The harmonization approach integrates diverse systems, standards, or processes to create a cohesive and efficient framework, reducing discrepancies and improving overall functionality. It ensures consistency across various platforms, facilitating smoother collaboration and data exchange. Discover how harmonization can transform Your operations by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
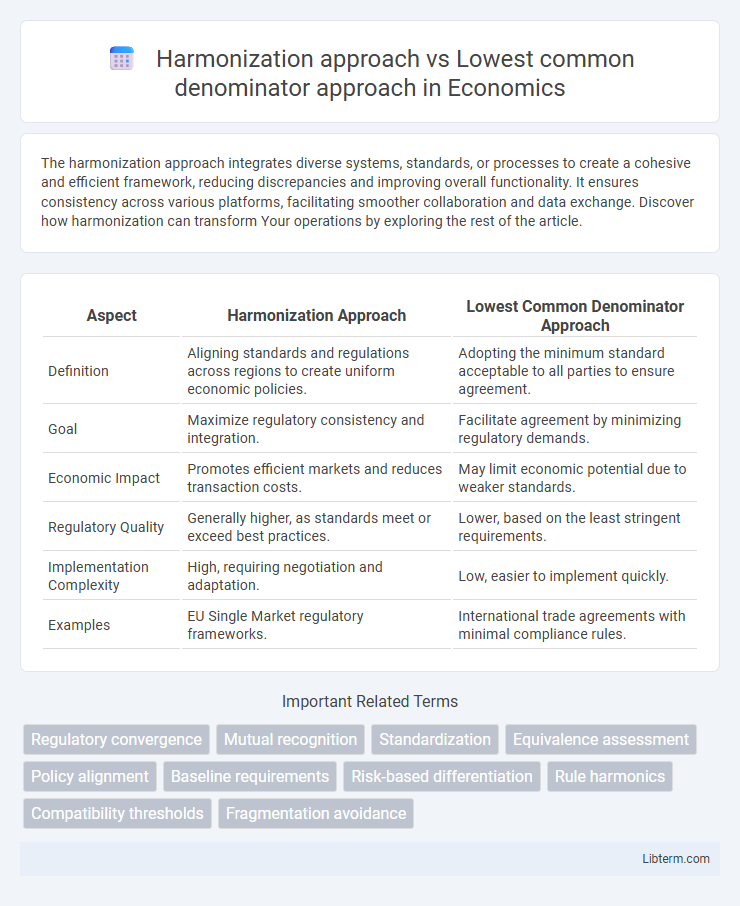
| Aspect | Harmonization Approach | Lowest Common Denominator Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aligning standards and regulations across regions to create uniform economic policies. | Adopting the minimum standard acceptable to all parties to ensure agreement. |
| Goal | Maximize regulatory consistency and integration. | Facilitate agreement by minimizing regulatory demands. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes efficient markets and reduces transaction costs. | May limit economic potential due to weaker standards. |
| Regulatory Quality | Generally higher, as standards meet or exceed best practices. | Lower, based on the least stringent requirements. |
| Implementation Complexity | High, requiring negotiation and adaptation. | Low, easier to implement quickly. |
| Examples | EU Single Market regulatory frameworks. | International trade agreements with minimal compliance rules. |
Defining the Harmonization Approach
The harmonization approach focuses on aligning standards, regulations, or practices across different entities to create consistency while allowing for some flexibility in achieving common goals. This method emphasizes collaborative negotiation and mutual recognition, ensuring that parties maintain core requirements while accommodating local variations. Unlike the lowest common denominator approach, harmonization aims to elevate standards rather than dilute them to the simplest acceptable level.
Understanding the Lowest Common Denominator Approach
The Lowest Common Denominator Approach emphasizes creating standards or policies that meet the minimum acceptable criteria shared across all involved parties, often resulting in the simplest or least stringent solution. This approach prioritizes broad acceptance and ease of implementation but may sacrifice innovation and optimal functionality. It contrasts with harmonization, which seeks to integrate and elevate standards to achieve consistency and higher quality across systems or regions.
Fundamental Differences Between the Two Approaches
The harmonization approach aims to create unified standards that integrate the best elements of various regulations to achieve consistency and efficiency across jurisdictions. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach sets minimal requirements that all parties can agree on, often sacrificing quality or rigor to ensure broader acceptance. The fundamental difference lies in harmonization striving for optimal regulatory alignment and improvement, while the lowest common denominator approach prioritizes basic compliance and minimal conflict.
Advantages of Harmonization
The harmonization approach streamlines compliance by creating unified standards across multiple jurisdictions, reducing complexity and administrative costs for businesses. It enhances market integration, facilitating smoother trade and regulatory cooperation while promoting innovation through consistent guidelines. Harmonization also improves legal clarity and enforcement, minimizing conflicts between differing regulations that often arise under the lowest common denominator approach.
Drawbacks of Harmonization Strategies
Harmonization strategies often face challenges such as increased complexity and higher costs due to the need to align diverse regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions. This approach may lead to resistance from stakeholders who benefit from localized standards and create delays in implementation caused by extensive negotiations. Moreover, harmonization can sometimes result in compromising higher regulatory standards to achieve broader consensus, thus weakening overall effectiveness.
Benefits of the Lowest Common Denominator Approach
The Lowest Common Denominator approach simplifies compliance by establishing uniform standards that apply across all parties, reducing complexity and administrative burden. This method enhances interoperability by ensuring all participants adhere to compatible regulations, facilitating smoother collaboration and integration. Cost savings emerge from avoiding tailored solutions and minimizing regulatory conflicts, making implementation more efficient and scalable.
Limitations of the Lowest Common Denominator Method
The Lowest Common Denominator (LCD) approach often results in minimal standards that satisfy all parties but fail to promote innovation or higher quality outcomes. This method can lead to compromised regulations that do not fully address the complexities or diversity of specific contexts, limiting overall effectiveness. In contrast, harmonization seeks to integrate varied standards into a coherent framework, improving consistency and raising the baseline for performance and compliance.
Practical Applications in Policy and Regulation
Harmonization approach in policy and regulation promotes uniform standards across jurisdictions, facilitating cross-border trade, reducing compliance costs, and enhancing regulatory clarity for businesses and governments. The lowest common denominator approach results in minimal standards that may hinder innovation and create loopholes, but often gains quicker consensus among diverse stakeholders due to its simplicity and reduced demands. Practical applications show harmonization is preferred in sectors like financial services and environmental regulation for ensuring safety and interoperability, while the lowest common denominator approach is common in broader international agreements where political feasibility trumps stringent measures.
Sector-Specific Case Studies and Examples
The harmonization approach in sector-specific regulation aligns standards across jurisdictions to enhance consistency and reduce compliance costs, exemplified by the European Union's financial regulations under MiFID II, which unify trading rules and investor protection. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach sets minimal standards allowing diverse regulatory practices, as seen in international environmental agreements where countries adopt baseline pollution controls, leading to varying enforcement levels. Sector-specific case studies highlight the harmonization approach's efficiency in financial services, while the lowest common denominator approach often results in fragmented outcomes in environmental and telecommunications policies.
Choosing the Right Approach: Key Considerations
Choosing the right approach between Harmonization and Lowest Common Denominator depends on organizational goals, regulatory environments, and stakeholder needs. Harmonization promotes consistency and efficiency by aligning standards across systems, while the Lowest Common Denominator approach prioritizes minimal compliance to ensure broad applicability and reduce complexity. Evaluating factors such as risk tolerance, operational flexibility, and long-term scalability guides decision-makers in selecting the optimal strategy for compliance and integration success.
Harmonization approach Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com