Hybrid technology combines the advantages of electric motors and internal combustion engines to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. This innovative system optimizes power usage by seamlessly switching between or simultaneously using both energy sources, offering a smoother and more economical driving experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how hybrid vehicles can transform your daily commute.
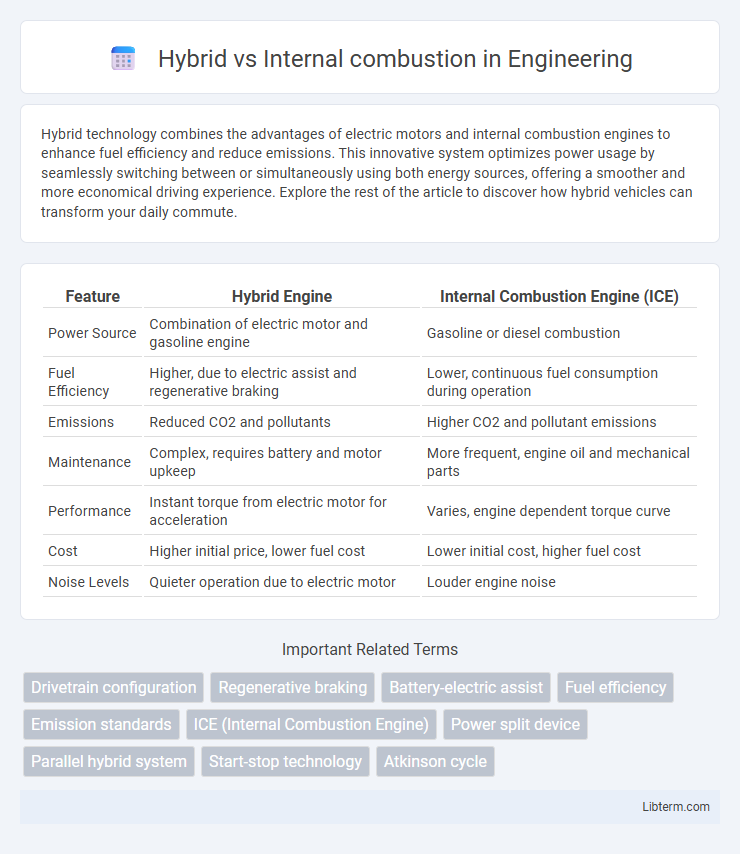
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hybrid Engine | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Combination of electric motor and gasoline engine | Gasoline or diesel combustion |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher, due to electric assist and regenerative braking | Lower, continuous fuel consumption during operation |
| Emissions | Reduced CO2 and pollutants | Higher CO2 and pollutant emissions |
| Maintenance | Complex, requires battery and motor upkeep | More frequent, engine oil and mechanical parts |
| Performance | Instant torque from electric motor for acceleration | Varies, engine dependent torque curve |
| Cost | Higher initial price, lower fuel cost | Lower initial cost, higher fuel cost |
| Noise Levels | Quieter operation due to electric motor | Louder engine noise |
Introduction to Hybrid and Internal Combustion Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles combine an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by optimizing power delivery. Internal combustion engine vehicles rely solely on fuel combustion to generate power, resulting in higher fuel consumption and greater environmental impact. Advancements in hybrid technology offer a transitional solution that leverages existing fuel infrastructure while promoting cleaner energy use.
Key Differences Between Hybrid and Internal Combustion Engines
Hybrid engines combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions compared to traditional internal combustion engines that rely solely on burning fuel for power. Hybrids utilize regenerative braking to recharge batteries, while internal combustion engines depend entirely on fossil fuels without energy recovery mechanisms. Maintenance costs are generally lower for hybrids due to reduced engine wear and advanced energy management systems, contrasting with the higher fuel consumption and frequent servicing required for internal combustion vehicles.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Hybrid vehicles achieve significantly higher fuel efficiency than internal combustion engine (ICE) cars by combining an electric motor with a gasoline engine, reducing fuel consumption during city driving and stop-and-go traffic. The regenerative braking system in hybrids recaptures energy that is typically lost in ICE vehicles, further improving miles per gallon (MPG). Studies indicate hybrids can deliver up to 50% better fuel economy compared to conventional internal combustion engines, especially in urban environments.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Hybrid vehicles significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions by combining an electric motor with a traditional internal combustion engine, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower carbon dioxide output compared to conventional gasoline engines. Internal combustion engines primarily emit carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing substantially to air pollution and climate change. The use of regenerative braking and electric-only driving modes in hybrids further minimizes harmful emissions, making them a cleaner alternative for reducing urban air pollution.
Performance and Driving Experience
Hybrid vehicles offer a balance of electric motor torque and internal combustion engine (ICE) power, resulting in smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional ICE cars. Internal combustion engines typically provide a more consistent and powerful driving experience, especially at higher speeds and extended performance demands. The integration of regenerative braking in hybrids enhances energy recovery, contributing to a quieter and more responsive ride, while ICE vehicles often deliver a more engaging exhaust note and throttle response favored by driving enthusiasts.
Maintenance and Longevity
Hybrid vehicles typically require less frequent maintenance compared to internal combustion engines due to reduced wear on the engine and brakes, benefiting from regenerative braking systems and electric motor assistance. Internal combustion engines often involve higher costs in routine maintenance such as oil changes, exhaust system repairs, and transmission servicing. Hybrid cars usually demonstrate greater longevity because the electric components reduce strain on the engine, leading to extended engine life and fewer mechanical failures over time.
Cost of Ownership and Incentives
Hybrid vehicles generally offer lower long-term cost of ownership due to improved fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance expenses compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. Many governments provide financial incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees to promote hybrid adoption, which further decreases the effective cost for buyers. In contrast, ICE vehicles often incur higher fuel and maintenance costs over time without similar levels of financial support.
Availability of Models and Options
Hybrid vehicles offer a growing variety of models across multiple segments, including sedans, SUVs, and trucks, with options from major manufacturers such as Toyota, Ford, and Honda. Internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles still dominate the market with a broader range of models, including budget, luxury, sports, and commercial vehicles with varied engine sizes and fuel types. Consumers seeking diverse features and customizations find more extensive options in ICE vehicles, but hybrids continue expanding their model availability and technological options rapidly.
Future Trends in Automotive Technologies
Hybrid vehicles are increasingly integrating advanced battery management systems and regenerative braking to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, signaling a shift towards more sustainable automotive technologies. Internal combustion engines (ICE) continue to evolve with innovations such as variable compression ratios and advanced fuel injection to improve performance and meet stricter environmental regulations. Future trends emphasize a gradual transition from ICE dominance to hybrid systems and ultimately fully electric platforms, driven by government policies and consumer demand for cleaner, more efficient transportation.
Choosing the Right Vehicle for Your Needs
Hybrid vehicles offer superior fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to internal combustion engines, making them ideal for environmentally conscious drivers and those with frequent city commutes. Internal combustion engines provide greater power and longer driving range, suitable for long-distance travel and areas with limited charging infrastructure. Evaluating factors such as driving habits, environmental impact priorities, and fuel availability helps determine the best vehicle choice for individual needs.
Hybrid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com