for high-pressure, high-temperature applications but cause significant pressure loss and require precise calibration. Rotameters are less suitable for turbulent or dirty fluids, whereas orifice plates handle a wider range of fluid types but involve more maintenance and higher operational costs.
Choosing the Right Flow Meter for Your Application
Rotameters offer direct visual flow measurement with reliable accuracy in low to medium flow rates, ideal for clean liquids and gases, while orifice plates provide cost-effective solutions for high-pressure, high-temperature applications requiring differential pressure measurement. Selecting the right flow meter depends on factors such as fluid type, flow range, pressure conditions, and installation requirements; rotameters excel in simplicity and maintenance simplicity, whereas orifice plates suit more demanding industrial environments with complex process parameters. Understanding application specifics, including compatibility with fluid properties and the needed precision level, ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Rotameter and Orifice Plate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com