Retention bonuses are financial incentives offered by companies to encourage employees to remain with the organization during critical periods. These bonuses help reduce turnover, maintain productivity, and protect valuable talent in competitive job markets. Discover how retention bonuses can benefit your career and what factors determine their effectiveness in the full article.
Table of Comparison
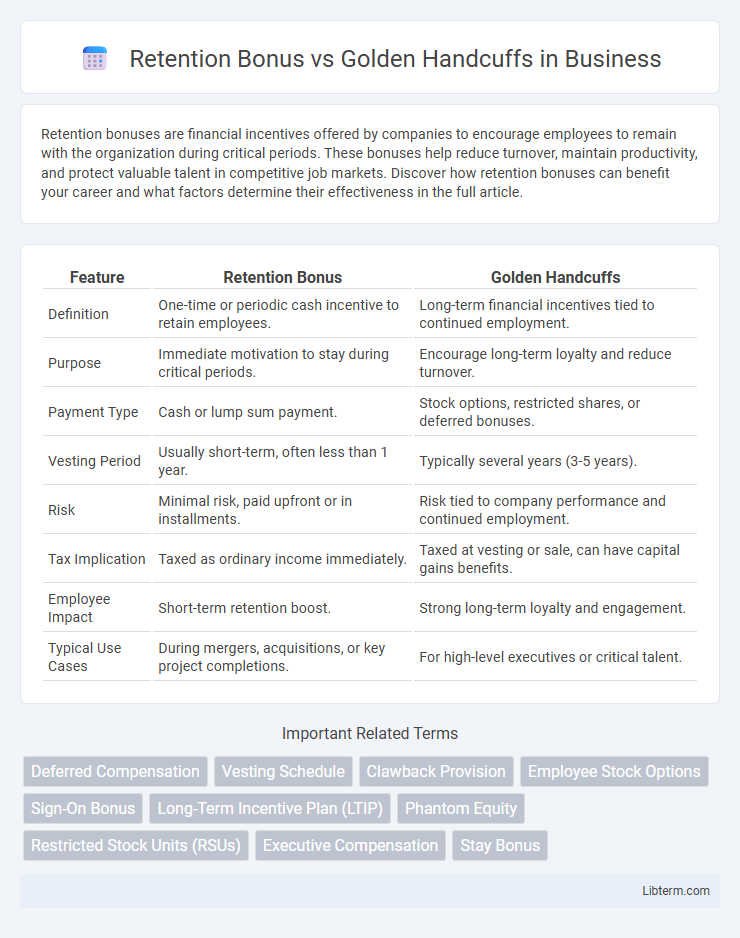
| Feature | Retention Bonus | Golden Handcuffs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-time or periodic cash incentive to retain employees. | Long-term financial incentives tied to continued employment. |
| Purpose | Immediate motivation to stay during critical periods. | Encourage long-term loyalty and reduce turnover. |
| Payment Type | Cash or lump sum payment. | Stock options, restricted shares, or deferred bonuses. |
| Vesting Period | Usually short-term, often less than 1 year. | Typically several years (3-5 years). |
| Risk | Minimal risk, paid upfront or in installments. | Risk tied to company performance and continued employment. |
| Tax Implication | Taxed as ordinary income immediately. | Taxed at vesting or sale, can have capital gains benefits. |
| Employee Impact | Short-term retention boost. | Strong long-term loyalty and engagement. |
| Typical Use Cases | During mergers, acquisitions, or key project completions. | For high-level executives or critical talent. |
Understanding Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses are financial incentives offered to key employees to encourage them to remain with a company during critical periods, often tied to specific timeframes or project milestones. These bonuses provide immediate monetary rewards as a direct compensation strategy, unlike golden handcuffs, which typically involve long-term benefits such as stock options or deferred compensation. Understanding the structure and timing of retention bonuses helps organizations effectively reduce turnover and maintain crucial talent during transitions or competitive industry shifts.
What Are Golden Handcuffs?
Golden handcuffs are financial incentives designed to retain key employees by offering substantial benefits or compensation, such as stock options, bonuses, or pension plans, that vest over a specified period. Unlike retention bonuses, which are typically one-time payments, golden handcuffs create long-term commitment by tying valuable rewards to continued employment. These agreements often make it costly for employees to leave, aligning their financial interests with the company's longevity and success.
Key Differences Between Retention Bonuses and Golden Handcuffs
Retention bonuses are one-time financial incentives offered to employees to encourage them to stay with a company for a specified period, often during critical projects or transitions. Golden handcuffs refer to a combination of long-term benefits, such as stock options, deferred bonuses, or pension plans, designed to create ongoing financial incentives that make leaving the company costly. The key difference lies in retention bonuses providing immediate, short-term rewards, while golden handcuffs tie employees to the organization through extended, multi-year financial commitments.
Common Objectives: Why Companies Use These Incentives
Retention bonuses and golden handcuffs both serve to reduce employee turnover by providing financial incentives tied to continued service. Companies use these strategies to secure key talent, align employee goals with long-term business objectives, and prevent valuable personnel from leaving during critical periods. These incentives enhance loyalty and performance by rewarding commitment and discouraging job-hopping in competitive industries.
Financial Structures: Lump Sum vs. Vesting Schedules
Retention bonuses typically involve a lump sum payment designed to incentivize employees to remain with a company for a specified period, offering immediate financial reward upon meeting retention criteria. In contrast, golden handcuffs use a vesting schedule structure, where employees earn financial benefits such as stock options or restricted shares incrementally over time, aligning long-term retention with company performance and loyalty. The lump sum model delivers upfront cash value, while vesting schedules encourage sustained commitment through deferred compensation and potential capital appreciation.
Pros and Cons of Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses offer immediate financial incentives that improve employee loyalty and reduce turnover costs, making them effective for retaining critical talent during key projects or transitions. However, they can create reliance on short-term rewards, potentially undermining intrinsic motivation and leading to dissatisfaction if bonuses are not renewed. Unlike golden handcuffs, retention bonuses do not typically impose long-term employment restrictions, providing more flexibility but less guarantee of prolonged commitment.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Golden Handcuffs
Golden Handcuffs offer a strategic advantage by incentivizing key employees to remain with a company through deferred compensation or stock options, aligning long-term interests. However, these arrangements can create retention challenges if employees feel trapped, potentially decreasing motivation and job satisfaction. The complexity of Golden Handcuffs agreements may also lead to administrative burdens and reduced flexibility compared to simpler retention bonuses.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Loyalty
Retention bonuses provide immediate financial rewards that boost employee motivation by recognizing short-term achievements and encouraging continued service. Golden handcuffs create long-term loyalty through deferred benefits such as stock options or pension plans, which tie employees to the company over extended periods. Both strategies enhance retention but influence motivation differently: retention bonuses drive short-term engagement, while golden handcuffs foster sustained commitment.
Legal and Tax Implications for Employers and Employees
Retention bonuses are typically treated as supplemental wages subject to ordinary income tax and payroll taxes, requiring employers to withhold accordingly, while golden handcuffs often involve stock options or deferred compensation with complex tax deferral rules under IRC Sections 83 and 409A. Employers must carefully draft golden handcuff agreements to comply with tax regulations, avoiding penalties and unintended immediate taxation for employees, whereas retention bonuses are straightforward but may create immediate employment tax liabilities. Legal implications include ensuring enforceability of golden handcuff restrictions versus the simpler contractual nature of retention bonuses, with potential disputes arising over vesting conditions and tax treatment.
Choosing the Right Incentive: Retention Bonus or Golden Handcuffs?
Retention bonuses provide immediate financial rewards to employees for staying through a critical period, making them effective for short-term retention during mergers or projects. Golden handcuffs involve deferred compensation or equity tied to long-term continued employment, incentivizing loyalty and reducing turnover over several years. Choosing between these incentives depends on the company's retention goals, financial capacity, and the desired duration of employee commitment.
Retention Bonus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com