A ribbed belt provides superior grip and flexibility compared to traditional belts, making it ideal for various mechanical applications. Its unique design improves power transmission efficiency and reduces slippage, enhancing the performance of engines and machinery. Discover how a ribbed belt can optimize your equipment's reliability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
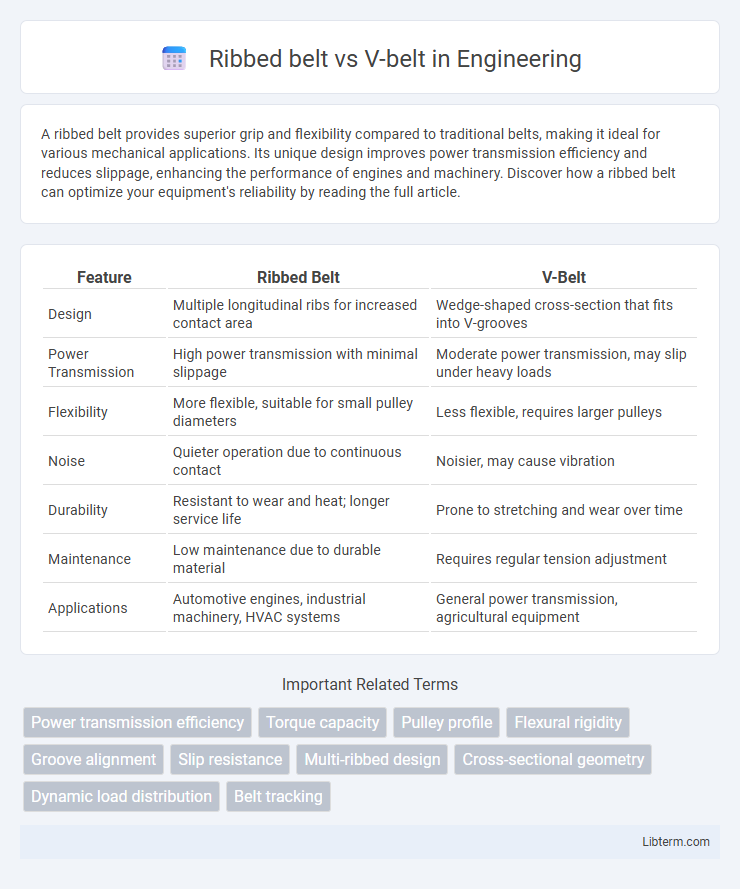
| Feature | Ribbed Belt | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Multiple longitudinal ribs for increased contact area | Wedge-shaped cross-section that fits into V-grooves |
| Power Transmission | High power transmission with minimal slippage | Moderate power transmission, may slip under heavy loads |
| Flexibility | More flexible, suitable for small pulley diameters | Less flexible, requires larger pulleys |
| Noise | Quieter operation due to continuous contact | Noisier, may cause vibration |
| Durability | Resistant to wear and heat; longer service life | Prone to stretching and wear over time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to durable material | Requires regular tension adjustment |
| Applications | Automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems | General power transmission, agricultural equipment |
Introduction to Ribbed Belts and V-Belts
Ribbed belts feature multiple longitudinal ribs that enhance flexibility and increase surface contact, making them ideal for high-speed applications and efficient power transmission. V-belts possess a trapezoidal cross-section designed to fit tightly into pulleys, providing exceptional grip and torque handling in heavy-duty machinery. Both belt types serve crucial roles in mechanical systems, with ribbed belts offering smoother operation and V-belts excelling in load capacity.
Design and Structural Differences
Ribbed belts feature multiple longitudinal ribs running parallel along the belt's length, allowing for superior flexibility and a larger contact area with pulleys, enhancing power transmission efficiency. V-belts have a trapezoidal cross-section designed to wedge into pulley grooves, providing high friction and grip but limited flexural capacity compared to ribbed belts. The structural difference results in ribbed belts being better suited for high-speed, compact pulley systems, while V-belts excel in transmitting higher torque loads in wider pulley configurations.
Material Composition Comparison
Ribbed belts are typically made from a combination of synthetic rubber compounds and embedded polyester or aramid fibers, providing superior flexibility and heat resistance compared to traditional V-belts, which are commonly constructed from neoprene or chloroprene rubber reinforced with polyester or fiberglass cords. The multi-rib design of ribbed belts allows for increased surface contact and reduced slippage, while V-belts feature a trapezoidal cross-section that relies on friction within pulley grooves for power transmission. Material advancements in ribbed belts contribute to enhanced durability and performance in high-speed, high-torque applications, distinguishing them from the more rigid and less flexible V-belt counterparts.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Ribbed belts offer higher efficiency and better power transmission compared to V-belts due to their increased contact surface and flexible design, which reduces slippage and heat buildup. V-belts generally provide reliable power transfer but can experience more friction losses and limited flexibility under high-load conditions. The enhanced grip and reduced energy loss of ribbed belts make them ideal for applications requiring consistent speed and torque.
Applications and Common Uses
Ribbed belts excel in high-speed applications and are commonly used in automotive engines, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery due to their flexibility and ability to drive multiple pulleys simultaneously. V-belts are preferred in heavy-duty industrial settings such as agricultural machinery, compressors, and conveyor systems because of their high power transmission and superior grip on pulleys. Both belt types cater to different torque, speed, and environmental conditions, making them essential in diverse mechanical power transmission applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ribbed belts feature multiple longitudinal ribs that provide enhanced flexibility and uniform load distribution, resulting in superior durability compared to traditional V-belts. V-belts, while effective in power transmission, tend to exhibit higher wear rates due to concentrated stress on the belt edges, leading to faster material fatigue. The advanced polymer compounds and reinforced fibers used in ribbed belts contribute significantly to their enhanced wear resistance, making them ideal for high-speed and high-load applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Ribbed belts feature multiple longitudinal ribs that align with corresponding grooves on pulleys, enabling easier installation without precise tension adjustments compared to V-belts which require careful alignment and tensioning to prevent slippage and premature wear. Maintenance of ribbed belts is generally simpler due to their flexibility and compatibility with smaller pulley diameters, reducing the need for frequent realignment or replacements. V-belts demand routine inspections to monitor tension and wear, as improper maintenance leads to reduced efficiency and increased operational downtime.
Cost and Longevity Analysis
Ribbed belts generally offer a lower initial cost compared to V-belts, making them a cost-effective choice for applications requiring smooth power transmission. In terms of longevity, V-belts tend to have a longer lifespan due to their robust construction and ability to handle higher tension and load variations without premature wear. When evaluating cost and durability, selecting between ribbed belts and V-belts depends on specific operational demands and maintenance budgets.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Ribbed belts offer superior flexibility and higher power transmission efficiency compared to V-belts, making them ideal for compact and high-speed applications. V-belts provide better grip and are more durable under heavy load conditions but tend to generate more heat and noise. Ribbed belts may wear faster in abrasive environments, while V-belts require careful alignment to prevent slippage and premature failure.
Choosing the Right Belt for Your Needs
Selecting the right belt depends on application requirements such as load capacity, flexibility, and space constraints. Ribbed belts offer superior flexibility and grip for high-speed, low-torque applications, while V-belts provide excellent power transmission for heavy-duty, high-torque machinery. Evaluating factors like operating environment, belt alignment, and maintenance ease ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Ribbed belt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com