RTU (Ready-to-Use) products provide efficient and convenient solutions for various applications, eliminating the need for mixing or preparation. These formulations ensure consistent performance and save valuable time in both industrial and consumer settings. Discover how RTU options can enhance your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
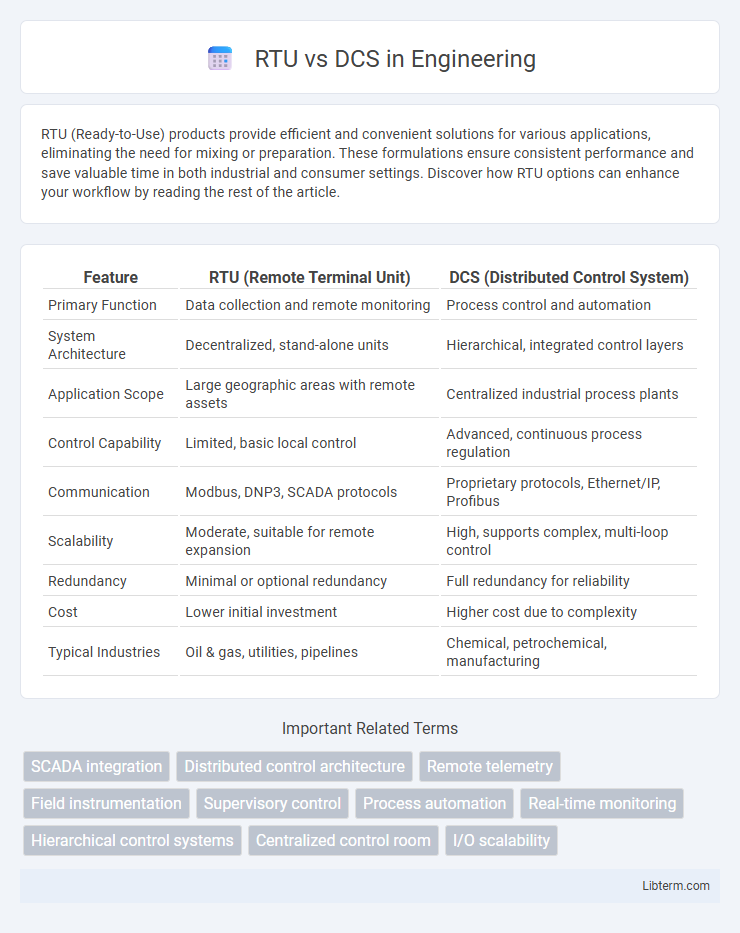
| Feature | RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) | DCS (Distributed Control System) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Data collection and remote monitoring | Process control and automation |
| System Architecture | Decentralized, stand-alone units | Hierarchical, integrated control layers |
| Application Scope | Large geographic areas with remote assets | Centralized industrial process plants |
| Control Capability | Limited, basic local control | Advanced, continuous process regulation |
| Communication | Modbus, DNP3, SCADA protocols | Proprietary protocols, Ethernet/IP, Profibus |
| Scalability | Moderate, suitable for remote expansion | High, supports complex, multi-loop control |
| Redundancy | Minimal or optional redundancy | Full redundancy for reliability |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Typical Industries | Oil & gas, utilities, pipelines | Chemical, petrochemical, manufacturing |
Introduction to RTU and DCS
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) are microprocessor-based devices used in distributed control systems to interface with field devices and transmit data to centralized control systems. Distributed Control Systems (DCS) integrate multiple controllers distributed throughout a plant to manage complex industrial processes with real-time data acquisition and control. RTUs are primarily deployed in remote and harsh environments for telemetry and SCADA applications, while DCS provides comprehensive automation solutions for process industries.
Core Functions: RTU vs DCS
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) primarily perform data acquisition, monitoring, and control in geographically dispersed locations, offering efficient communication with central control systems. Distributed Control Systems (DCS) provide integrated process control with real-time data processing, automation, and operator interface functions, enabling centralized management of complex industrial processes. RTUs excel in remote site control and telemetry, while DCS delivers comprehensive process automation and control within industrial plants.
Architecture Comparison: RTU and DCS
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) architecture is decentralized, designed for field-level data acquisition and control, connecting multiple remote sites to a central control system via communication networks. DCS (Distributed Control System) architecture is centralized with distributed controllers and integrated operator stations, facilitating real-time process monitoring and control within a plant. RTUs emphasize ruggedness and remote communication protocols, while DCSs prioritize high-speed data processing, redundancy, and complex process automation.
Key Components and Features
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) primarily feature input/output modules for data acquisition, communication interfaces supporting protocols like Modbus and DNP3, and onboard processing for real-time control in remote locations. DCS (Distributed Control Systems) integrate controllers, human-machine interfaces (HMIs), engineering workstations, and networked field devices, offering centralized process control with advanced automation and diagnostics. Key distinctions include RTU's rugged design for field deployment and DCS's comprehensive control strategies and scalability for complex industrial processes.
Applications and Use Cases
RTUs are widely used in remote monitoring and control applications within distributed infrastructure such as oil and gas pipelines, water treatment plants, and electrical substations, where reliable communication over long distances is critical. DCS systems excel in centralized control environments like manufacturing plants, chemical processing, and power generation facilities, providing integrated control loops, advanced process automation, and real-time process optimization. The choice between RTU and DCS depends on factors including scale, complexity, geographic distribution, and the need for real-time data processing versus remote data acquisition.
Communication Protocols
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) primarily use protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, and IEC 60870-5-101 for reliable communication over long distances in SCADA systems. Distributed Control Systems (DCS) typically employ high-speed Ethernet-based protocols like PROFINET, Foundation Fieldbus, and Modbus TCP/IP to enable real-time data exchange and tight control integration. The choice of communication protocol directly impacts system scalability, latency, and interoperability between field devices and control networks.
Scalability and Flexibility
RTU systems offer higher scalability by easily integrating numerous remote devices across vast geographic areas, making them ideal for large, distributed control networks. DCS architecture emphasizes flexibility within centralized environments, allowing seamless adaptation to complex process control tasks and modular expansions. Scalability in RTUs supports expanding remote monitoring, while DCS flexibility optimizes centralized operations and process customization.
Reliability and Maintenance
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) offer high reliability in distributed monitoring systems due to their modular design and ease of isolated fault management, resulting in reduced downtime. DCS (Distributed Control Systems) provide centralized control with advanced diagnostics that streamline predictive maintenance and improve system availability. Maintenance of RTUs typically involves simplified component replacement at remote sites, while DCS requires skilled technicians for system-wide calibration and software updates to ensure optimal performance.
Cost Considerations
RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) systems generally offer lower initial installation costs compared to DCS (Distributed Control System) due to their simpler architecture and reduced hardware requirements. However, long-term operational expenses for DCS may be more cost-effective because of enhanced scalability, integrated control capabilities, and centralized management that reduce maintenance and downtime. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including hardware, software, installation, and lifecycle maintenance, is critical when choosing between RTU and DCS for industrial automation projects.
Choosing Between RTU and DCS
Choosing between RTU and DCS depends on the scale and complexity of the control system; RTUs are ideal for remote monitoring and control in distributed environments, while DCS offers integrated control for complex, centralized processes. RTUs excel in low-bandwidth, geographically dispersed sites due to their flexibility and ease of installation, whereas DCS provides advanced process automation, real-time data analysis, and enhanced reliability. Evaluating factors such as system size, communication infrastructure, and process criticality ensures optimal selection for efficient industrial operations.
RTU Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com