Crosstalk occurs when unwanted signals interfere with the transmission of desired information, often degrading the quality of communication systems. This interference can impact audio, video, and data transmissions, leading to reduced clarity and accuracy. Explore the rest of this article to understand how crosstalk affects your devices and the methods to minimize its impact.
Table of Comparison
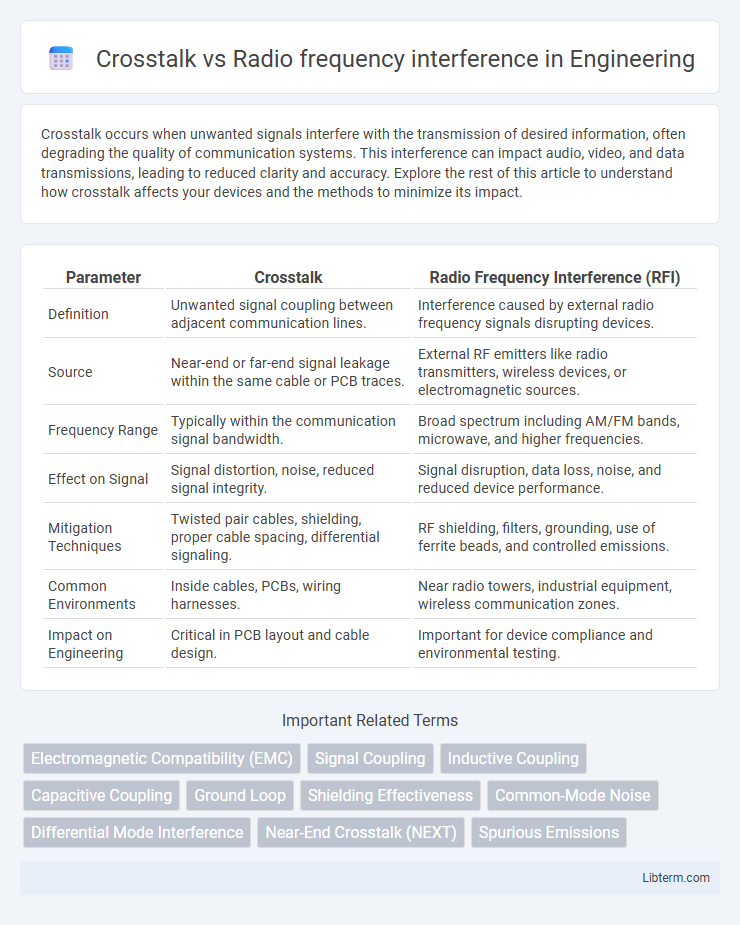
| Parameter | Crosstalk | Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwanted signal coupling between adjacent communication lines. | Interference caused by external radio frequency signals disrupting devices. |
| Source | Near-end or far-end signal leakage within the same cable or PCB traces. | External RF emitters like radio transmitters, wireless devices, or electromagnetic sources. |
| Frequency Range | Typically within the communication signal bandwidth. | Broad spectrum including AM/FM bands, microwave, and higher frequencies. |
| Effect on Signal | Signal distortion, noise, reduced signal integrity. | Signal disruption, data loss, noise, and reduced device performance. |
| Mitigation Techniques | Twisted pair cables, shielding, proper cable spacing, differential signaling. | RF shielding, filters, grounding, use of ferrite beads, and controlled emissions. |
| Common Environments | Inside cables, PCBs, wiring harnesses. | Near radio towers, industrial equipment, wireless communication zones. |
| Impact on Engineering | Critical in PCB layout and cable design. | Important for device compliance and environmental testing. |
Understanding Crosstalk: Definition and Causes
Crosstalk is an electromagnetic interference phenomenon where a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel creates an undesired effect on another circuit or channel, commonly seen in telephone lines and data cables. It occurs due to capacitive, inductive, or conductive coupling between adjacent wires, resulting in signal leakage that degrades communication quality. Understanding the causes of crosstalk, such as poor cable shielding, improper wiring, and close proximity of conductors, is essential for minimizing its impact in telecommunications and networking.
What is Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)?
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) is the disruption caused by external radio frequency signals affecting the performance of electronic devices and communication systems. It originates from various sources such as radios, cell phones, electrical circuits, and microwave ovens, which emit electromagnetic waves that interfere with the intended signal. Unlike crosstalk, which is a leakage of signals between adjacent communication channels, RFI involves external electromagnetic noise that degrades signal integrity and transmission quality.
Key Differences Between Crosstalk and RFI
Crosstalk occurs when a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel creates an undesired effect on another circuit, primarily due to electromagnetic coupling in closely spaced wires or cables. Radio frequency interference (RFI) is caused by external radio waves disrupting the operation of electronic devices and communication systems, typically originating from sources like radio transmitters, motors, or fluorescent lights. Unlike crosstalk, which is an internal issue within wiring or circuits, RFI involves interference from external electromagnetic signals affecting device performance.
Sources of Crosstalk in Electronic Systems
Crosstalk in electronic systems primarily arises from capacitive, inductive, and conductive coupling between adjacent signal lines or components, often due to poor PCB layout or inadequate shielding. Common sources include closely spaced cables, parallel traces on circuit boards, and unbalanced transmission lines, which allow signals from one channel to induce unwanted interference in another. Unlike general radio frequency interference (RFI) caused by external electromagnetic sources, crosstalk is an internal issue predominantly linked to the physical proximity and routing of circuit elements.
Common Sources of Radio Frequency Interference
Common sources of Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) include wireless communication devices, electrical circuits, and industrial machinery that emit electromagnetic signals disrupting nearby electronic equipment. Crosstalk, a specific type of interference, occurs when signal transmission from one circuit or channel unintentionally affects another, often caused by inadequate shielding or poor cable management. Unlike crosstalk, which arises primarily within wired communication systems, RFI originates from both internal and external electromagnetic sources affecting wireless and wired transmissions.
Effects of Crosstalk on Signal Integrity
Crosstalk causes undesired coupling between adjacent signal lines, leading to signal distortion and reduced integrity in communication systems. This interference manifests as noise that degrades data transmission, increases bit error rates, and impacts the performance of high-speed digital circuits. Effective shielding, proper cable routing, and maintaining adequate spacing between conductors are critical for minimizing crosstalk and preserving signal quality.
Impact of RFI on Communication Systems
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) disrupts communication systems by introducing unwanted noise that degrades signal quality and reduces data transmission accuracy. RFI sources, such as electronic devices and broadcasting equipment, cause signal distortion, leading to increased error rates and loss of critical information in wireless and wired networks. Effective mitigation techniques, including shielding and filtering, are essential to maintain system reliability and prevent communication failures attributed to RFI.
Methods to Detect Crosstalk and RFI
Methods to detect crosstalk include using time-domain reflectometers (TDR) and spectrum analyzers to identify signal leakage between adjacent communication lines or circuits. Radio frequency interference (RFI) detection involves deploying electromagnetic interference (EMI) receivers and field strength meters to measure unwanted radio signals disrupting electronic equipment. Advanced detection techniques use signal analyzers combined with specialized sensors to differentiate between crosstalk and RFI sources effectively.
Prevention and Reduction Techniques for Crosstalk
Crosstalk prevention techniques include proper cable shielding, maintaining adequate physical separation between cables, and using twisted pair wiring to minimize electromagnetic coupling. Implementing balanced lines and using differential signaling helps reduce susceptibility to crosstalk by canceling out interference. Regular testing and adherence to industry standards such as TIA/EIA can ensure optimal cable installation and minimize signal degradation.
Strategies to Minimize Radio Frequency Interference
Minimizing radio frequency interference (RFI) involves implementing strategies such as using shielded cables, maintaining proper grounding, and ensuring adequate separation between signal lines and sources of electromagnetic radiation. Employing ferrite beads and filters can further reduce high-frequency noise, while frequency planning and spectrum management help avoid overlapping channel interference. Proper equipment maintenance and adherence to regulatory standards also play crucial roles in mitigating RFI effects in communication systems.
Crosstalk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com