Geotextiles are permeable fabrics used in civil engineering to improve soil stabilization, erosion control, and drainage. These materials enhance ground support by reinforcing soil, promoting filtration, and preventing soil mixing. Discover how geotextiles can optimize your construction projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
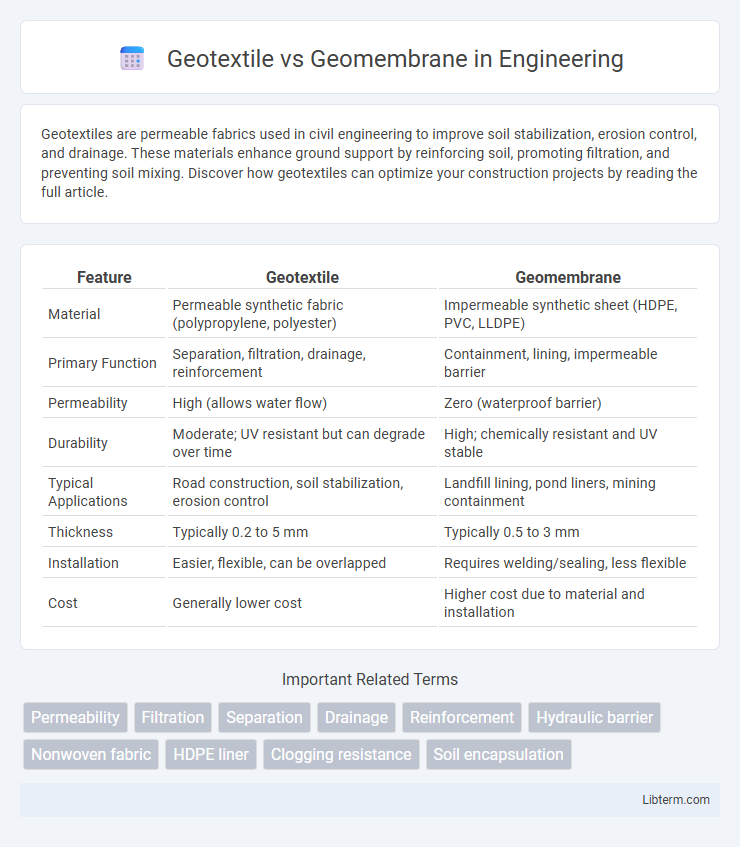
| Feature | Geotextile | Geomembrane |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Permeable synthetic fabric (polypropylene, polyester) | Impermeable synthetic sheet (HDPE, PVC, LLDPE) |
| Primary Function | Separation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement | Containment, lining, impermeable barrier |
| Permeability | High (allows water flow) | Zero (waterproof barrier) |
| Durability | Moderate; UV resistant but can degrade over time | High; chemically resistant and UV stable |
| Typical Applications | Road construction, soil stabilization, erosion control | Landfill lining, pond liners, mining containment |
| Thickness | Typically 0.2 to 5 mm | Typically 0.5 to 3 mm |
| Installation | Easier, flexible, can be overlapped | Requires welding/sealing, less flexible |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to material and installation |
Introduction to Geotextile and Geomembrane
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics made from synthetic fibers like polypropylene or polyester, designed to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain soil. Geomembranes are impermeable liners typically composed of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), used to prevent fluid migration in environmental and civil engineering projects. Both materials serve critical roles in land reclamation, waste containment, and erosion control by enhancing soil stability and controlling fluid movement.
Definition and Primary Functions
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics used in civil engineering to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain soil, enhancing soil stability and erosion control. Geomembranes are impermeable synthetic membranes primarily designed to act as barriers preventing fluid migration in projects like landfills, ponds, and tunnels. While geotextiles provide filtration and drainage functions, geomembranes ensure containment and waterproofing essential for environmental protection.
Types of Geotextiles
Nonwoven geotextiles consist of randomly oriented fibers bonded mechanically or chemically, offering excellent filtration and drainage properties. Woven geotextiles are made from interlaced yarns in a grid pattern, providing high tensile strength and durability for soil reinforcement. Knitted geotextiles, less common, feature looped fibers creating a stretchable fabric suited for specialized applications requiring flexibility.
Types of Geomembranes
Geomembranes are typically classified into several types, including High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), each offering distinct chemical resistance and flexibility properties. HDPE geomembranes are widely used for landfill liners due to their high durability and resistance to punctures, while PVC and EPDM membranes provide superior elasticity for applications requiring movement or sealing irregular surfaces. Unlike geotextiles, which are primarily permeable fabrics used for filtration and separation, geomembranes function as impermeable barriers critical in containment and environmental protection systems.
Material Composition Comparison
Geotextiles are typically made from synthetic fibers such as polypropylene or polyester, designed to provide filtration, separation, and reinforcement in soil applications. Geomembranes consist primarily of impermeable materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), offering effective barriers against fluid migration. The material composition of geotextiles emphasizes permeability and durability, while geomembranes prioritize impermeability and chemical resistance.
Key Applications and Use Cases
Geotextiles are primarily used for soil stabilization, filtration, and drainage in road construction, erosion control, and landscaping projects, offering permeability and strength to reinforce ground structures. Geomembranes serve as impermeable barriers in landfill liners, wastewater containment, and pond liners, preventing fluid migration and ensuring environmental protection. Both materials are critical in civil engineering and environmental management, selected based on permeability requirements and site conditions.
Performance Characteristics
Geotextiles offer high permeability and flexibility, enabling effective filtration, separation, and drainage in soil stabilization projects. Geomembranes provide superior impermeability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for containment and barrier applications in landfills and ponds. Both materials exhibit varying degrees of tensile strength and durability, with geomembranes typically excelling in resistance to punctures and environmental degradation.
Installation Methods
Geotextile installation involves unrolling and anchoring the fabric on prepared surfaces, ensuring proper overlap to prevent infiltration or erosion. Geomembrane installation requires precise welding of seams using thermal or extrusion techniques, followed by careful inspection to avoid leaks in containment applications. Both methods demand specialized equipment and skilled labor to maintain material integrity and functionality during deployment.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Geotextiles typically offer lower upfront costs compared to geomembranes, making them a cost-effective choice for filtration and drainage applications. Geomembranes, while more expensive initially, provide superior impermeability ideal for containment projects, leading to potential long-term savings by minimizing leakage and environmental damage. Economic considerations include installation complexity and maintenance expenses, where geomembranes may incur higher costs but deliver greater durability and lifecycle value.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Selecting between geotextile and geomembrane depends on project requirements such as drainage, filtration, or impermeable barriers. Geotextiles are ideal for soil stabilization and water filtration, while geomembranes provide effective waterproofing and containment for liquids or gases. Evaluating project site conditions, environmental impact, and long-term performance ensures the optimal choice for infrastructure durability and cost efficiency.
Geotextile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com