Planetary gears offer compact, efficient power transmission by distributing load across multiple gear teeth for enhanced durability and torque density. Their unique arrangement allows for versatile speed and torque combinations, making them ideal for applications in automotive transmissions, robotics, and industrial machinery. Discover how understanding planetary gear systems can optimize Your mechanical designs in the detailed insights ahead.
Table of Comparison
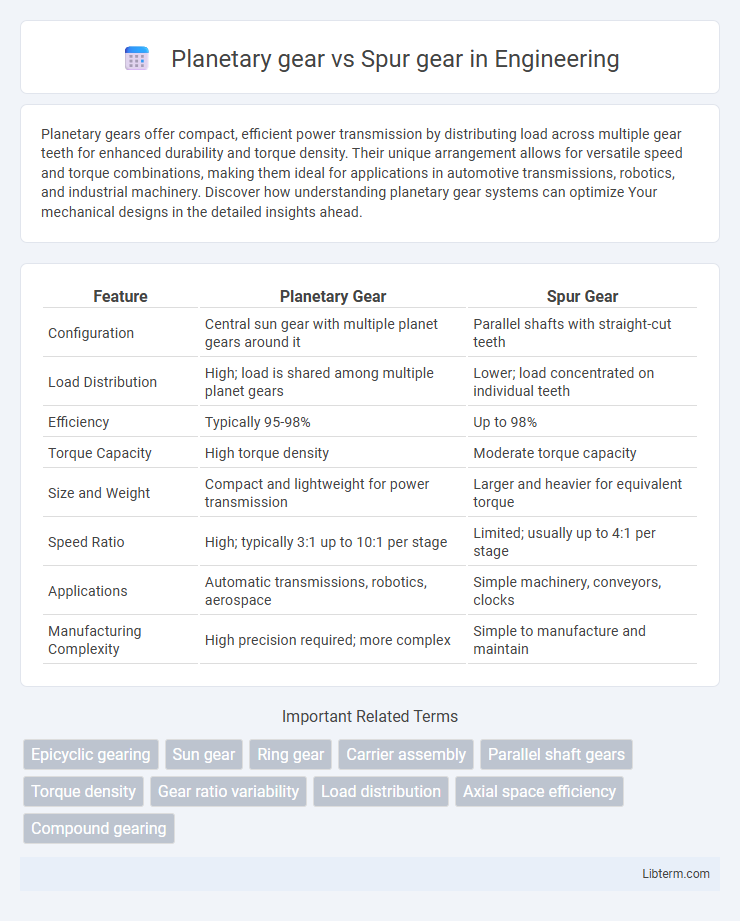
| Feature | Planetary Gear | Spur Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Central sun gear with multiple planet gears around it | Parallel shafts with straight-cut teeth |
| Load Distribution | High; load is shared among multiple planet gears | Lower; load concentrated on individual teeth |
| Efficiency | Typically 95-98% | Up to 98% |
| Torque Capacity | High torque density | Moderate torque capacity |
| Size and Weight | Compact and lightweight for power transmission | Larger and heavier for equivalent torque |
| Speed Ratio | High; typically 3:1 up to 10:1 per stage | Limited; usually up to 4:1 per stage |
| Applications | Automatic transmissions, robotics, aerospace | Simple machinery, conveyors, clocks |
| Manufacturing Complexity | High precision required; more complex | Simple to manufacture and maintain |
Introduction to Gear Systems
Planetary gear systems feature a central sun gear surrounded by multiple planet gears, offering compactness, high torque density, and efficient power transmission ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Spur gears consist of parallel teeth mounted on shafts, providing straightforward design, ease of manufacture, and effective speed reduction or increase in mechanical devices. Understanding the structural differences highlights how planetary gears excel in load distribution and space-saving designs, while spur gears are preferred for simplicity and cost-effectiveness in gear systems.
What is a Spur Gear?
A spur gear is a cylindrical gear with straight teeth that are parallel to the axis of rotation, commonly used for transmitting motion and power between parallel shafts. It offers high efficiency and simplicity in design, making it suitable for applications requiring precise speed and torque control. Spur gears typically produce more noise compared to planetary gears due to the direct tooth contact during meshing.
What is a Planetary Gear?
A planetary gear system consists of a central sun gear, multiple planet gears revolving around it, and an outer ring gear with internal teeth. This arrangement enables high torque transmission and compact design, making it ideal for applications needing efficient power density and smooth operation, such as automatic transmissions and industrial machinery. Compared to spur gears, planetary gears distribute load across several contact points, reducing wear and increasing gear life.
Key Differences Between Planetary and Spur Gears
Planetary gears feature a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and a ring gear, providing compact design and high torque transmission, whereas spur gears consist of parallel teeth on two shafts, suited for straightforward power transfer. Planetary gear systems offer higher load distribution and efficiency in confined spaces, while spur gears are simpler, easier to manufacture, and ideal for low-speed, moderate-load applications. The key differences include arrangement complexity, torque capacity, size efficiency, and noise levels during operation.
Efficiency Comparison: Planetary vs Spur Gears
Planetary gears generally offer higher efficiency compared to spur gears due to their load distribution among multiple planet gears, which reduces stress and friction. Spur gears, with their simpler design and direct tooth engagement, may experience higher energy losses from sliding friction, particularly at high speeds. Efficiency in planetary gear systems can reach up to 98%, while spur gears typically range between 94% and 96%, depending on lubrication and operating conditions.
Torque and Load Capacity Analysis
Planetary gears offer higher torque transmission and load capacity due to their multiple gear contacts distributing the load evenly across the system, resulting in increased efficiency and durability compared to spur gears. Spur gears, while simpler and cost-effective, concentrate load on fewer teeth which limits their torque handling and can lead to faster wear under high-stress conditions. The compact design of planetary gear systems allows for better torque density and smooth power transmission in applications requiring high load capacity and precise motion control.
Space and Design Considerations
Planetary gears offer a more compact design with higher power density, making them ideal for applications with limited space and requiring multiple gear ratios in a single stage. Spur gears, characterized by their simpler layout and ease of manufacturing, typically occupy more axial space and are suited for straightforward power transmission where size constraints are minimal. The concentric arrangement of planets around a sun gear in planetary systems enables better load distribution and reduced vibration compared to the parallel teeth engagement in spur gears.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Planetary gears are commonly used in applications requiring high torque density and compact design, such as automatic transmissions in automobiles, industrial machinery, and robotics. Spur gears find extensive use in simpler mechanical systems like conveyor systems, clocks, and basic machinery where noise is less critical and efficiency at moderate speeds is essential. Both gear types serve distinct roles, with planetary gears excelling in load distribution and torque multiplication, while spur gears prioritize straightforward power transmission and ease of manufacturing.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Planetary gears exhibit higher durability due to their load distribution across multiple planet gears, reducing wear and extending maintenance intervals compared to spur gears, which concentrate stress on individual teeth. Maintenance of planetary gears involves periodic lubrication and inspection of multiple gear meshes to prevent premature failure, whereas spur gears require more frequent inspections for tooth wear and alignment issues. The enclosed design of planetary gear systems often provides better protection from contaminants, enhancing longevity relative to the more exposed spur gear setups.
Choosing the Right Gear System for Your Needs
Planetary gears offer higher torque density and compact design, making them ideal for applications requiring space-saving and high load capacity, such as robotics and automotive transmissions. Spur gears provide simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and efficiency in low to moderate speed applications, commonly used in machinery and conveyor systems. Selection depends on considering load requirements, space constraints, efficiency needs, and maintenance capabilities to ensure optimal gear system performance.
Planetary gear Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com