Corrective maintenance involves identifying and fixing faults or failures in equipment after they have occurred to restore optimal functionality. This approach minimizes downtime and ensures your systems continue to operate efficiently without prolonged disruptions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how corrective maintenance can enhance your operational reliability.
Table of Comparison
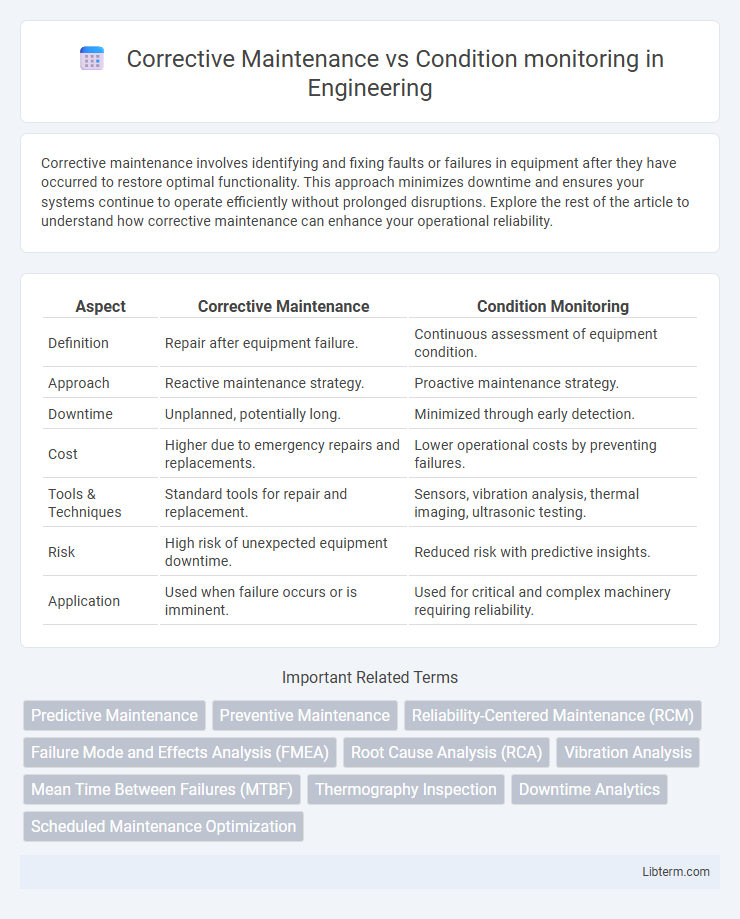
| Aspect | Corrective Maintenance | Condition Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repair after equipment failure. | Continuous assessment of equipment condition. |
| Approach | Reactive maintenance strategy. | Proactive maintenance strategy. |
| Downtime | Unplanned, potentially long. | Minimized through early detection. |
| Cost | Higher due to emergency repairs and replacements. | Lower operational costs by preventing failures. |
| Tools & Techniques | Standard tools for repair and replacement. | Sensors, vibration analysis, thermal imaging, ultrasonic testing. |
| Risk | High risk of unexpected equipment downtime. | Reduced risk with predictive insights. |
| Application | Used when failure occurs or is imminent. | Used for critical and complex machinery requiring reliability. |
Understanding Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure has occurred, focusing on restoring operational functionality quickly. It contrasts with condition monitoring, which relies on continuous data collection to predict and prevent potential breakdowns. Understanding corrective maintenance is crucial for managing unexpected downtime and minimizing repair costs in industries where immediate fixes are essential.
Defining Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring is a proactive maintenance strategy involving continuous or periodic assessment of equipment health through sensors, vibration analysis, temperature measurement, and oil analysis to detect early signs of wear or failure. Unlike corrective maintenance, which addresses equipment repairs only after a breakdown occurs, condition monitoring enables predictive actions that reduce downtime and extend asset life. Implementing condition monitoring systems improves operational efficiency by identifying potential issues before they escalate into costly failures.
Key Differences Between Corrective Maintenance and Condition Monitoring
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, leading to unplanned downtime and higher repair costs. Condition monitoring continuously assesses the health of machinery through sensors and diagnostic tools to detect faults early and schedule maintenance proactively. Key differences include the reactive nature of corrective maintenance versus the predictive approach of condition monitoring, where the latter enhances equipment reliability and reduces unexpected breakdowns.
When to Use Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance is best used when unexpected equipment failures occur, requiring immediate repair to restore functionality and minimize downtime. This approach is ideal for non-critical systems where the cost of monitoring outweighs the benefits or when failure consequences are manageable. Employing corrective maintenance is practical in scenarios lacking predictive data or when condition monitoring resources are unavailable.
Advantages of Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring offers significant advantages over corrective maintenance by enabling early detection of equipment faults, which reduces unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime. It allows for precise scheduling of maintenance activities based on real-time data, leading to improved asset lifespan and operational efficiency. This proactive approach minimizes repair costs and enhances overall system reliability compared to the reactive nature of corrective maintenance.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan
Corrective maintenance addresses equipment failures after they occur, often leading to increased wear and shorter equipment lifespan due to unplanned downtime and potential damage. Condition monitoring utilizes real-time data from sensors to predict and prevent failures, significantly extending equipment lifespan by enabling timely interventions and reducing operational stress. Optimizing maintenance through condition monitoring enhances asset reliability and reduces total cost of ownership by minimizing unexpected breakdowns.
Cost Comparison: Corrective Maintenance vs Condition Monitoring
Corrective maintenance typically incurs higher costs due to unplanned downtime, emergency repairs, and potential equipment damage. Condition monitoring reduces overall expenses by enabling early fault detection, minimizing unexpected failures, and optimizing maintenance schedules. Investing in condition monitoring technology leads to lower lifecycle costs and improved asset reliability compared to corrective maintenance.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Corrective maintenance faces implementation challenges such as unpredictable equipment failures and high downtime costs, requiring rapid response teams and robust spare parts inventory to minimize disruptions. Condition monitoring implementation struggles with sensor accuracy, data integration, and real-time analytics, which can be addressed by investing in advanced IoT devices, machine learning algorithms, and centralized monitoring platforms. Both approaches benefit from tailored training programs and continuous process optimization to enhance reliability and operational efficiency.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment after failure, often leading to unplanned downtime and higher costs, while condition monitoring uses real-time data from sensors to predict and prevent failures, optimizing asset performance in industries like manufacturing and energy. Case studies in the automotive sector show condition monitoring reduced emergency repairs by 40%, increasing productivity and safety. In contrast, industries relying solely on corrective maintenance reported up to 30% more operational interruptions and higher maintenance expenditures.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy
Selecting between corrective maintenance and condition monitoring depends on equipment criticality and failure consequences; corrective maintenance is suitable for non-critical assets with low impact downtime, while condition monitoring optimizes uptime by detecting early signs of wear in high-value machinery. Implementing condition monitoring technologies such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis enables predictive insights that reduce unexpected failures and maintenance costs. Balancing budget constraints and operational risks ensures the chosen strategy maximizes asset lifespan and maintains production efficiency.
Corrective Maintenance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com