Demand management involves forecasting, planning, and controlling customer demand to balance supply with market needs efficiently. Effective strategies help reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize inventory levels. Discover how your business can master demand management techniques by reading the full article.
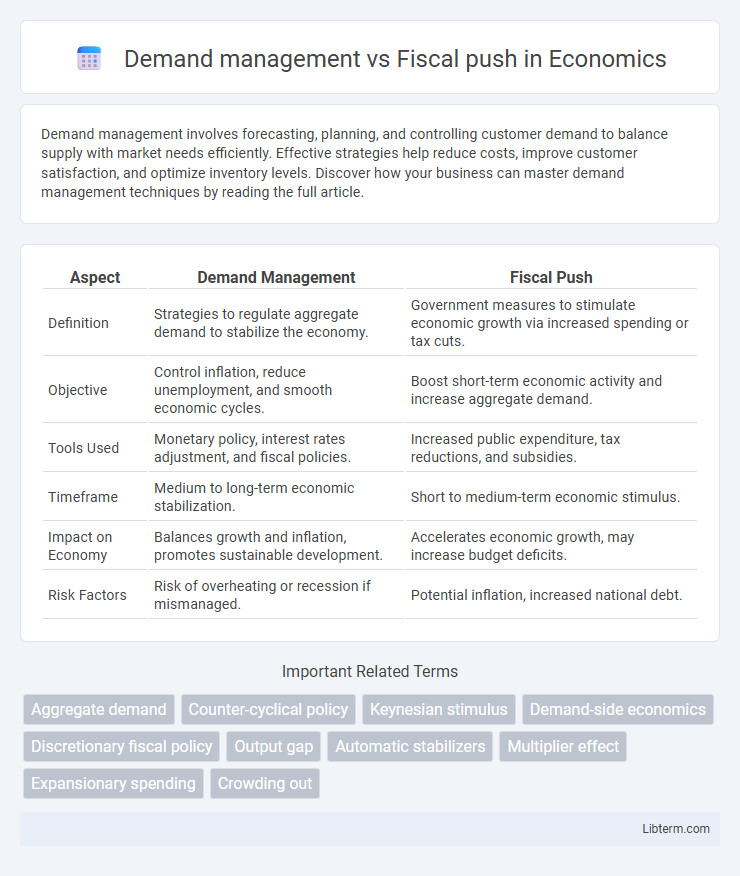
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Demand Management | Fiscal Push |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategies to regulate aggregate demand to stabilize the economy. | Government measures to stimulate economic growth via increased spending or tax cuts. |
| Objective | Control inflation, reduce unemployment, and smooth economic cycles. | Boost short-term economic activity and increase aggregate demand. |
| Tools Used | Monetary policy, interest rates adjustment, and fiscal policies. | Increased public expenditure, tax reductions, and subsidies. |
| Timeframe | Medium to long-term economic stabilization. | Short to medium-term economic stimulus. |
| Impact on Economy | Balances growth and inflation, promotes sustainable development. | Accelerates economic growth, may increase budget deficits. |
| Risk Factors | Risk of overheating or recession if mismanaged. | Potential inflation, increased national debt. |
Understanding Demand Management
Demand management involves regulating consumer demand to stabilize economic growth by adjusting policies such as interest rates and taxation, ensuring balanced consumption and investment. In contrast, fiscal push emphasizes direct government spending to stimulate demand, which can lead to inflation if not carefully controlled. Effective demand management targets long-term economic stability through strategic policy adjustments rather than solely relying on short-term fiscal stimulus.
Defining Fiscal Push
Fiscal push refers to government-initiated financial strategies aimed at stimulating economic activity by increasing public expenditure or reducing taxes to boost aggregate demand. Unlike demand management, which encompasses broader policies including monetary measures and market interventions, fiscal push specifically involves direct fiscal tools to inject liquidity and encourage consumption or investment. Effective fiscal push can accelerate economic growth during downturns by addressing liquidity constraints and promoting higher spending levels.
Key Differences Between Demand Management and Fiscal Push
Demand management focuses on regulating consumer demand through policies like interest rate adjustments and monetary control, aiming to stabilize economic fluctuations. Fiscal push involves government expenditure and taxation strategies to directly influence economic activity, emphasizing budgetary measures to stimulate growth or contraction. The key difference lies in demand management's reliance on monetary tools, while fiscal push depends primarily on fiscal policy interventions.
Objectives and Goals of Demand Management
Demand management aims to stabilize economic fluctuations by regulating consumer spending and overall demand to achieve sustainable growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment. It focuses on influencing aggregate demand through monetary and fiscal policies to balance supply and demand in the economy effectively. Unlike fiscal push, which emphasizes government spending to stimulate growth, demand management targets optimal resource allocation and demand stabilization for long-term economic equilibrium.
Implementation Strategies for Fiscal Push
Fiscal push implementation strategies focus on direct government spending to stimulate economic growth, including targeted subsidies, infrastructure investments, and tax incentives. These strategies prioritize immediate increases in aggregate demand through public sector intervention and efficient allocation of financial resources to high-impact sectors. Effective fiscal push requires coordinated policy frameworks, transparent budgeting processes, and robust monitoring to maximize multiplier effects and ensure sustainable economic outcomes.
Economic Scenarios Favoring Demand Management
Economic scenarios favoring demand management typically involve recessionary periods characterized by high unemployment and underutilized capacity. In such environments, policies aimed at boosting aggregate demand, like government spending and tax cuts, can stimulate consumption and investment to revive economic growth. These demand management strategies are preferred over fiscal push approaches when the priority is to increase economic activity without risking inflationary pressures or overheating the economy.
Fiscal Push in Practice: Case Studies
Fiscal push involves targeted government spending and tax incentives to stimulate economic growth, as demonstrated by South Korea's investment in technology sectors during the 1990s, which accelerated industrial modernization. In Brazil, fiscal push strategies during the early 2000s included increased infrastructure spending and social programs, contributing to significant poverty reduction and GDP growth. These case studies highlight fiscal push as an effective tool for long-term economic development by directly influencing supply-side factors and infrastructure expansion.
Impacts on Inflation and Economic Growth
Demand management influences inflation by controlling aggregate demand through monetary and fiscal policies, stabilizing price levels and promoting sustainable economic growth. Fiscal push, characterized by increased government spending and tax reductions, can stimulate short-term economic growth but may risk higher inflation if aggregate demand exceeds supply capacity. Balancing demand management with fiscal push is critical to managing inflationary pressures while fostering long-term economic expansion.
Policy Challenges and Risks
Demand management policies aim to regulate aggregate demand through fiscal measures such as taxation and government spending, but they risk causing inflation or unemployment if misapplied. Fiscal push strategies involve direct government expenditure to stimulate economic growth, often increasing public debt and potentially leading to fiscal imbalances. Both approaches face policy challenges including timing, magnitude, and coordination with monetary policy to avoid overheating or stagnation in the economy.
Choosing the Right Approach: Demand Management vs Fiscal Push
Choosing the right economic approach involves analyzing demand management and fiscal push strategies based on current market conditions and government objectives. Demand management focuses on regulating consumer spending and investment through monetary policies to stabilize economic cycles, while fiscal push employs direct government spending and taxation adjustments to stimulate growth or control inflation. Evaluating factors such as inflation rates, unemployment, and public debt levels ensures selecting the most effective method for achieving sustainable economic stability and growth.
Demand management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com