Universal motors are powerful electric motors that operate on both AC and DC power sources, making them highly versatile for various applications. Known for their high speed and compact size, these motors are commonly found in household appliances and power tools where variable speed control is essential. Discover how understanding the workings of a universal motor can enhance your ability to choose the right motor for your needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
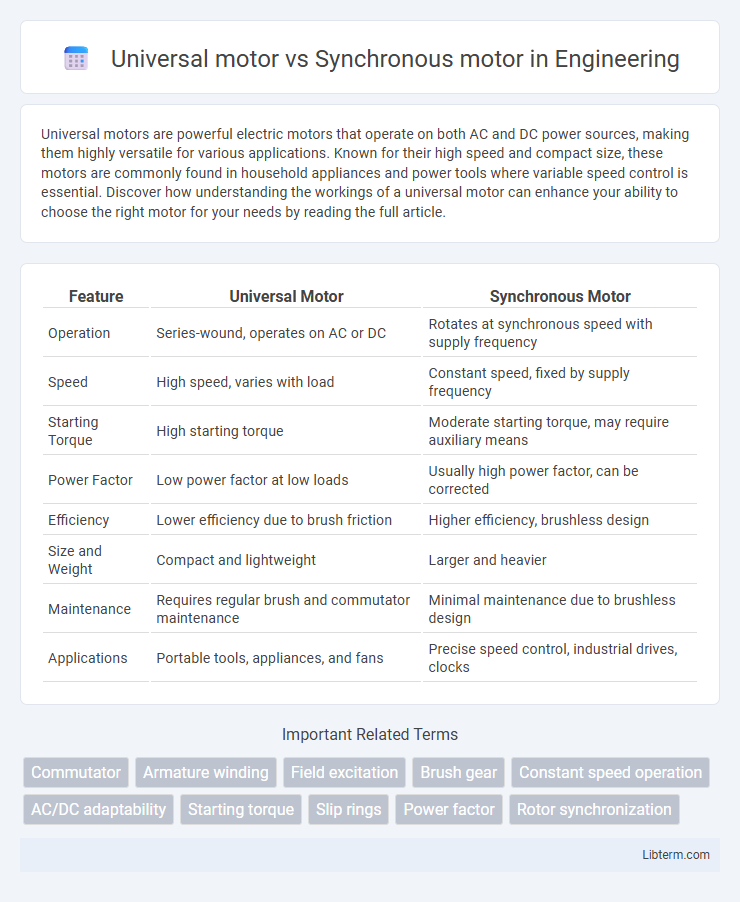
| Feature | Universal Motor | Synchronous Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Series-wound, operates on AC or DC | Rotates at synchronous speed with supply frequency |
| Speed | High speed, varies with load | Constant speed, fixed by supply frequency |
| Starting Torque | High starting torque | Moderate starting torque, may require auxiliary means |
| Power Factor | Low power factor at low loads | Usually high power factor, can be corrected |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to brush friction | Higher efficiency, brushless design |
| Size and Weight | Compact and lightweight | Larger and heavier |
| Maintenance | Requires regular brush and commutator maintenance | Minimal maintenance due to brushless design |
| Applications | Portable tools, appliances, and fans | Precise speed control, industrial drives, clocks |
Introduction to Universal Motor and Synchronous Motor
Universal motors operate on both AC and DC power sources, featuring a series-wound armature and field coils that enable high-speed and compact designs ideal for portable tools and appliances. Synchronous motors run at a constant speed synchronized with the supply frequency, utilizing rotor magnets or electromagnets that lock in step with the stator's rotating magnetic field, making them suitable for applications requiring precise speed control. The universal motor's ability to achieve high speeds and variable loads contrasts with the synchronous motor's efficiency and stability in constant-speed operations.
Fundamental Working Principles
Universal motors operate based on the interaction between the magnetic field generated by the stator and the armature current, enabling them to run on both AC and DC power sources with high-speed rotation due to series-wound coils. Synchronous motors function by rotating at a constant speed synchronized with the frequency of the AC supply, relying on a rotor magnet or electromagnet that locks in step with the stator's rotating magnetic field. The fundamental distinction lies in the universal motor's reliance on commutation and brush assembly for operation, whereas synchronous motors maintain speed through electromagnetic synchronization without brushes.
Construction Differences
Universal motors feature a series-wound armature and field coils on a common stator frame, enabling high-speed operation and compact construction suitable for portable devices. Synchronous motors consist of a rotor with either permanent magnets or salient poles and a stationary stator winding energized by AC supply, maintaining synchronous speed without slip. The key construction difference lies in the universal motor's commutator and brushes versus the synchronous motor's brushless rotor design.
Power Supply and Compatibility
Universal motors operate on both AC and DC power supplies, making them highly compatible with household appliances and portable tools due to their ability to run at high speeds with variable voltage. Synchronous motors require a constant frequency AC power supply to maintain their precise rotational speed, limiting their use to industrial applications with stable power systems. The compatibility of universal motors with diverse power sources contrasts with the synchronous motor's dependence on synchronized AC supply for optimal performance.
Speed Control Capabilities
Universal motors offer superior speed control capabilities due to their ability to operate at varying voltages and frequencies, allowing for wide speed ranges without complex electronics. Synchronous motors maintain a constant speed synchronized with supply frequency, limiting their speed variability but providing precise control at fixed speeds. Variable frequency drives are typically required for speed control in synchronous motors, making universal motors more flexible for applications requiring frequent speed adjustments.
Efficiency and Performance
Universal motors offer high-speed operation and compact design but exhibit lower efficiency due to brush friction and commutator losses, typically around 20-30%. Synchronous motors deliver higher efficiency, often exceeding 90%, by maintaining constant speed under varying loads and eliminating rotor current losses. Performance-wise, synchronous motors provide better power factor and precision control, making them ideal for applications requiring stable speed and high efficiency.
Typical Applications
Universal motors are commonly used in portable power tools, household appliances like vacuum cleaners, and kitchen equipment due to their high starting torque and ability to operate on both AC and DC supplies. Synchronous motors find typical applications in precision timing, synchronous clocks, and industrial drives where constant speed operation is essential. Universal motors excel in speed variability and compact design, whereas synchronous motors are vital for applications requiring exact speed and power factor correction.
Maintenance and Durability
Universal motors require frequent maintenance due to brushes and commutators wearing out quickly, impacting durability in demanding applications. Synchronous motors benefit from brushless construction, resulting in lower maintenance and longer operational life, especially in industrial settings. Their robust design and steady speed performance enhance longevity and reliability over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Universal motors offer high starting torque and operate efficiently on both AC and DC power, making them ideal for portable power tools and household appliances, but they tend to be noisy and have lower efficiency compared to synchronous motors. Synchronous motors provide precise speed control and higher efficiency, making them suitable for industrial applications requiring constant speed, but they require a separate DC excitation source and have more complex control systems. While universal motors excel in versatility and initial cost-effectiveness, synchronous motors are preferred for stability and energy savings in demanding environments.
Selection Criteria: Which Motor to Use
Universal motors are preferred for applications requiring high speed, variable speed control, and compact size, such as household appliances and power tools. Synchronous motors are ideal for constant speed applications with high efficiency and precise speed control, commonly used in industrial processes and timing devices. Selection depends on factors like speed regulation, load type, power supply, size constraints, and efficiency requirements.
Universal motor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com