Flexible staffing allows businesses to adjust their workforce based on fluctuating demands, reducing labor costs and increasing operational efficiency. By leveraging temporary, part-time, or contract workers, companies can quickly scale their team to meet project needs without committing to long-term employment. Discover how flexible staffing can transform your workforce strategy by exploring the benefits and best practices in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
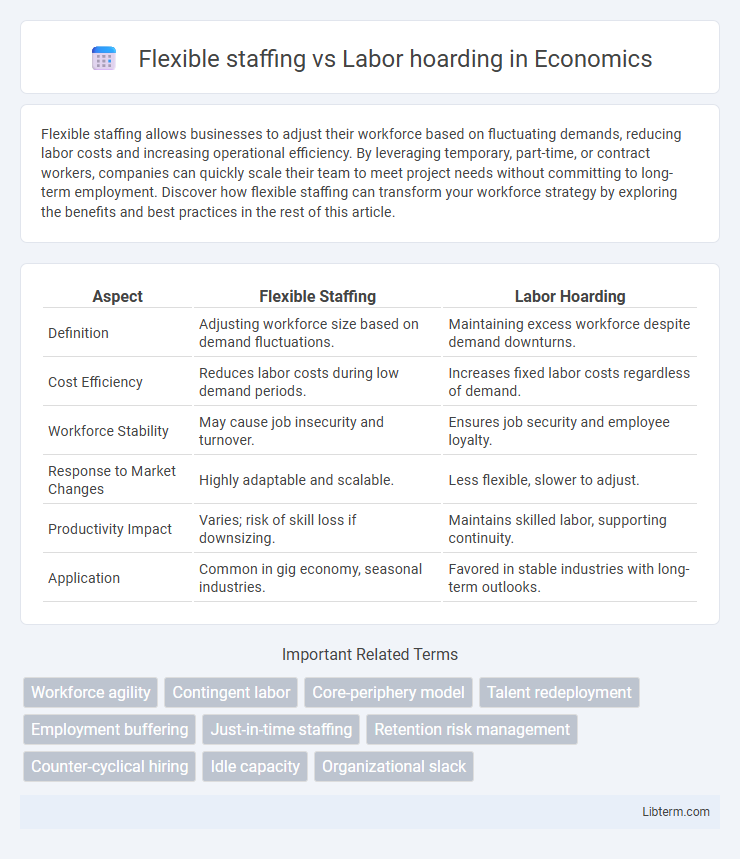
| Aspect | Flexible Staffing | Labor Hoarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting workforce size based on demand fluctuations. | Maintaining excess workforce despite demand downturns. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor costs during low demand periods. | Increases fixed labor costs regardless of demand. |
| Workforce Stability | May cause job insecurity and turnover. | Ensures job security and employee loyalty. |
| Response to Market Changes | Highly adaptable and scalable. | Less flexible, slower to adjust. |
| Productivity Impact | Varies; risk of skill loss if downsizing. | Maintains skilled labor, supporting continuity. |
| Application | Common in gig economy, seasonal industries. | Favored in stable industries with long-term outlooks. |
Introduction to Flexible Staffing and Labor Hoarding
Flexible staffing involves adjusting workforce size according to demand fluctuations by using temporary, part-time, or contract employees to optimize labor costs and maintain operational agility. Labor hoarding refers to retaining excess employees during downturns to preserve firm-specific skills, enhance employee morale, and avoid future recruitment costs despite short-term inefficiencies. Understanding the balance between flexible staffing and labor hoarding is crucial for businesses aiming to navigate economic volatility while sustaining productivity and workforce stability.
Defining Flexible Staffing: Key Characteristics
Flexible staffing involves adjusting workforce size and composition based on fluctuating business demands, emphasizing temporary contracts, part-time roles, and outsourcing. Key characteristics include adaptability to market changes, cost efficiency through reduced fixed labor costs, and enhanced organizational agility. Unlike labor hoarding, which retains excess staff during downturns to preserve human capital, flexible staffing prioritizes workforce scalability and responsiveness.
Understanding Labor Hoarding: Concepts and Practices
Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than needed during economic downturns to preserve organizational knowledge and avoid future rehiring costs. This practice can maintain workforce stability and morale but may increase short-term labor costs and reduce operational flexibility. In contrast, flexible staffing adjusts employee levels according to demand, optimizing costs but risking loss of skilled workers and institutional knowledge.
Economic Drivers Behind Flexible Staffing
Flexible staffing models adapt labor supply to fluctuating demand, reducing costs linked to permanent employment and improving organizational agility. Economic drivers such as market volatility, cost minimization pressures, and technological advancements encourage firms to use contingent workers and temporary contracts. This approach contrasts with labor hoarding, where companies retain excess staff during downturns to avoid rehiring costs and preserve firm-specific human capital.
Why Companies Resort to Labor Hoarding
Companies resort to labor hoarding to maintain workforce stability during economic downturns and avoid the high costs associated with rehiring and retraining staff. This strategy preserves institutional knowledge and employee morale, which can enhance long-term productivity. Labor hoarding provides a buffer against market volatility, enabling quicker recovery and sustained competitive advantage.
Advantages of Flexible Staffing for Businesses
Flexible staffing offers businesses enhanced agility, allowing quick adjustments to workforce size based on demand fluctuations, which reduces labor costs and minimizes idle employee time. It enables access to specialized skills on a temporary basis, improving project efficiency and innovation without long-term commitments. This approach also supports better risk management by aligning labor expenses directly with business activity, enhancing overall financial stability.
Risks and Drawbacks of Labor Hoarding
Labor hoarding can lead to increased operational costs and reduced workforce productivity due to maintaining excess staff during downturns. It creates financial strain from wages paid to underutilized employees and can hinder organizational agility by limiting the ability to adjust labor quickly in response to market changes. This inflexibility may result in inefficient resource allocation and long-term competitive disadvantages.
Impact on Employee Well-being and Morale
Flexible staffing enhances employee well-being by providing adaptable schedules that reduce burnout and accommodate work-life balance, boosting overall morale. Labor hoarding may protect jobs during downturns but often leads to employee dissatisfaction due to increased workloads and job insecurity. Companies adopting flexible staffing models report higher employee engagement and lower turnover rates compared to those practicing labor hoarding.
Choosing the Right Workforce Strategy: Key Factors
Choosing the right workforce strategy hinges on balancing flexibility and cost-efficiency, with flexible staffing offering adaptability through temporary or contract workers to manage fluctuating demand. Labor hoarding emphasizes retaining permanent employees during downturns to preserve skills and minimize rehiring costs, which can enhance long-term productivity but increase short-term expenses. Key factors include industry volatility, cost tolerance, organizational agility, and the ability to maintain workforce morale and institutional knowledge.
Future Trends: Balancing Flexibility and Stability
Flexible staffing models are increasingly favored for their ability to rapidly adjust workforce size in response to market fluctuations, enhancing organizational agility. Labor hoarding, while ensuring stability and employee retention during downturns, may lead to higher fixed labor costs and reduced operational efficiency. Future trends emphasize hybrid approaches that combine flexible staffing's responsiveness with strategic labor hoarding to maintain long-term workforce stability and competitive advantage.
Flexible staffing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com