Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions characterized by inflammation, redness, and itching, but they differ in their underlying causes and appearance. While eczema typically results from an allergic reaction and often presents with dry, cracked skin, psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder marked by thick, scaly patches. Discover how to identify symptoms, manage flare-ups, and explore effective treatments in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
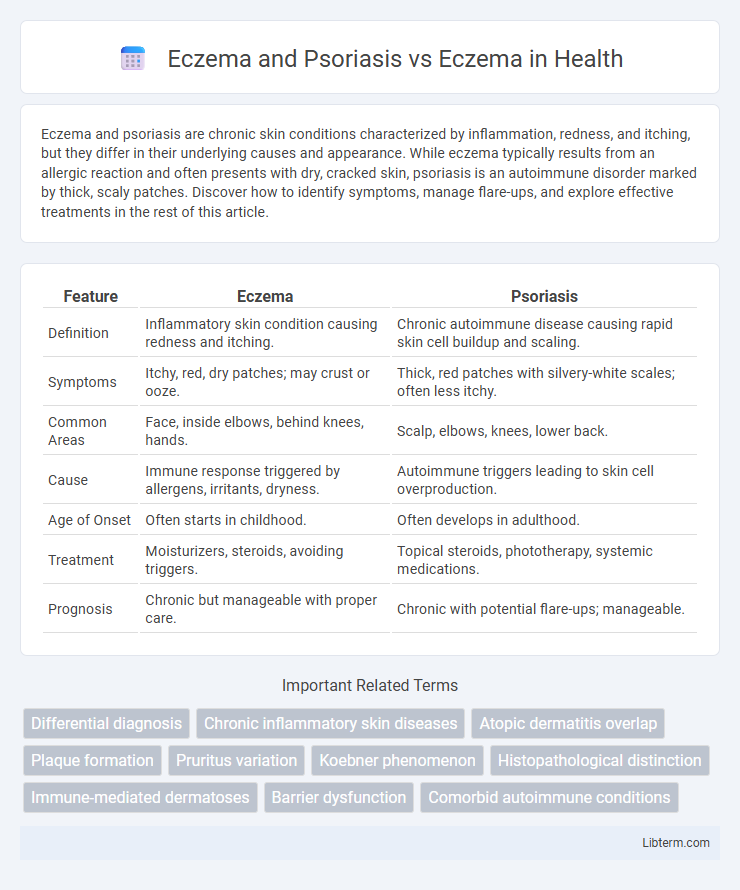
| Feature | Eczema | Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammatory skin condition causing redness and itching. | Chronic autoimmune disease causing rapid skin cell buildup and scaling. |
| Symptoms | Itchy, red, dry patches; may crust or ooze. | Thick, red patches with silvery-white scales; often less itchy. |
| Common Areas | Face, inside elbows, behind knees, hands. | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back. |
| Cause | Immune response triggered by allergens, irritants, dryness. | Autoimmune triggers leading to skin cell overproduction. |
| Age of Onset | Often starts in childhood. | Often develops in adulthood. |
| Treatment | Moisturizers, steroids, avoiding triggers. | Topical steroids, phototherapy, systemic medications. |
| Prognosis | Chronic but manageable with proper care. | Chronic with potential flare-ups; manageable. |
Understanding Eczema: Causes and Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness caused primarily by genetic and environmental factors. Psoriasis differs from eczema in its autoimmune origin, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and the formation of thick, scaly plaques. Understanding eczema involves recognizing triggers such as allergens, irritants, stress, and weather changes, which exacerbate symptoms and disrupt the skin barrier function.
What Is Psoriasis? Key Differences from Eczema
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by rapid skin cell production, leading to thick, red, scaly patches, primarily on the scalp, elbows, and knees. Unlike eczema, which is an inflammatory condition caused by a hypersensitive immune response often triggered by allergens or irritants, psoriasis results from immune system dysfunction affecting skin cell regeneration. Key differences include psoriasis's distinct well-defined plaques with silvery scales, whereas eczema presents as itchy, inflamed, and often oozing skin without the thick scale buildup.
Eczema and Psoriasis: How They Overlap
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic inflammatory skin conditions that share overlapping symptoms such as redness, itching, and scaling, but differ in their underlying causes and cellular mechanisms. Both disorders involve immune system dysregulation, with eczema characterized by a defective skin barrier and eczema-associated allergens, while psoriasis features excessive keratinocyte proliferation driven by T-cell activation. Understanding the common inflammatory pathways in eczema and psoriasis improves diagnostic accuracy and informs targeted treatment strategies for patients presenting with mixed or ambiguous skin lesions.
Distinct Triggers: Eczema vs Psoriasis
Eczema, primarily triggered by irritants, allergens, and environmental factors, often flares due to contact with soaps, fabrics, and stress. Psoriasis, in contrast, is driven by an autoimmune response where triggers include infections, cold weather, and certain medications. Understanding these distinct triggers enables tailored treatment strategies and effective management of each condition.
Visual Differences: Eczema and Psoriasis Side by Side
Eczema typically presents as red, inflamed patches with dry, flaky skin that may ooze or crust, often found in flexural areas like the elbows and behind the knees. Psoriasis is characterized by thick, silvery-white scales overlaying red plaques, commonly appearing on extensor surfaces such as the elbows, knees, and scalp. Unlike eczema's irregular patches, psoriasis lesions are well-defined with sharper borders, making their visual differences distinct when examined side by side.
Diagnosing Eczema and Psoriasis: What to Expect
Diagnosing eczema and psoriasis involves a thorough clinical evaluation of skin symptoms, including redness, scaling, and inflammation, with eczema often presenting as itchy, dry patches and psoriasis displaying well-defined plaques with silvery scales. Medical history and physical examination guide dermatologists in differentiating conditions, sometimes requiring skin biopsies for accurate diagnosis. Laboratory tests and dermoscopy may assist in complex cases to distinguish between eczema and psoriasis, ensuring targeted treatment approaches.
Treatment Approaches: Eczema vs Psoriasis
Eczema treatment primarily involves moisturizing the skin regularly and using topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, while psoriasis often requires stronger therapies such as systemic medications, phototherapy, and biologics targeting immune system dysfunction. Both conditions benefit from avoiding triggers and maintaining a consistent skincare routine, but psoriasis may need long-term management with immune-modulating drugs due to its chronic autoimmune nature. Effective treatment plans for eczema focus on barrier repair and inflammation control, whereas psoriasis treatment targets abnormal skin cell production and immune response.
Lifestyle Management: Coping with Eczema and Psoriasis
Effective lifestyle management for eczema and psoriasis includes maintaining a consistent skincare routine using fragrance-free moisturizers and avoiding known triggers such as stress, allergens, and harsh soaps. Regularly managing stress through techniques like mindfulness or gentle exercise can reduce flare-ups in both conditions. Ensuring proper hydration, balanced nutrition, and wearing breathable fabrics also plays a critical role in minimizing symptoms and improving skin barrier function.
When Eczema and Psoriasis Coexist: Dual Diagnosis
Eczema and psoriasis often present overlapping symptoms such as red, itchy, and inflamed skin, complicating diagnosis and treatment strategies when they coexist. Dual diagnosis requires tailored therapy combining topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and sometimes systemic agents like biologics to manage the distinct inflammatory pathways of both conditions effectively. Understanding the immunological differences--eczema's Th2-driven response versus psoriasis' Th1/Th17 dominance--guides dermatologists in optimizing patient outcomes with personalized care.
Prevention and Long-Term Outlook: Eczema vs Psoriasis
Effective prevention of eczema involves maintaining skin hydration, avoiding known irritants, and managing stress levels, which helps reduce flare-ups and supports long-term skin health. Psoriasis prevention focuses on minimizing triggers such as infections, skin injuries, and certain medications, alongside consistent use of prescribed treatments to control symptoms and decrease exacerbations. Long-term outlook for eczema often includes periods of remission and flare-ups with proper skin care, while psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition requiring ongoing management to prevent progression and complications like psoriatic arthritis.
Eczema and Psoriasis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com