Time value is a crucial concept in finance and investment, representing the principle that money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity. Understanding time value can help you make informed decisions about loans, investments, and savings by factoring in interest rates and inflation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how mastering time value can optimize your financial strategy.
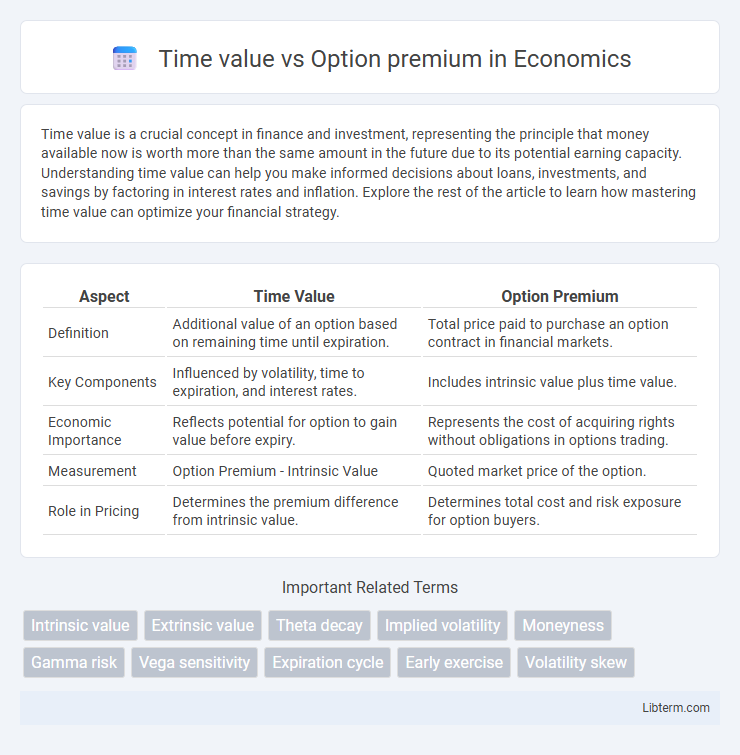
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Time Value | Option Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Additional value of an option based on remaining time until expiration. | Total price paid to purchase an option contract in financial markets. |
| Key Components | Influenced by volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates. | Includes intrinsic value plus time value. |
| Economic Importance | Reflects potential for option to gain value before expiry. | Represents the cost of acquiring rights without obligations in options trading. |
| Measurement | Option Premium - Intrinsic Value | Quoted market price of the option. |
| Role in Pricing | Determines the premium difference from intrinsic value. | Determines total cost and risk exposure for option buyers. |
Understanding the Time Value in Options
Time value in options reflects the additional premium traders are willing to pay over the intrinsic value due to the potential for favorable price movement before expiration. It diminishes as the option nears its expiration date, a phenomenon known as time decay or theta erosion. Understanding time value is crucial for options traders to evaluate the cost of holding options and to strategize entry and exit points effectively.
What Is an Option Premium?
An option premium is the price paid by the buyer to acquire the rights conveyed by an option contract, reflecting intrinsic value plus time value. Time value represents the potential for the option to increase in value before expiration, influenced by factors like volatility, time remaining, and underlying asset price movement. Understanding the option premium is essential for traders to evaluate the cost and potential profitability of options trading strategies.
Components of Option Premium Explained
Option premium consists of intrinsic value and time value, with intrinsic value representing the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the strike price if favorable. Time value reflects the potential for the option to increase in value before expiration, influenced by factors such as volatility, time remaining, and interest rates. Traders closely monitor time value as it decays over the option's lifespan, impacting the premium's overall price dynamics.
Relationship Between Time Value and Option Premium
Time value directly influences the option premium as it represents the additional amount buyers are willing to pay above the intrinsic value, reflecting the potential for favorable price movement before expiration. Longer time until expiration generally increases the option premium due to greater uncertainty and opportunity for profit. As expiration approaches, the time value decays, causing the option premium to converge toward its intrinsic value.
Factors Influencing Time Value
Time value in options is primarily influenced by the duration until expiration, with longer times increasing the likelihood of profitable price movements, thereby raising the option premium. Volatility plays a crucial role, as higher expected fluctuations in the underlying asset's price enhance the potential for advantageous outcomes, boosting time value. Interest rates and dividends also affect time value, with rising interest rates generally increasing call option premiums and dividends potentially reducing them due to expected price adjustments.
Intrinsic Value vs. Time Value
Option premium consists of intrinsic value and time value, where intrinsic value represents the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the strike price when favorable, reflecting immediate exercise profitability. Time value accounts for the potential of future price movement before expiration, diminishing as the option approaches maturity due to time decay or theta. Investors price options understanding intrinsic value as guaranteed profit and time value as speculative benefit based on volatility and time left.
How Time Decay Impacts Option Premium
Time decay, or theta, erodes the option premium as the expiration date approaches, reducing the option's extrinsic value. The rate of premium decline accelerates in the final 30 days before expiration, significantly impacting out-of-the-money options. Traders must carefully consider time decay when holding options, as the loss in time value can outweigh potential gains from underlying price movements.
Strategies to Manage Time Value
Managing time value in option premiums involves employing strategies like calendar spreads, which capitalize on time decay differences by buying longer-term options and selling shorter-term ones. Traders often use theta-neutral portfolios to balance time decay effects, minimizing losses as expiration approaches. Utilizing options with different expiration dates or rolling positions forward can optimize the impact of time value on overall returns.
Maximizing Gains: Timing and Option Premium
Maximizing gains in options trading hinges on understanding the time value embedded in an option premium, which represents the extra amount investors are willing to pay beyond intrinsic value due to potential favorable price movement before expiration. The time decay, or theta, erodes this time value as the expiration date approaches, making timing critical to capture the highest premium. Strategic entry when implied volatility is high and managing exit before significant time decay maximizes option premium and enhances overall returns.
Practical Examples: Time Value and Option Premium
An option premium consists of intrinsic value plus time value, reflecting the potential for price movement before expiration. For example, if a stock is trading at $50 and a call option's strike price is $45, the intrinsic value is $5, while the remaining part of a $7 premium is the time value. As expiration approaches, time value decreases, making options with longer durations generally have higher premiums due to increased uncertainty and potential profit.
Time value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com